J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2012 Jun;53(6):767-774.
Comparison of Six-Month Outcomes in Eyes with Two Hydrophilic Aspheric Intraocular Lenses after Cataract Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jykim2311@gmail.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the six-month clinical outcomes of Tek-Lens II model 872 (Tekia, Inc.) and Akreos MI-60 (Bausch & Lomb, Inc.) hydrophilic aspheric intraocular lenses (IOLs) implanted in-the-bag.
METHODS
After phacoemulsification was performed by a single surgeon (JY Kim), two different hydrophilic aspheric IOLs were implanted: the Tek-Lens II IOL in 57 eyes and the MI60 IOL in 49 eyes. The best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), refractive error (RE), total high-order aberration (HOA), anterior chamber depth (ACD), and contrast sensitivity (CS) were measured preoperatively and one, three, and six months postoperatively. All parameters were analyzed using the independent t-test to compare the two IOL groups.
RESULTS
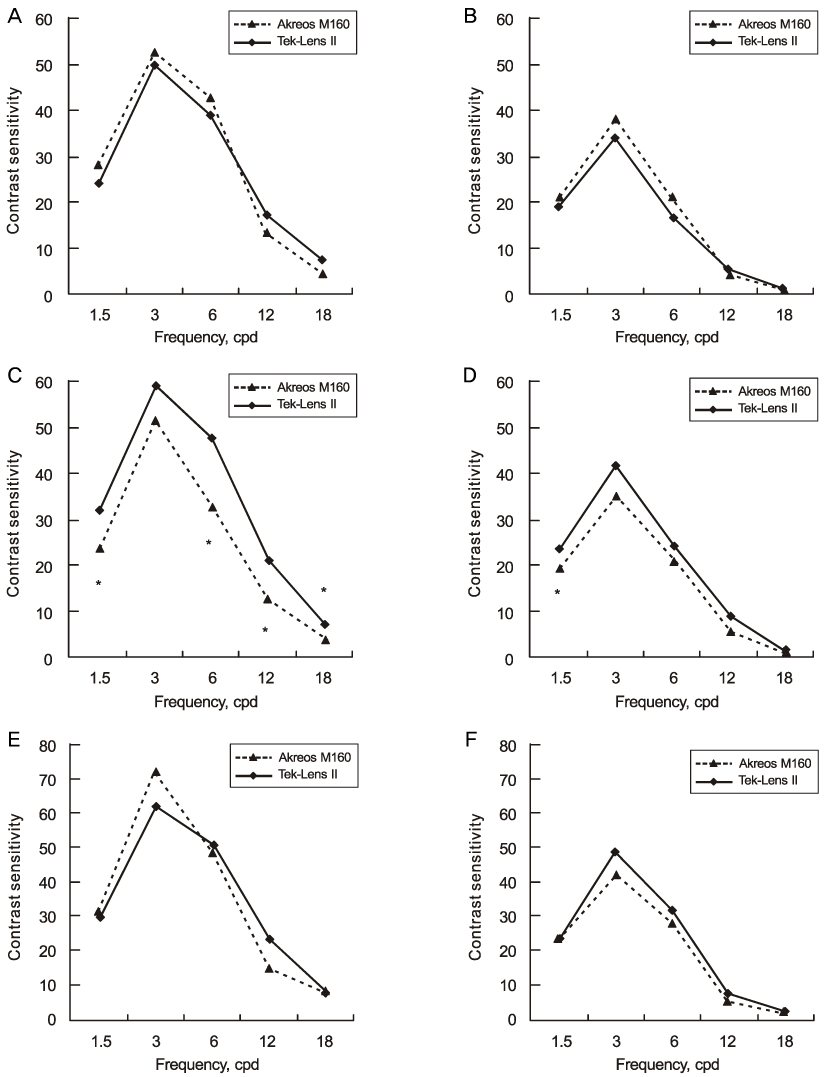
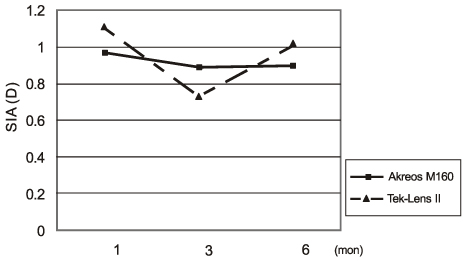
There was no significant difference in the BCVA, RE, or HOA between the two groups at any of the follow-up visits. Three months postoperatively, the ACD of the TEK-Lens II group as measured by corneal topography was significantly shallower than that of the MI60 group (3.67 +/- 0.52 mm vs. 4.10 +/- 0.40 mm; p = 0.008), and most of the photopic CS in the Tek-Lens II group was significantly higher than that in the MI60 group (all p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The Tek-Lens II IOL showed comparable clinical outcomes with a proven hydrophilic aspheric IOL for the postoperative six months.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ginsburg AP, Evans DW, Sekule R, Harp SA. Contrast sensitivity predicts pilots' performance in aircraft simulators. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1982. 59:105–109.2. Pesudovs K, Hazel CA, Doran RM, Elliott DB. The usefulness of Vistech and FACT contrast sensitivity charts for cataract and refractive surgery outcomes research. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004. 88:11–16.3. Applegate RA, Hilmantel G, Howland HC, et al. Corneal first surface optical aberrations and visual performance. J Refract Surg. 2000. 16:507–514.4. Bhattacharjee H, Bhattacharjee K, Medhi J. Visual performance: Comparison of foldable intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006. 32:451–455.5. Mierdel P, Kaemmerer M, Mrochen M, et al. Ocular optical aberrometer for clinical use. J Biomed Opt. 2001. 6:200–204.6. Holladay JT, Piers PA, Koranyi G, et al. A new intraocular lens design to reduce spherical aberration of pseudophakic eyes. J Refract Surg. 2002. 18:683–691.7. Son SW, Seo JW, Shin SJ, Chung SK. Comparison of the stability between three-piece and single-piece aspheric intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. 51:1584–1589.8. Jeong JH, Kim MK, Wee WR, Lee JH. Comparison of optical performances in eyes implanted with aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses after cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. 51:1445–1452.9. Mun GH, Im SK, Park HY, Yoon KC. Comparison of clinical results between two spherical aberraion-free intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. 51:670–676.10. Bae HW, Kim EK, Kim TI. Spherical aberration, contrast sensitivity and depth of focus with three aspherical intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009. 50:1639–1644.11. Botelho PJ, Johnson LN, Arnold AC. The effect of aspirin on the visual outcome of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996. 121:450–451.12. Artal P, Berrio E, Guirao A, Piers P. Contribution of the cornea and internal surfaces to the change of ocular aberrations with age. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2002. 19:137–143.13. Chalita MR, Chavala S, Xu M, Krueger RR. Wavefront analysis in post-LASIK eyes and its correlation with visual symptoms, refraction, and topography. Ophthalmology. 2004. 111:447–453.14. Rawer R, Stork W, Spraul CW, Lingenfelder C. Imaging quality of intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. 31:1618–1631.15. Bach M, Wesemann W, Kolling G, et al. [Photopic contrast sensitivity. Local contrast perception]. Ophthalmologe. 2008. 105:46–48.16. Kaufman PL, Alm A, Adler FH. Adler's Physiology of the Eye : Clinical Application. 2003. 10th ed. St. Louis: Mosby.17. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS. Contrast sensitivity and measuring cataract outcomes. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2006. 19:521–533.18. Shandiz JH, Derakhshan A, Daneshyar A, et al. Effect of cataract type and severity on visual acuity and contrast sensitivity. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2011. 6:26–31.19. Hayashi K, Hayashi H. Comparison of the stability of 1-piece and 3-piece acrylic intraocular lenses in the lens capsule. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. 31:337–342.20. Wirtitsch MG, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Effect of haptic design on change in axial lens position after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004. 30:45–51.21. Shin CJ, Lee JE, Lee JH, et al. Clinical outcomes after microincision cataract surgery and in-the-bag implantation of a new intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. 51:677–683.22. Alió J, Rodríguez-Prats JL, Galal A, Ramzy M. Outcomes of microincision cataract surgery versus coaxial phacoemulsification. Ophthalmology. 2005. 112:1997–2003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Nd:YAG Capsulotomy Rates between Spherical and Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Comparison of Nd:YAG Laser Capsulotomy Rates between Implantation of Two Different Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Comparison of the Stability Between Three-piece and Single-piece Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Comparison of Anterior Chamber Parameter and Refractive Change between Three-Piece and Single-Piece Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Refractive Power Outcomes with an Intraocular Lens with 0.25-diopter Intervals