Comparison of Wavefront Analysis and Visual Function Between Monofocal and Multifocal Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Institute of Vision Research, Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tikim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Siloam Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2212042
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.2.195
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To compare postoperative vision, high-order aberrations, contrast sensitivity, power of accommodation, and depth of focus of monofocal aspheric (TECNIS ZA9003) and multifocal aspheric (TECNIS ZM900) intraocular lenses (IOL).
METHODS
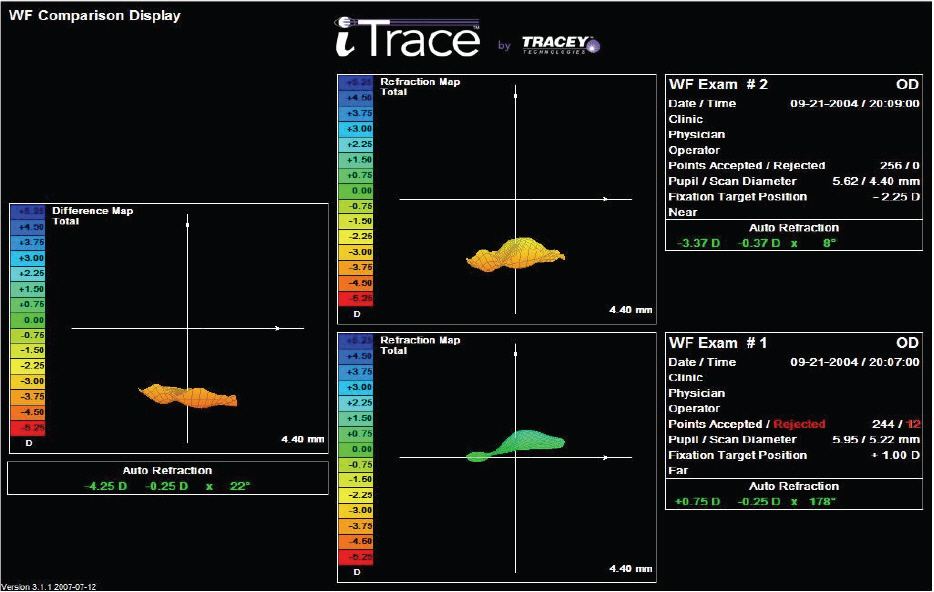
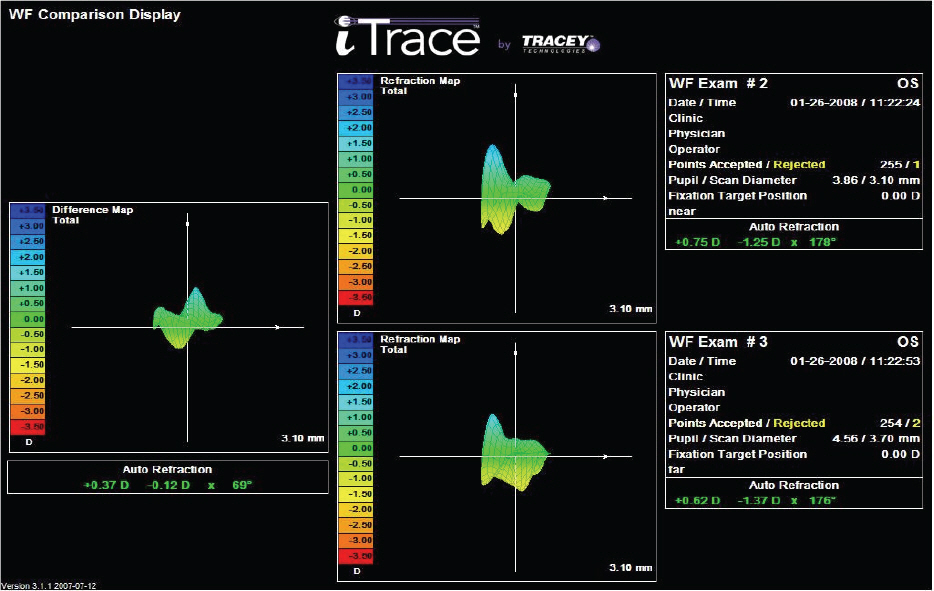
Thirty-four eyes which received intraocular lens implantation in the posterior chamber were equally divided into two groups: TECNIS ZA9003 (17 eyes) and TECNIS ZM900 (17 eyes). Before and three months after surgery, visual acuities at near, intermediate, and far distances, and depth of focus were recorded. High order aberrations, spherical aberrations and accommodation power were measured with iTrace, and contrast sensitivity was evaluated using Optec 6500. An independent T-test analysis was used to compare the two groups.
RESULTS
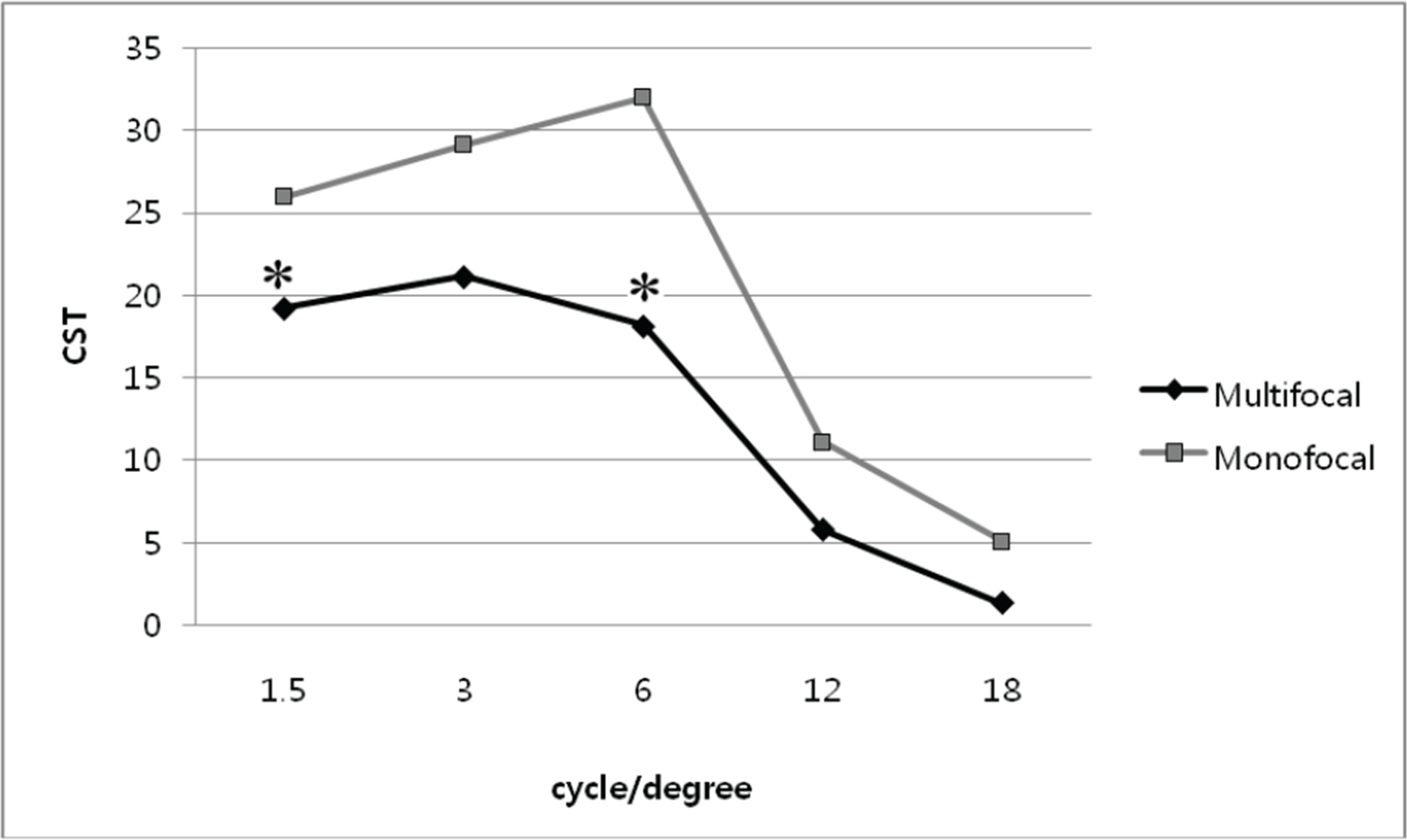
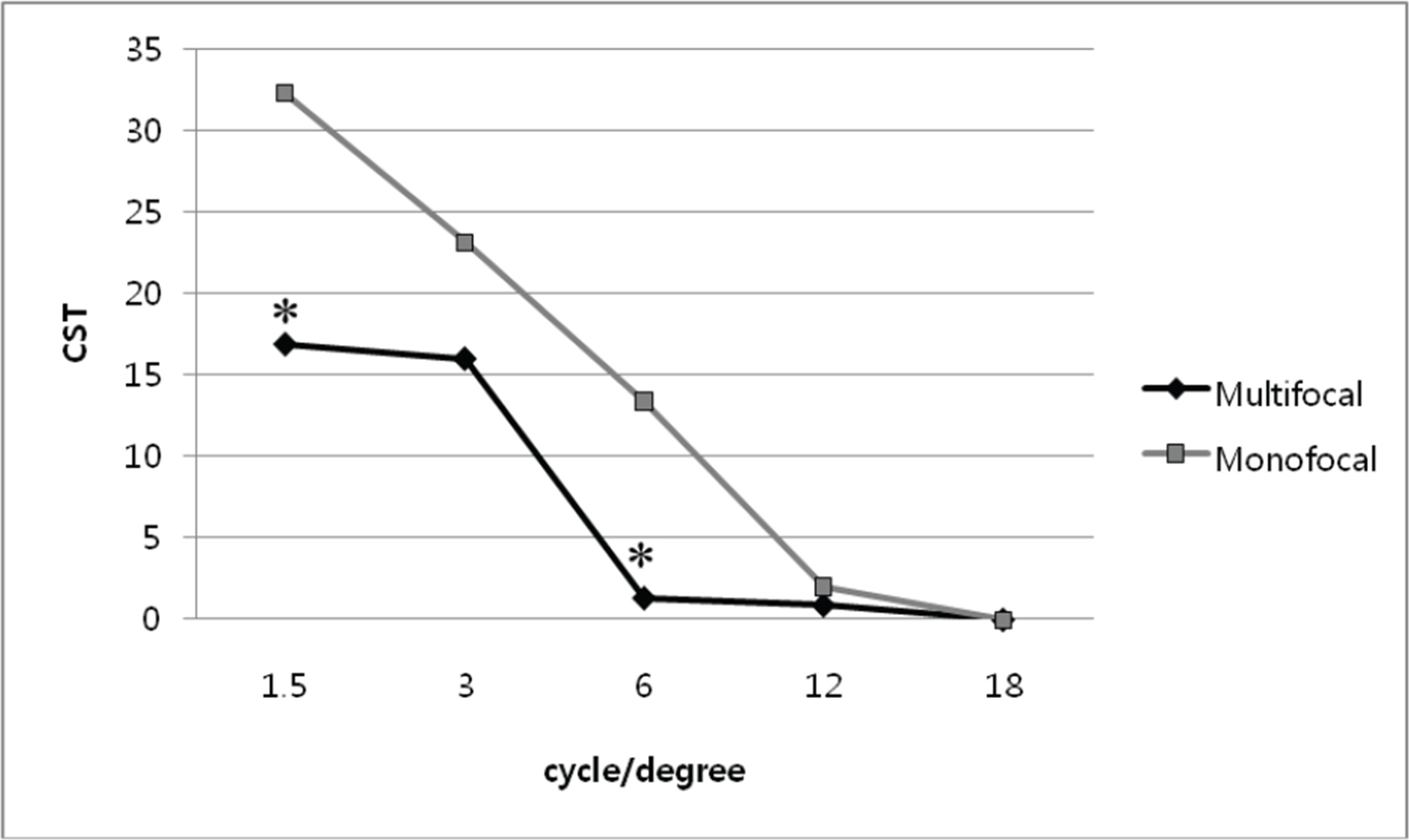
There were no significant differences of high order aberrations, spherical aberrations, accommodation power, or distance vision between the two groups at three months postoperatively. The multifocal IOL (TECNIS ZM900) group revealed better intermediate and near vision (p<0.01) and deeper depth of focus, and lower contrast sensitivities (p=0.03) than the monofocal IOL group.
CONCLUSIONS
There was no difference in accommodation power between the two groups, but multifocal TECNIS ZM900 IOL exceeds monofocal TECNIS ZA9003 IOL in intermediate and near vision due to diffractive lens design and less spherical aberration by its asphericity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 8 articles
-
Comparison of Optical Performances in Eyes Implanted With Aspheric and Spherical Intraocular Lenses After Cataract Surgery
Jin Ho Jeong, Mee Kum Kim, Won Ryang Wee, Jin Hak Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010;51(11):1445-1452. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.11.1445.Clinical Outcome of in-the-Bag Single-Piece Aspheric Intraocular Lens Implantation after Microincision Cataract Surgery
Yoon Jeon Kim, Mi Hyun Cheon, Dong Ah Ko, Jae Yong Kim, Myoung Joon Kim, Hung Won Tchah
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(4):595-601. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.4.595.Clinical Results and Optical Quality of Diffractive Multifocal IOL Implantation after Myopic Refractive Surgery
Jae Hong Park, Dong Seob Ahn, Sang Jeong Moon, Dong Jun Lee, Sang Youp Han, Kyung Heon Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(12):1779-1786. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1779.Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Refractive Aspheric Multifocal IOL Implantation
Sung Yu, Jee Hyun Kim, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(7):991-1000. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.7.991.Clinical Results and Optical Quality of Diffractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens
Jeong Jae Oh, Jin Seok Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(12):1867-1873. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1867.One-year Outcome of Monocular Implant of Aspheric Multifocal IOL
Mi Hyun Cheon, Joo Eun Lee, Jae Hyung Kim, Kyung Hoon Kim, Hee Gyung Lee, Jae Yong Kim, Myoung Joon Kim, Hung Won Tchah
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010;51(6):822-828. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.6.822.Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
Jee Hyun Kim, Sung Yu, Sung Hyun Koo, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(8):1139-1149. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.8.1139.Comparison of the Visual Outcomes after Cataract Surgery with Implantation of a Bifocal and Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens
Sung Yu, Yong Il Kim, Sang Won Ha, Gwang Ja Lee, Kyoo Won Lee, Young Jeung Park
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016;57(3):405-412. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.3.405.
Reference
-
References
1. Javitt JC, Steinert RF. Cataract extraction with multifocal intraocular lens implantation: a multinational clinical trial evaluating clinical, functional, and quality-of-life outcomes. Ophthalmology. 2000; 107:2040–8.2. Steinert RF, Post CT Jr, Brint SF, et al. A prospective, randomized, double-masked comparison of a zonal-progressive multifocal intraocular lens and a monofocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:853–60.
Article3. Leyland MD, Langan L, Goolfee F, et al. Prospective randomised double-masked trial of bilateral multifocal, bifocal or monofocal intraocular lenses. Eye. 2002; 16:481–90.
Article4. Pineda-Fernández A, Jaramillo J, Celis V, et al. Refractive outcomes after bilateral multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:685–8.
Article5. Lee JM, Seo KY, Kim EK. Comparison of optical aberrations and contrast sensitivity between monofocal and multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1882–6.6. Song MJ, Lee MK, Park BI. A Clinical study of 3M multifocal intraocular lens implant. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:234–40.7. Monte´s-Mico´ R, Espana E, Bueno I, et al. Visual performance with multifocal intraocular lenses mesopic contrast sensitivity under distance and near conditions. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:85–96.8. Sen HN, Sarikkola A-U, Uusitalo RJ, Laatikainen L. Quality of vision after AMO Array multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2483–93.
Article9. Schmitz S, Dick HB, Krummenauer F, et al. Contrast sensitivity and glare disability by halogen light after monofocal and multifocal lens implantation. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:1109–12.
Article10. Allen ED, Burton RL, Webber SK, et al. Comparison of a diffractive bifocal and a monofocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996; 22:446–51.
Article11. Rossetti L, Carraro F, Rovati M, Orzalesi N. Performance of diffractive multifocal intraocular lenses in extracapsular cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994; 20:124–8.
Article12. Kamlesh , Dadeya S, Kaushik S. Contrast sensitivity and depth of focus with aspheric multifocal versus conventional monofocal intraocular lens. Can J Ophthalmol. 2001; 36:197–201.
Article13. Kang SG, Lee JH. The Effect of Illumination on Visual Acuity and Visual Field in Eyes with Multifocal Intraocular Lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:78–82.14. Barbero S, Marcos S, Jime´nez-Alfaro I. Optical aberrations of intraocular lenses measured in vivo and in vitro. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2003; 20:1841–51.
Article15. Claoue´ C, Parmar D. Multifocal intraocular lenses. Dev Ophthalmol. 2002; 34:217–37.16. Kim YS, Han TW, Kim MS, Kim JH. Clinical experience of 3M multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:1308–17.17. Heo JY, Kim YH, Joo CK. Clinical results of AMO ARRAY multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:978–86.18. Choi HS, Lim SJ, Kim HB. Clinical results of unilateral implantation of AMO Array multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:702–8.19. Simpson MJ. The diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. Eur J Implant Ref Surg. 1989; 1:115–21.
Article20. Toto L, Falconio G, Vecchiarino L, et al. Visual performance and biocompatibility of 2 multifocal diffractive IOLs. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1419–25.
Article21. Weghaupt H, Pieh S, Skorpik C. Comparison of pseudo-accommodation and visual quality between a diffractive and refractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:663–5.
Article22. Walkow L, Klemen UM. Patient satisfaction after implantation of diffractive designed multifocal intraocular lenses in dependence on objective parameters. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2001; 239:683–7.
Article23. Schmidinger G, Geitzenauer W, Hahsle B, et al. Depth of focus in eyes with diffractive bifocal and refractive multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1650–6.
Article24. Rocha KM, Soriano ES, Chamon W, et al. Spherical Aberration and Depth of Focus in Eyes Implanted with Aspheric and Spherical Intraocular Lenses. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:2050–4.
Article25. Hütz WW, Eckhardt HB, Röhrig B, Grolmus R. Intermediate vision and reading speed with array, TECNIS, and ReSTOR intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:251–6.
Article26. Goes FJ. Refractive lens exchange with the diffractive multifocal TECNIS ZM900 intraocular lens. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:243–50.
Article27. Im YW, Lee KH, Park SC. The difference of the near visual acuity between multifocal IOL and monofocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1027–32.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The change of visual acuity and visual field by diminished illumination in eyes with multifocal intraocular lens
- Wavefront and Visual Function Analysis After Aspherical and Spherical Intraocular Lenses Implantation
- Clinical outcomes of currently available multifocal intraocular lenses
- Comparison of Higher-Order Aberration and Contrast Sensitivity in Monofocal and Multifocal Intraocular Lenses
- Comparison of Optical Aberrations and Contrast Sensitivity between Monofocal and Multifocal Intraocular Lens