J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Nov;54(11):1688-1693. 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1688.
Accuracy of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients with AL-Scan(R)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Saevit Eye Hospital, Goyang, Korea. 76drhoon@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2217915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2013.54.11.1688
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the axial lengths, anterior chamber depths, and keratometric measurements and to predict postoperative refractions of AL-Scan(R), IOL master(R), and ultrasound.
METHODS
A total of 40 eyes in 30 patients who received cataract surgery were included in the present study. The axial length, anterior chamber depth, and keratometry were measured by 2 types of partial coherence interferometry (AL-Scan(R) and IOL master(R)) and ultrasound. The SRK/T formula was used to calculate IOL power, and the predictive error which subtracts predictive refraction from postoperative refraction was compared among the ocular biometry devices.
RESULTS
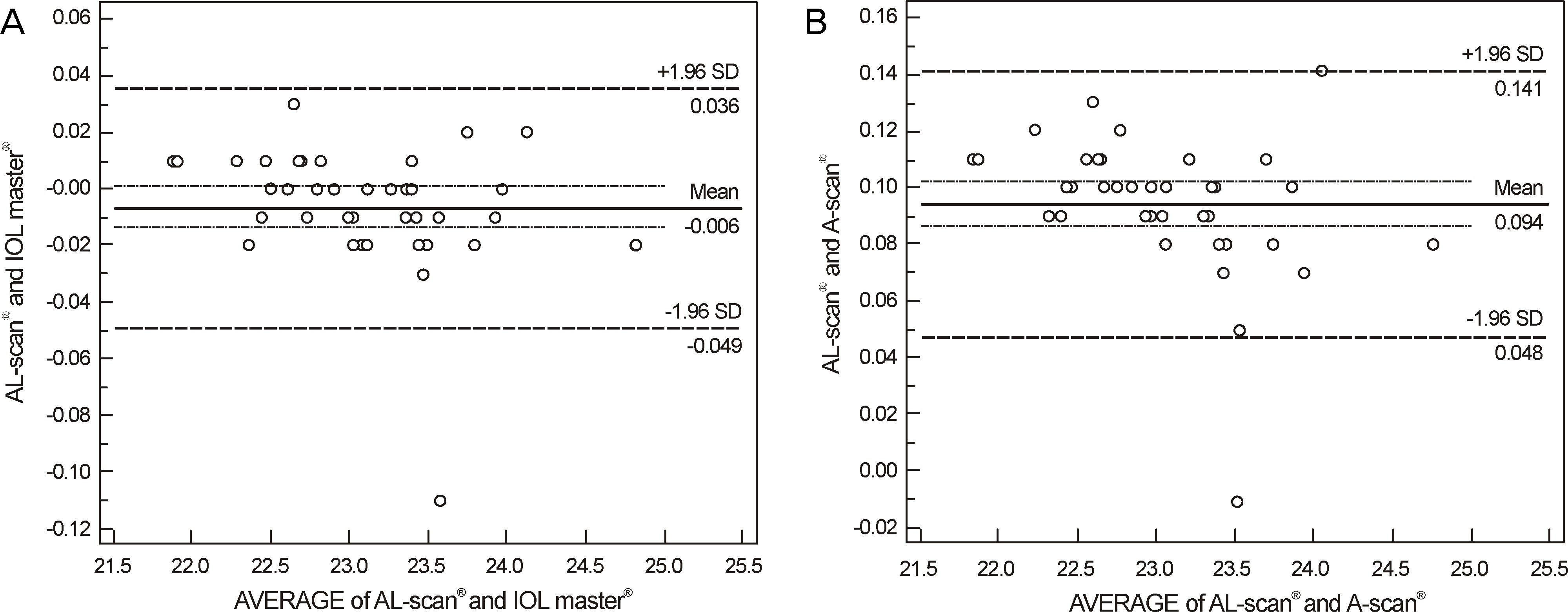
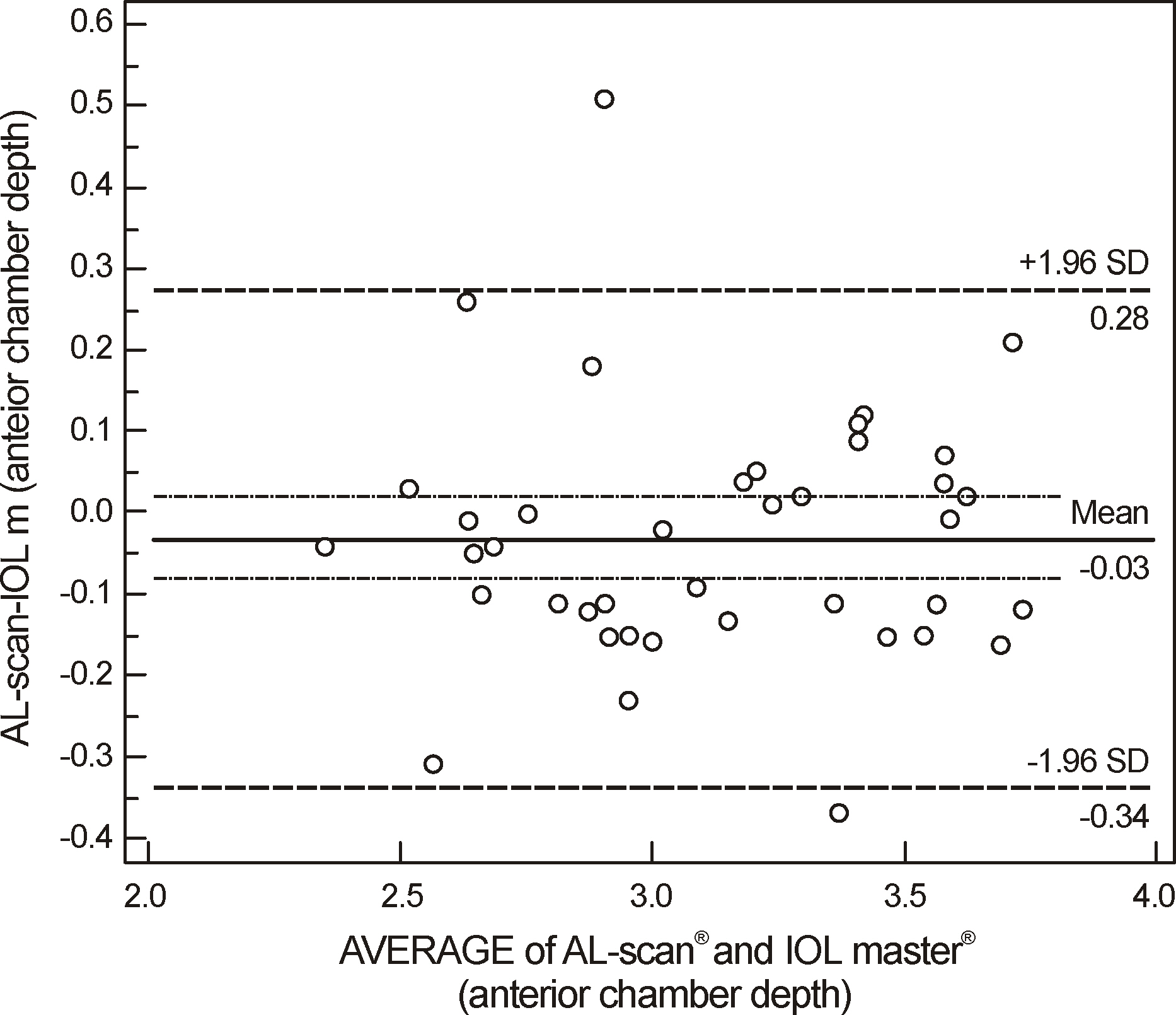
Axial lengths were 23.08 +/- 0.62 mm, 23.09 +/- 0.62 mm, and 22.99 +/- 0.62 mm measured by AL scan(R), IOL master(R), and ultrasound, respectively. Axial length measured by ultrasound was statistically significantly shorter than AL scan(R) and IOL master(R) (p < 0.001, p < 0.001, respectively). The anterior chamber depth and keratometry were 3.11 +/- 0.06 mm and 44.82 +/- 1.34 D measured by AL scan(R), and 3.13 +/- 0.06 mm and 44.85 +/- 1.26 D measured by IOL master(R), respectively. The differences of anterior chamber depth and keratometry between the 2 devices were not statistically significant (p = 0.226, p = 0.331, respectively). The mean absolute prediction errors were 0.44 +/- 0.35 D, 0.40 +/- 0.34 D, and 0.39 +/- 0.30 D in AL-Scan(R), IOL master(R) and ultrasound, respectively, and were not statistically significantly different (p = 0.843, p = 0.847, p = 1.000, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
The ocular biometric measurements and prediction of postoperative refraction using AL-Scan(R) were as accurate as IOL master(R) and ultrasound.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of Three Formulas for Intraocular Lens Power Formula Accuracy
Ki Woong Lee, Jinsoo Kim, Dong Hyun Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2020;61(1):27-33. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2020.61.1.27.Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measured Using Four Applanation Ultrasonographic Biometry Devices
Byung Su Lim, Sang Kyu Lee, Eun Chul Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(11):1631-1635. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.11.1631.
Reference
-
References
1. Drexler W, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Partial coherence inter- ferometry: a novel approach to biometry in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 126:524–34.2. Gimbel HV, Sun R. Accuracy and predictability of intraocular lens power calculation after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:571–6.
Article3. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article4. Drexler W, Hitzenberger CK, Baumgartner A, et al. Investigation of dispersion effects in ocular media by multiple wavelength parti- al coherence interferometry. Exp Eye Res. 1998; 66:25–33.5. Lam AK, Chan R, Pang PC. The repeatability and accuracy of axial length and anterior chamber depth measurements from the IOLMaster. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2001; 21:477–83.6. Retzlaff JA Sand, ers DR, Kraff MC. Development of the SRK/T intraocular lens implant power calculation formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:333–40.7. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1992; 18:125–9.
Article8. Giers U, Epple C. Comparison of A-scan device accuracy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:235–42.
Article9. Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, Schneider B. Comparison of im- mersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:765–73.10. Hoffer KJ, Shammas HJ, Savini G. Comparison of 2 laser instru- ments for measuring axial length. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:644–8.11. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. Improved prediction of in- traocular lens power using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:861–7.12. Rajan MS, Keilhorn I, Bell JA. Partial coherence laser inter- ferometry vs conventional ultrasound biometry in intraocular lens power calculations. Eye (Lond). 2002; 16:552–6.13. Rose LT, Moshegov CN. Comparison of the Zeiss IOLMaster and applanation A-scan ultrasound: biometry for intraocular lens calculation. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2003; 31:121–4.
Article14. Eleftheriadis H. IOLMaster biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003; 87:960–3.
Article15. Santodomingo-Rubido J, Mallen EA, Gilmartin B, Wolffsohn JS. A new non-contact optical device for ocular biometry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:458–62.
Article16. Buckhurst PJ, Wolffsohn JS, Shah S, et al. A new optical low co- herence reflectometry device for ocular biometry in cataract patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:949–53.17. Utine CA, Altin F, Cakir H, Perente I. Comparison of anterior chamber depth measurements taken with the Pentacam, Orbscan IIz and IOLMaster in myopic and emmetropic eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009; 87:386–91.
Article18. Lackner B, Schmidinger G, Skorpik C. Validity and repeatability of anterior chamber depth measurements with Pentacam and Orbscan. Optom Vis Sci. 2005; 82:858–61.
Article19. Rabsilber TM, Becker KA, Frisch IB, Auffarth GU. Anterior chamber depth in relation to refractive status measured with the Orbscan II Topography System. J Cataract Refract Surgy. 2003; 29:2115–21.
Article20. Reddy AR Pand, e MV, Finn P, El-Gogary H. Comparative estimation of anterior chamber depth by ultrasonography, Orbscan II, and IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:1268–71.21. Shin JW, Seong MC, Kang MH, et al. Comparison of ocular bio- metry and postoperative refraction in cataract patients between Lenstar® and IOL master®. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:833–8.22. Kwag JY, Choi SH. Comparison of ocular biometry measured by ultrasound and two kinds of partial coherence interferometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:169–74.
Article23. Kim DY, Kim MJ, Kim JY, Tchah HW. Comparison of formulas for intraocular lens power calculation installed in a parital coherence interferometer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:523–8.24. Jun RM, Kang SY, Kim BY. Accuracy of biometry and intraocular lens power calculation with partial coherence interferometry in high myopia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1746–51.
Article25. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL master® and A-scan ul- trasound: refractive results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:27–32.26. Chung JK, Choe CM, You YS, Lee SJ. Biometry with partial co- herence interferometry and ultrasonography in high myopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:355–61.27. Song BY, Yang KJ, Yoon KC. Accuracy of partial coherence inter- ferometry in intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:775–80.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Accuracy of Biometry for Intraocular Lens Implantation Using the New Partial Coherence Interferometer, AL-scan
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Postoperative Refraction in Cataract Patients Between Lenstar(R) and IOL Master(R)
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measurements Using A-Scan Ultrasound and Two Types of Partial Coherence Interferometers
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry Measured Using Four Applanation Ultrasonographic Biometry Devices
- Comparison of Ocular Biometry and Refractive Outcomes Using IOL Master 700, IOL Master 500, and Ultrasound