Prog Med Phys.
2016 Jun;27(2):86-91. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.86.
Image-based Absorbed Dosimetry of Radioisotope
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of RI-Convergence Research, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea. skwoo@kirams.re.kr
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2328193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.86
Abstract
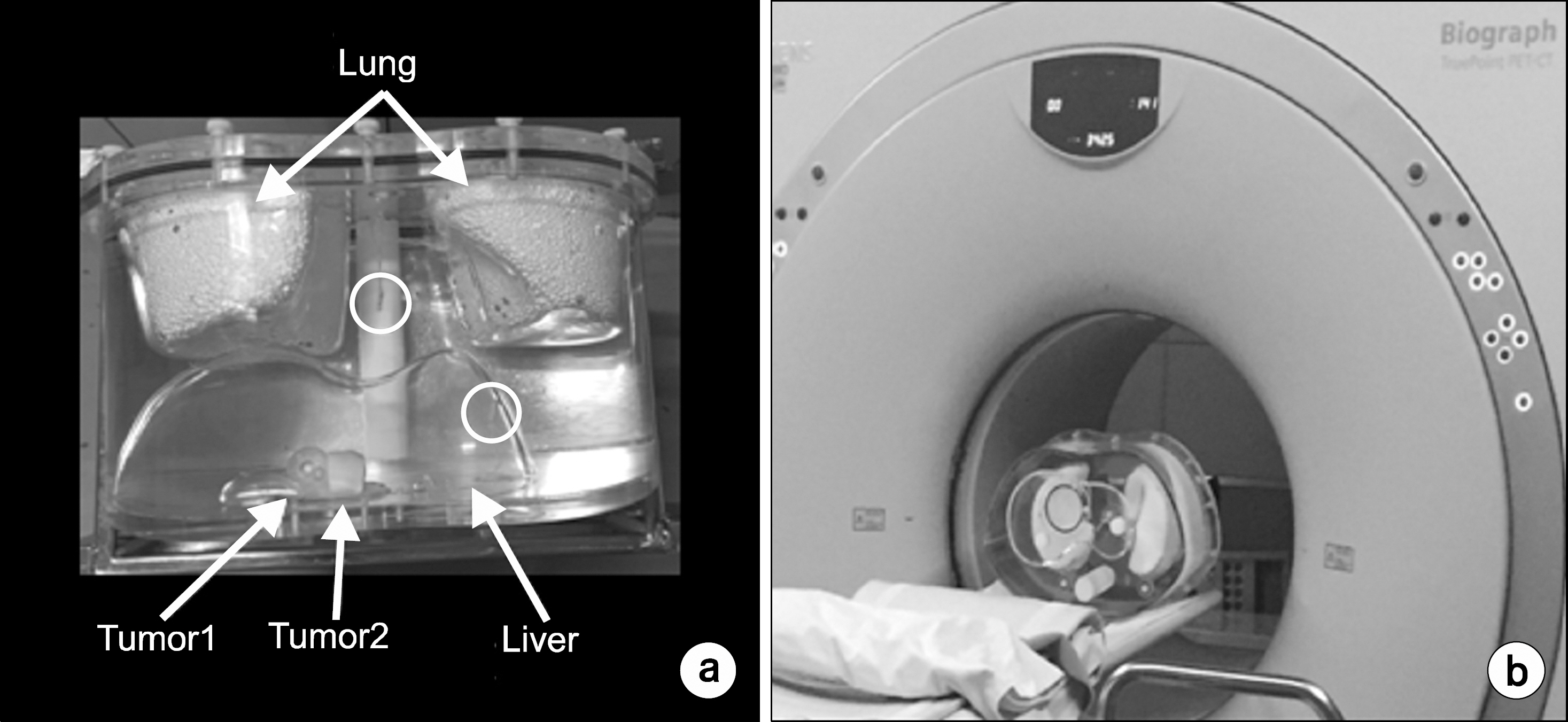
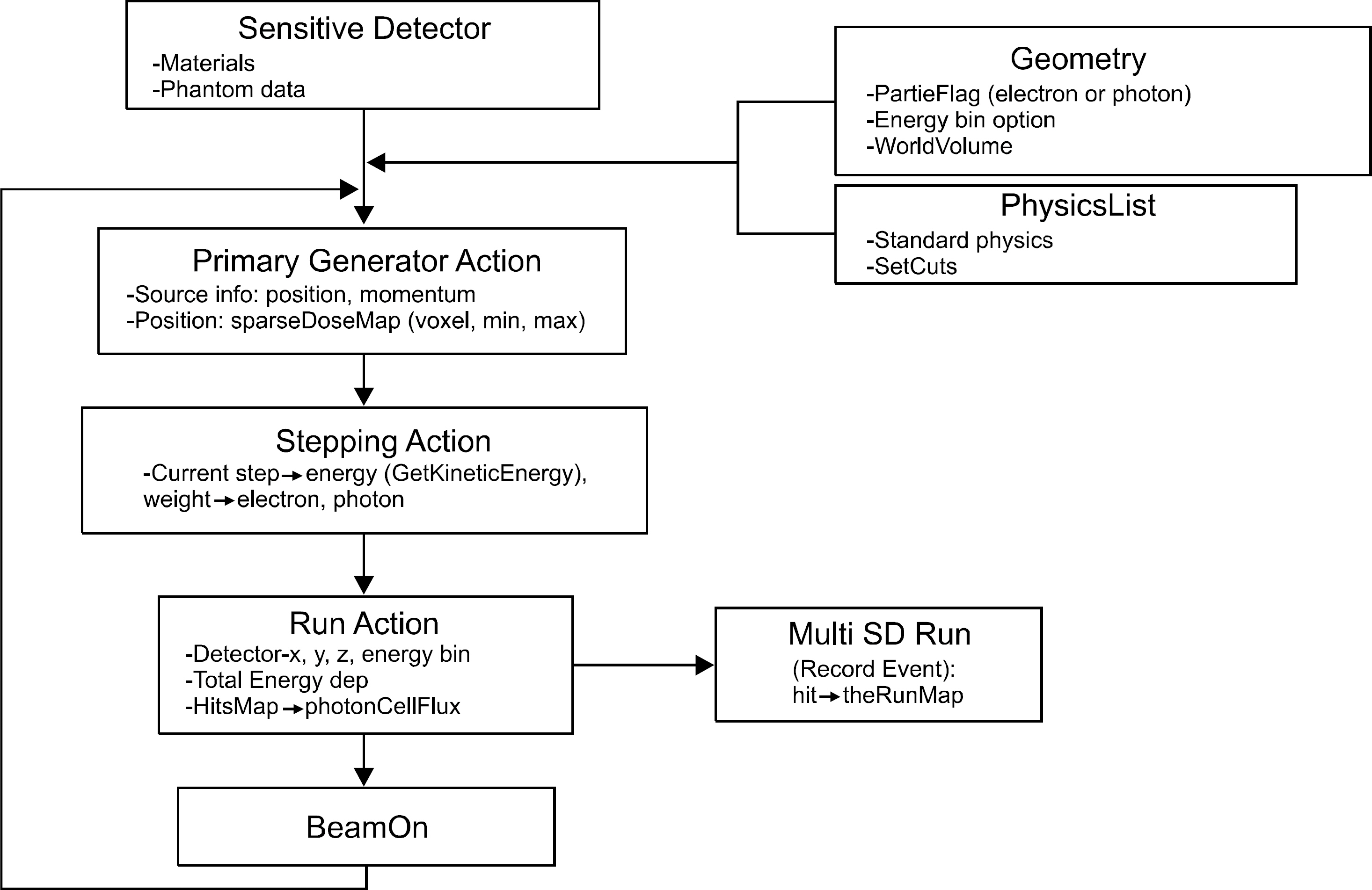
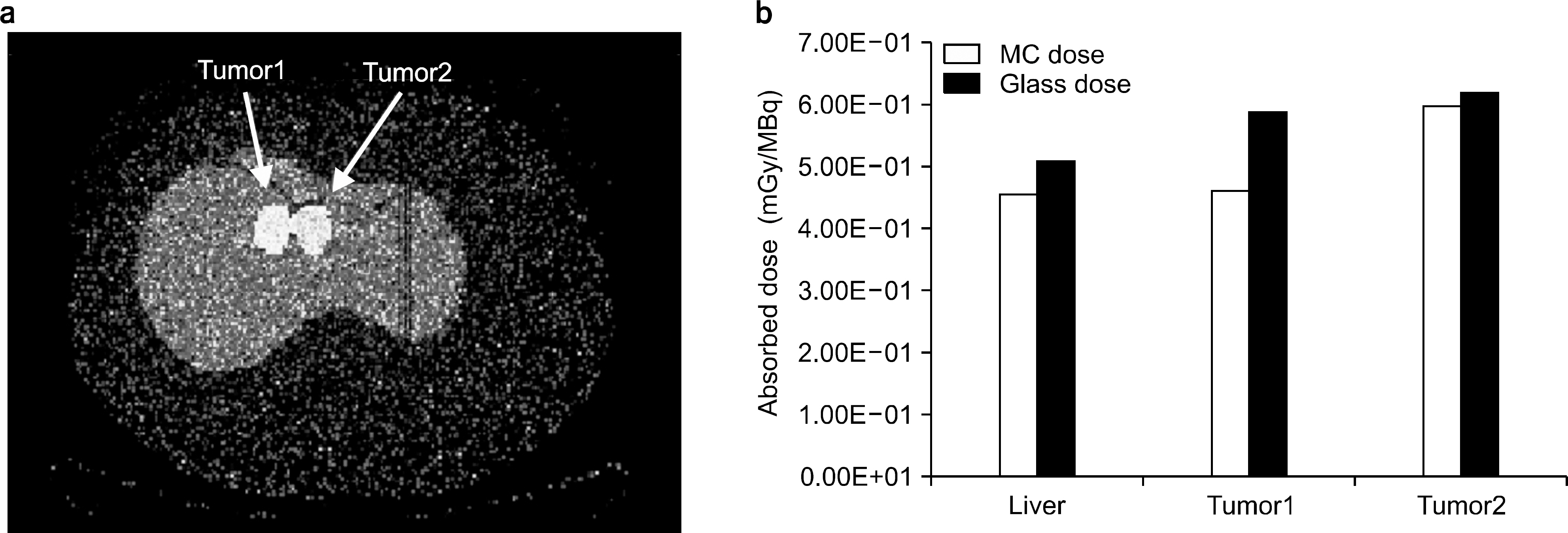
- An absorbed dose calculation method using a digital phantom is implemented in normal organs. This method cannot be employed for calculating the absorbed dose of tumor. In this study, we measure the S-value for calculating the absorbed dose of each organ and tumor. We inject a radioisotope into a torso phantom and perform Monte Carlo simulation based on the CT data. The torso phantom has lung, liver, spinal, cylinder, and tumor simulated using a spherical phantom. The radioactivity of the actual absorbed dose is measured using the injected dose of the radioisotope, which is Cu-64 73.85 MBq, and detected using a glass dosimeter in the torso phantom. To perform the Monte Carlo simulation, the information on each organ and tumor acquired using the PET/CT and CT data provides anatomical information. The anatomical information is offered above mean value and manually segmented for each organ and tumor. The residence time of the radioisotope in each organ and tumor is calculated using the time activity curve of Cu-64 radioactivity. The S-values of each organ and tumor are calculated based on the Monte Carlo simulation data using the spatial coordinate, voxel size, and density information. The absorbed dose is evaluated using that obtained through the Monte Carlo simulation and the S-value and the residence time in each organ and tumor. The absorbed dose in liver, tumor1, and tumor2 is 4.52E-02, 4.61E-02, and 5.98E-02 mGy/MBq, respectively. The difference in the absorbed dose measured using the glass dosimeter and that obtained through the Monte Carlo simulation data is within 12.3%. The result of this study is that the absorbed dose obtained using an image can evaluate each difference region and size of a region of interest.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rise of the Visible Monkey: Sectioned Images of Rhesus Monkey
Beom Sun Chung, Chang-Yeop Jeon, Jae-Won Huh, Kang-Jin Jeong, Donghwan Har, Kyu-Sung Kwack, Jin Seo Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(8):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e66.
Reference
-
References
1. Bar-Shalom R, Yefremov N, Guralnik L, et al. Clinical performance of PET/CT in evaluation of cancer: additional value for diagnostic imaging and patient management. J Nucl Med. 44(8):1200–1209. 2003.2. Antoch G, Saoudi N, Kuehl H, et al. Accuracy of whole-body dual-modality fluorine-18–2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) for tumor staging in solid tumors: comparison with CT and PET. J Clin Oncol. 22(21):4357–4368. 2004.
Article3. Mack A, Scheib SG, Major J, et al. Precision dosimetry for narrow photon beams used in radiosurgery Determination of Gamma Knife output factors. Med Phys. 29:2080–2089. 2002.4. Huang SY, Bolch WE, Lee C, et al. Patientspecific dosimetry using pretherapy [124I]m-iodobenzylguanidine ([124I]mIBG) dynamic PET/CT imaging before [131I]mIBG targeted radionuclide therapy for neuroblastoma. Mol Imaging Biol. 17(2):284–294. 2015.
Article5. Neto VL, Vieira JW, Lima FR. Application for internal dosimetry using biokinetic distribution of photons based on nuclear medicine images. Radiol Bras. Set. 47:275–282. 2014.6. Miller G, Martz HF, Little TT, et al. Bayesian internal dosimetry calculations using Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Radiation Protection Dosimetry. 98:191–198. 2002.
Article7. Berger MJ. MIRD Pamphlet No. 7: distribution of absorbed doses around point sources of electrons and beta particles in water and other media. J Nucl Med. 12:5–23. 1971.8. Snyder WS, Ford MR, Warner GG, et al. MIRD Pamphlet No. 11: ‘S', Absorbed dose per unit cumulated activity for selected radionuclides and organs, The Society of Nuclear Medicine, New York (. 1975.9. Stabin MG. MIRDOSE: personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 37:538–546. 1996.10. Caon M. Voxel-based computational models of real human anatomy: a review. Radiat Environ Biophys. 42:229–235. 2004.
Article11. Stabin MG; Richard B. Sparks, Eric Crowe: OLINDA/EXM: The Second-Generation Personal Computer Software for Internal Dose Assessment in Nuclear Medicine. THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE. 46:1023–1027. 2005.12. Thomas SR, Stabin MG, Chen CT, et al. MIRD Pamphlet No. 14: A Dynamic Urinary Bladder Model for Radiation Dose Calculations. The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 33:783–802. 1992.13. Koepfli P, Hany TF, Wyss CA, et al. CT attenuation correction for myocardial perfusion quantification using a PET/CT hybrid scanner. J Nucl Med. 45(4):537–542. 2004.14. Stabin MG, Flux GD. Internal dosimetry as a tool for radiation protection of the patient in nuclear medicine. Biomed Imaging Interv J 3 (2)e. 28:1–11. 2007.
Article15. Treyer V, Streffer J, Ametamey SM, et al. Radiation dosimetry and biodistribution of 11C-ABP688 measured in healthy volunteers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 35:766–770. 2008.
Article16. Stabin MG, Yoriyaz H. Photon specific absorbed fractions calculated in the trunk of an adult male voxel-based phantom. Health Phys. 82:21–44. 2002.
Article17. Stabin MG. Nuclear medicine dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 51:R187–R202. 2006.
Article18. Loevinger R, Budinger T, Watson E. MIRD Primer for Absorbed Dose Calculations, Society of Nuclear Medicine, New York (. 1988.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Image-Based Dosimetry of Radionuclide Therapy
- Proficiency Test for the Dosimetry Audit Service Provider
- Development of Web-based Dosimetry Calibration Program for High Energy Radiation
- Difference in radiation absorbed dose according to the panoramic radiographic machines
- High Energy Electron Dosimetry by Alanine/ESR Spectroscopy