J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Nov;53(11):1630-1636.
Clinical Course of Submacular Hemorrhage Due to Various Chorioretinal Diseases According to Pneumatic Displacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3HanGil Medical Foundation, Incheon, Korea. eyedrnam@naver.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
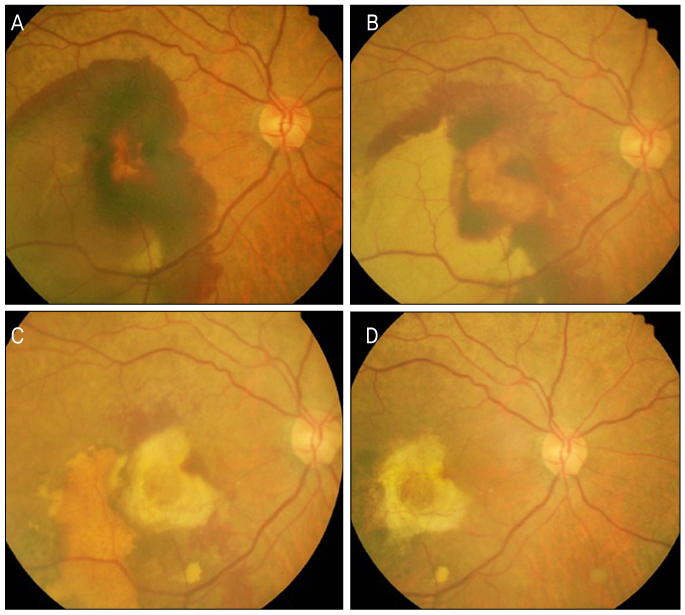
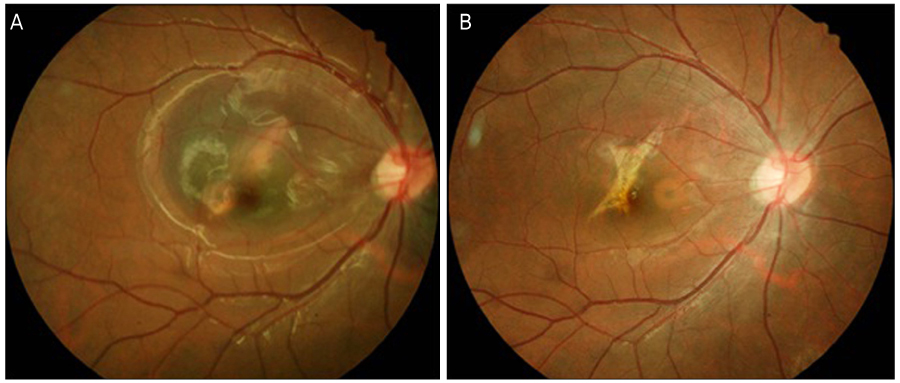
To assess the clinical course of submacular hemorrhage (SMH) due to various chorioretinal diseases with or without pneumatic displacement and the factors related with the final visual outcome.
METHODS
The authors of the present study retrospectively reviewed the charts of 12 eyes (group 1) which underwent pneumatic displacement for SMH and the charts of 14 eyes (group 2) which did not receive pneumatic displacement. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) at baseline was compared with the BCVA at 1, 3, and 6 months and on the final visit. Association between final BCVA and other clinical features was analyzed including age, baseline BCVA, duration of symptoms, and size of SMH.
RESULTS
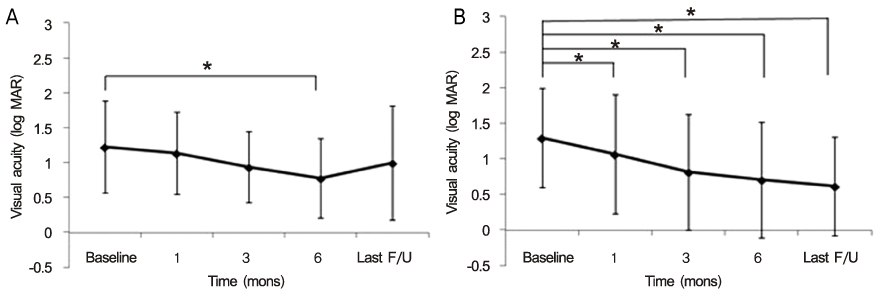
In group 1, log MAR BCVA was 1.22 +/- 0.66 at baseline and there was a significant BCVA improvement of 0.77 +/- 0.57 at 6 months compared with baseline (p = 0.045). On the final visit, 6 eyes (50%) had gained 2 Snellen lines or more. In group 2, BCVA was significantly improved from 1.29 +/- 0.70 at baseline to 1.06 +/- 0.84 at 1 month (p = 0.045). Ten eyes (71.4%) had gained 2 Snellen lines or more on the final visit. In group 1, there were no factors correlated with final BCVA (p > 0.05), while the final BCVA was significantly correlated with age and baseline BCVA in group 2.
CONCLUSIONS
Clinicians may expect conservative treatment to lead to significant improvement of BCVA in patients with SMH due to various chorioretinal diseases who did not undergo any procedures to displace the hemorrhage.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berrocal MH, Lewis ML, Flynn HW Jr. Variations in the clinical course of submacular hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996. 122:486–493.2. Shultz RW, Bakri SJ. Treatment for submacular hemorrhage associated with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Semin Ophthalmol. 2011. 26:361–371.3. Tennant MT, Borrillo JL, Regillo CD. Management of submacular hemorrhage. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2002. 15:445–452.4. Thompson JT, Sjaarda RN. Vitrectomy for the treatment of submacular hemorrhages from macular degeneration: a comparison of submacular hemorrhage/membrane removal and submacular tissue plasminogen activator-assisted pneumatic displacement. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 103:98–107.5. Lee SJ, You YS, Koh HJ, Kwon OW. Pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreal injection of tPA and SF6 gas. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001. 42:724–729.6. Guthoff R, Guthoff T, Meigen T, Goebel W. Intravitreous injection of bevacizumab, tissue plasminogen activator, and gas in the treatment of submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2011. 31:36–40.7. Kamei M, Tano Y. Tissue plasminogen activator-assisted vitrectomy: surgical drainage of submacular hemorrhage. Dev Ophthalmol. 2009. 44:82–88.8. Mizutani T, Yasukawa T, Ito Y, et al. Pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage with or without tissue plasminogen activator. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011. 249:1153–1157.9. Ron Y, Ehrlich R, Axer-Siegel R, et al. Pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage due to age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica. 2007. 221:57–61.10. Yoon JY, Park IW. Two cases of aggravation of submacular hemorrhage after intravitreal gas injection. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:1954–1958.11. Toth CA, Morse LS, Hjelmeland LM, Landers MB 3rd. Fibrin directs early retinal damage after experimental hemorrhage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991. 109:723–729.12. Sanders D, Peyman GA, Fishman G, et al. The toxicity of intravitreal whole blood and hemoglobin. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975. 197:255–267.13. Glatt H, Machemer R. Experimental subretinal hemorrhage in rabbits. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982. 94:762–773.14. Johnson MW, Olsen KR, Hernandez E, et al. Retinal toxicity of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in the rabbit. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990. 108:259–263.15. Dellaporta A. Retinal damage from subretinal hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983. 95:568–570.16. Chen CY, Hooper C, Chiu D, et al. Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreal injection of tissue plasminogen activator and expansile gas. Retina. 2007. 27:321–328.17. Schulze SD, Hesse L. Tissue plasminogen activator plus gas injection in patients with subretinal hemorrhage caused by age-related macular degeneration: predictive variables for visual outcome. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2002. 240:717–720.18. Saika S, Yamanaka A, Yamanaka A, et al. Subretinal administration of tissue-type plasminogen activator to speed the drainage of subretinal hemorrhage. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1998. 236:196–201.19. Gopalakrishan M, Giridhar A, Bhat S, et al. Pneumatic displacement of submacular hemorrhage: safety, efficacy, and patient selection. Retina. 2007. 27:329–334.20. Ohji M, Saito Y, Hayashi A, et al. Pneumatic displacement of subretinal hemorrhage without tissue plasminogen activator. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998. 116:1326–1332.21. Daneshvar H, Kertes PJ, Leonard BC, Peyman GA. Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreal sulfur hexafluoride: a pilot study. Can J Ophthalmol. 1999. 34:385–388.22. Avery RL, Fekrat S, Hawkins BS, Bressler NM. Natural history of subfoveal subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 1996. 16:183–189.23. Scupola A, Coscas G, Soubrane G, Balestrazzi E. Natural history of macular subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica. 1999. 213:97–102.24. Bennett SR, Folk JC, Blodi CF, Klugman M. Factors prognostic of visual outcome in patients with subretinal hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990. 109:33–37.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pneumatic Displacement of Submacular Hemorrhage with Intravitreal Injection of SF6 Gas without Tissue Plasminogen Activator
- Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Monotherapy and Pneumatic Displacement for Submacular Hemorrhage in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
- Pneumatic Displacement of Submacular Hemorrhage with Intravitreal Injection of tPA and SF6 Gas
- Retinal Toxicity of Intravitreal Tissue Plasminogen Activator on Submacular Hemorrhage
- Natural Visual Outcome of Submacular Hemorrhage Associated with Retinal Arterial Macroaneurysm