J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Sep;52(9):1071-1076.
Association between Weight Gain and the Occurrence and Severity of Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ysyu@snu.ac.kr
- 2Seoul Artificial Eye Center, Seoul National University Hospital Clinical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the association between the occurrence and severity of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and postnatal weight gain.
METHODS
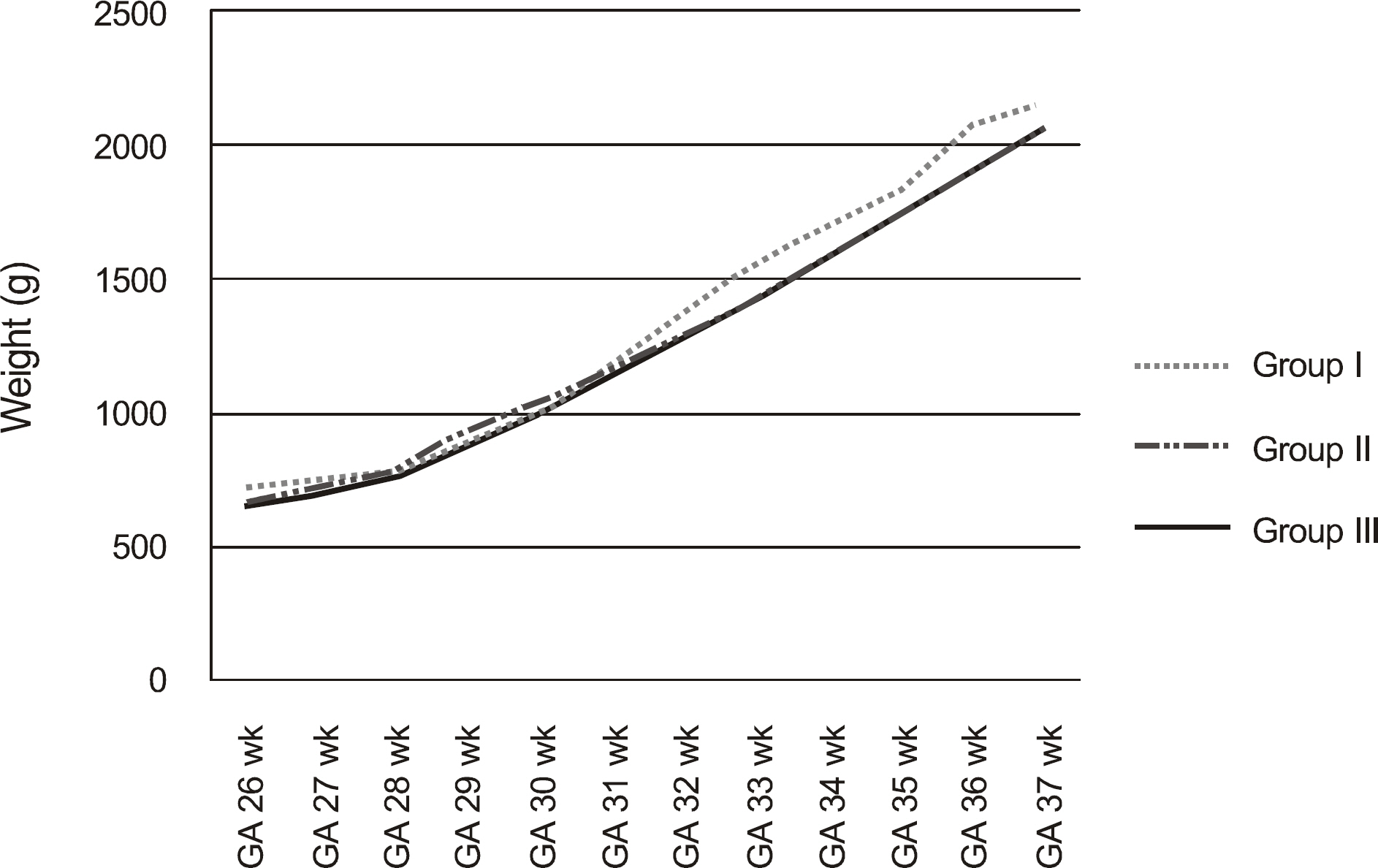
The medical records and mean rate of postnatal weekly weight gain measurements for 275 premature infants were retrospectively reviewed. According to fundus examination findings, 275 infants were divided into the following three groups according to the international classification of ROP: Group I; infants with no ROP, Group II; infants with mild ROP (stage 1 or stage 2 with no additional disease or spontaneous regression), and Group III; infants with moderate to severe ROP (stage 3, threshold or Type I ROP according to ET-ROP). The mean rates of postnatal weekly weight gain in each group were compared and other risk factors were evaluated.
RESULTS
There was a tendency of decrement in the mean rate of postnatal weekly weight gain in association with the severity of the disease (Group I: 13.54 +/- 11.87%; Group II: 12.38 +/- 1.33%; Group III: 11.41 +/- 1.70%) but no statistical significance was found. Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference between the group without ROP and the group with ROP. Significant risk factors related to ROP were low birth weight, low gestational age, low Apgar score, long duration of oxygen therapy, high incidence of respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
CONCLUSIONS
The change in postnatal weight gain has limited usage as a main prognostic factor in predicting the progression of ROP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rhim WI, Lew H, Yun YS. Clinical features of risk factors and regression of retinopathy of prematurity. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1199–205.2. Chung TY, Yu YS. Clinical outcome of spontaneously regressed ROP. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1444–50.3. Vander JF, McNamara JA, Tasman W, Brown GC. Revised indications for early treatment of retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:406–7.
Article4. Early Treatment For Retinopathy Of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Revised indications for the treatment of retinopathy of prematurity: results of the early treatment for retinopathy of prematurity randomized trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:1684–94.5. Palmer EA, Hardy RJ, Dobson V, et al. 15-year outcomes following threshold retinopathy of prematurity: final results from the multicenter trial of cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:311–8.6. Multicenter trial of cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity: preliminary results. Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Pediatrics. 1988; 81:697–706.7. Park EA, Kim GH. A clinical study for the time of development and risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics. 1997; 40:945–54.8. Kim TI, Sohn JH, Yoon YH, et al. Postnatal risk factors of retinopathy of prematurity. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1229–35.
Article9. Park JD, Kweon JH, Kim WH, et al. Incidence and risk factors of the retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics. 1996; 39:326–37.10. Kim JH, Yu YS. Assessment of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) revisited. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:22–7.
Article11. Yang MB, Donovan EF, Wagge JR. Race, gender, and clinical risk index for babies (CRIB) score as predictors of severe retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2006; 10:253–61.
Article12. Fortes Filho JB, Eckert GU, Valiatti FB, et al. The influence of gestational age on the dynamic behavior of other risk factors associated with retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010; 248:893–900.
Article13. International Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. The International Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity revisited. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005; 123:991–9.14. Yang MB, Donovan EF. Risk analysis and an alternative protocol for reduction of screening for retinopathy of prematurity. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:539–45.
Article15. Rush R, Rush S, Nicolau J, et al. Systemic manifestations in response to mydriasis and physical examination during screening for retinopathy of prematurity. Retina. 2004; 24:242–5.
Article16. Hellstrom A, Hard AL, Engstrom E, et al. Early weight gain predicts retinopathy in preterm infants: new, simple, efficient approach to screening. Pediatrics. 2009; 123:638–45.17. Hellstrom A, Ley D, Hansen-Pupp I, et al. New insights into the development of retinopathy of prematurity–importance of early weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 2010; 99:502–8.18. Lofqvist C, Hansen-Pupp I, Andersson E, et al. Validation of a new retinopathy of prematurity screening method monitoring longitudinal postnatal weight and insulinlike growth factor I. Arch Ophthalmol. 2009; 127:622–7.
Article19. Wu C, Vanderveen DK, Hellstrom A, et al. Longitudinal postnatal weight measurements for the prediction of retinopathy of prematurity. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010; 128:443–7.
Article20. Drenser KA, Trese MT, Capone A Jr. Aggressive posterior retinopathy of prematurity. Retina. 2010; 30(4 Suppl):S37–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Postnatal weight gain in the first two weeks as a predicting factor of severe retinopathy of prematurity requiring treatment
- Effect of Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity
- Clinical analysis of retinopathy of prematurity
- The Effect of Cryotherapy and Laser Photocoagulation for the Retinopathy of Prematurity
- A Clinical Study of Retinopathy of Prematurity