J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Feb;52(2):169-174.
Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measured by Ultrasound and Two Kinds of Partial Coherence Interferometers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. shchoi@cnu.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
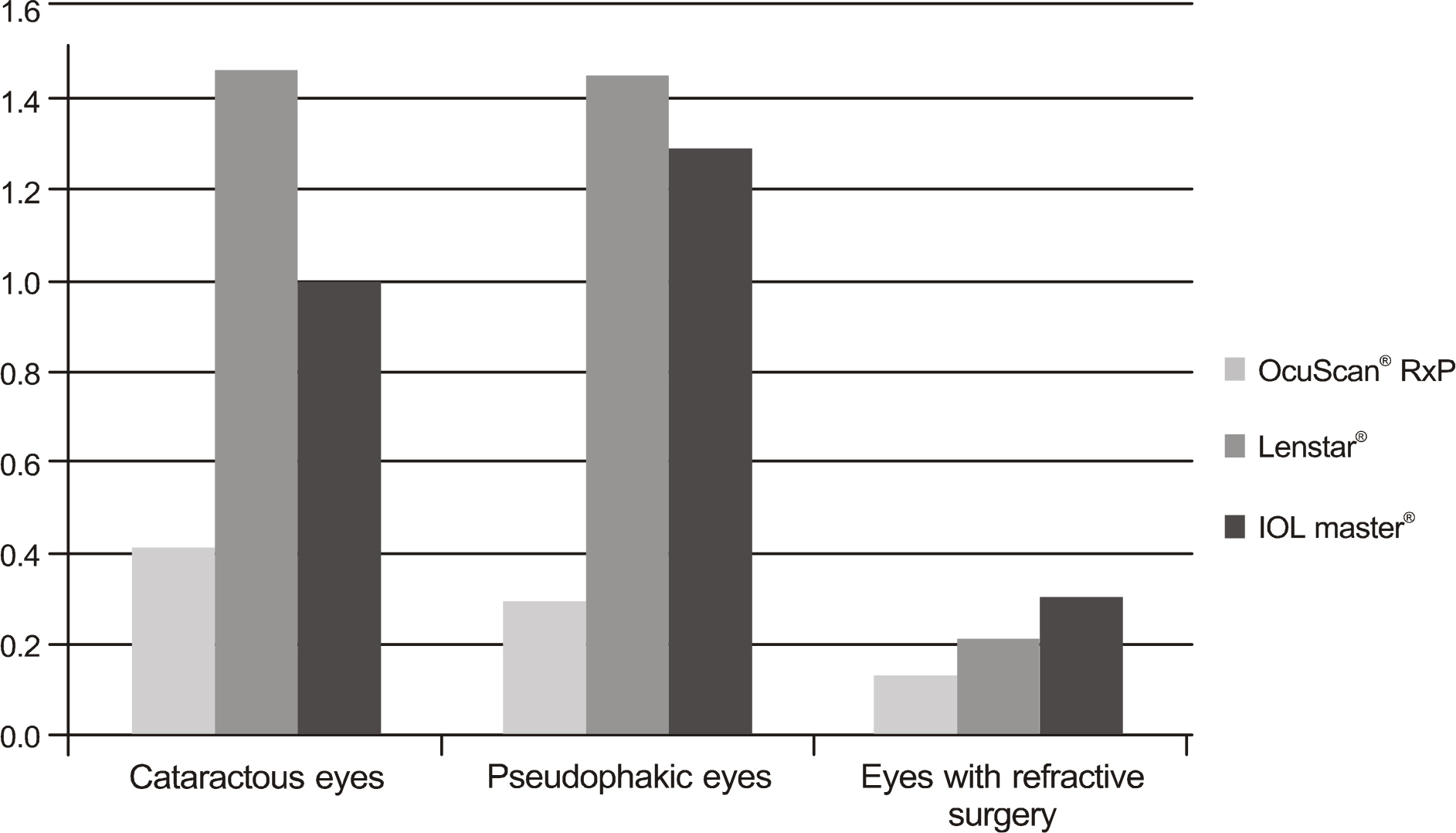
To evaluate the reproducibility and repeatibility of biometry in cataractous eyes, pseudophakic eyes and eyes having undergone refractive surgery. The OcuScan(R)RxP, LENSTAR(R) and IOL Master(R) instruments were compared, as were. The accuracies of the refractive results after cataract surgery.
METHODS
The biometries of 45 cataractous eyes, 31 pseudophakic eyes, and 32 eyes having undergone refractive surgery were measured by two practitioners using OcuScan(R)RxP, LENSTAR(R) and IOL Master(R) instruments. The paired t-test was used to compare the reproducibilities in the three groups.
RESULTS
There were no differences in axial length among the groups when using any of the instruments. There was no significant difference in the repeatibility regardless of the instrument used, although. In the cataractous eyes, pseudophakic eyes and eyes with refractive surgery, OcuScan(R)RxP showed the highest repeatability. However, we knew that all three instruments were excellent in the repeatability because the difference was less than 1.5%. The Prediction error of the instruments with regard to refractive results could not be determined after cataract surgery. In some patients with severe cataract, measurement was impossible for both the LENSTAR(R) and IOL Master(R) instruments.
CONCLUSIONS
In all groups, OcuScan(R)RxP, LENSTAR(R) and IOL Master(R) showed no significant differences with regard to reproducibility or prediction of refractive power after surgery. Among three groups, the repeatability was rather high in the existing ultrasound method than in the partial coherence interferometers. In some patients with severe cataract, measurement was impossible for both the LENSTAR(R) and IOL Master(R) instruments.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence interferometry: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:524–34.
Article2. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article3. Hitzenberger CK. Optical measurement of the axial eye length by laser Doppler interferometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991; 32:616–24.4. Gimbel HV, Sun R. Accuracy and predictability of intraocular lens power calculation after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:571–6.
Article5. Holladay JT. Standardizing constants for ultrasonic biometry, keratometry and intraocular lens power calculations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997; 23:1356–70.
Article6. Doh HJ, Sah WJ, Myong YW, et al. Accuracy of intraocular lens power in cataract patients underwent excimer laser PRK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2145–51.7. Cruysberg LP, Doors M, Verbakel F, et al. Evaluation of the LENSTAR LS 900 non-contact biometer. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 94:106–10.
Article8. Kim HS, Kim JH, Kim HM, Song JS. Comparison of corneal thickness measured by specular, US pachymetry, and Orbscan in post-PKP eyes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:245–50.9. Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician. 1983; 32:307–17.
Article10. Moon SW, Kim ES, Kim YG, et al. The comparison of macular thickness measurements and repeatabilities between time domain and spectral domain OCT. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1050–9.
Article11. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL master(R) and A-scan ultrasound: refractive results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:27–32.12. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article13. Chung JK, Choe CM, You YS, Lee SJ. Biometry with partial coherence interferometry and ultrasoundgraphy in high myopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:355–61.14. Hitzenberger CK. Optical measurement of the axial eye length by laser Doppler interferometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991; 32:616–24.15. Butcher JM, O'Brien C. The reproducibility of biometry and keratometry measurements. Eye. 1991; 5:708–11.
Article16. Raj PS, Ilango B, Watson A. Measurement of axial length in the calculation of intraocular lens power. Eye. 1998; 12:227–9.
Article17. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS, et al. Immersion A-scan compared with partial coherence interferometry: outcomes analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:239–42.18. Hill W, Angeles R, Otani T. Evaluation of a new IOLMaster algo-rithm to measure axial length. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:920–4.
Article19. Rose LT, Moshegov CN. Comparison of the Zeiss IOLMaster and applanation A-scan ultrasound: biometry for intraocular lens calculation. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2003; 31:121–4.
Article20. Connors R 3rd, Boseman P 3rd, Olson RJ. Accuracy and reproducibility of biometry using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:235–8.
Article21. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–3.
Article22. Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry: intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1961–8.
Article23. Kiss B, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Biometry of cataractous eyes using partial coherence interferometry: clinical feasibility study of a commercial prototype I. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002; 28:224–9.24. Lam AK, Chan R, Pang PC. The repeatability and accuracy of axial length and anterior chamber depth measurements from the IOLMaster. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2001; 21:477–83.25. Kielhorn I, Rajan MS, Tesha PM, et al. Clinical assessment of the Zeiss IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:518–22.
Article26. Choi JH, Roh GH. The reproducibility and accuracy of biometry parameter measurement from IOL Master (R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1665–73.27. Németh J, Fekete O, Pesztenlehrer N. Optical and ultrasound measurement of axial length and anterior chamber depth for intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:85–8.
Article28. Tehrani M, Krummenauer F, Blom E, Dick HB. Evaluation of the practicality of opticalbiometry and applanation ultrasound in 253 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003; 29:741–6.29. Freeman G, Pesudovs K. The impact of cataract severity on measurement acquisition with the IOLMaster. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005; 83:439–42.
Article30. Parravano M, Oddone F, Sampalmieri M, Gazzaniga D. Reliability of the IOLMaster in axial length evaluation in silicone oil-filled eyes. Eye. 2007; 21:909–11.
Article31. Buckhurst PJ, Wolffsohn JS, Shah S, et al. A new optical low coherence reflectometry device for ocular biometry in cataract patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:949–53.
Article32. Fercher AF, Mengedoht K, Werner W. Eye-length measurement by interferometry with partial coherent light. Opt Lett. 1988; 13:186–8.33. Song BY, Yang KJ, Yoon KC. Accuracy of partial coherence interferometry in intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:775–80.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measurements Using A-Scan Ultrasound and Two Types of Partial Coherence Interferometers
- Comparison of the Refractive Results Measured by Ultrasound and Partial Coherence Interferometers
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients Between Lenstar(R) and IOL Master(R)
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometer and Partial Coherence Interferometer
- Accuracy of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients with AL-Scan(R)