Prog Med Phys.
2022 Dec;33(4):72-79. 10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.72.
Proficiency Test for the Dosimetry Audit Service Provider
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ionizing Radiation Metrology Group, Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS), Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2537874
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.72
Abstract
- Purpose
The proficiency test was conducted to assess the performance of the dosimetry audit service provider in the readout practice of the dose delivered to patients in medical institutions.
Methods
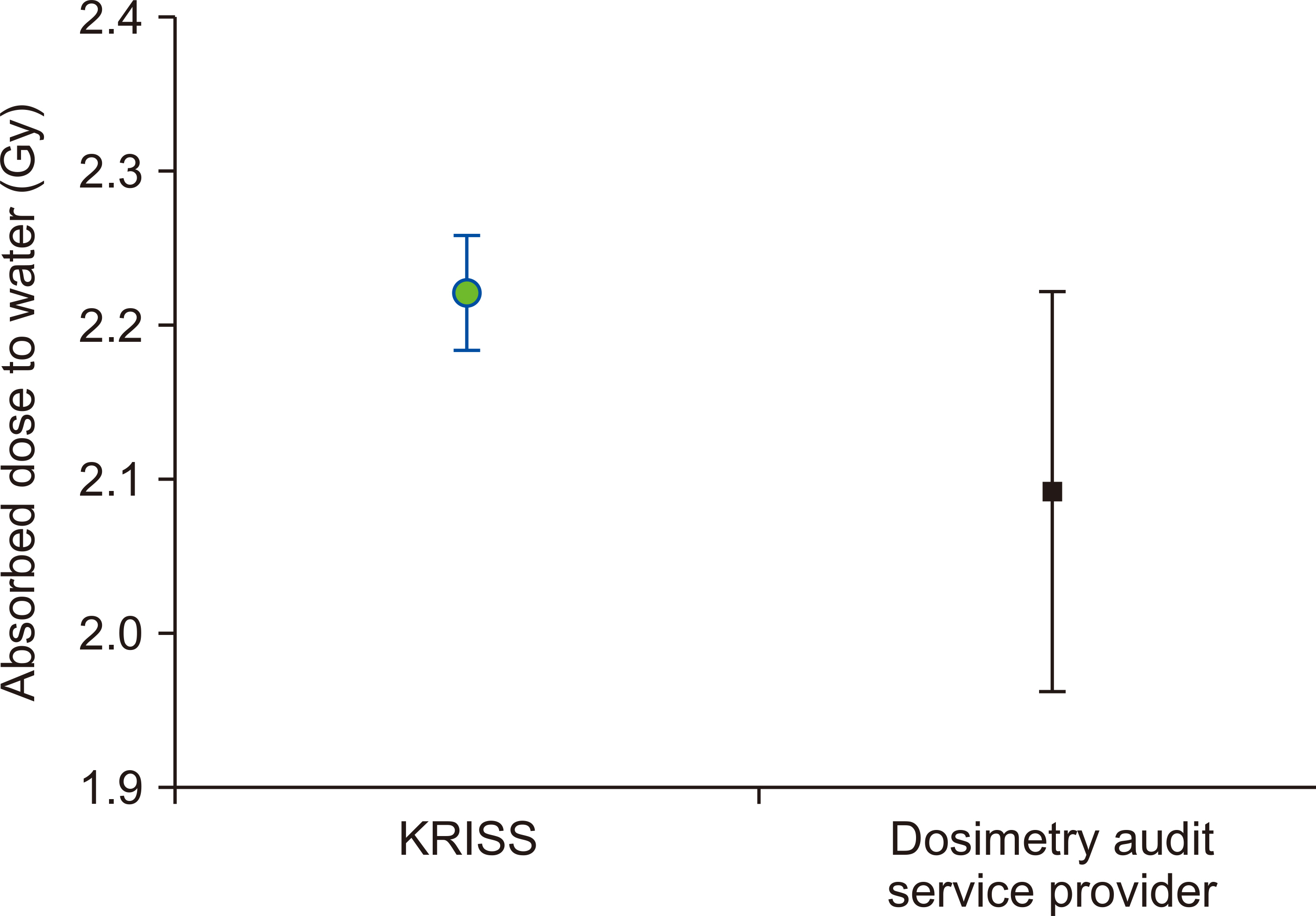
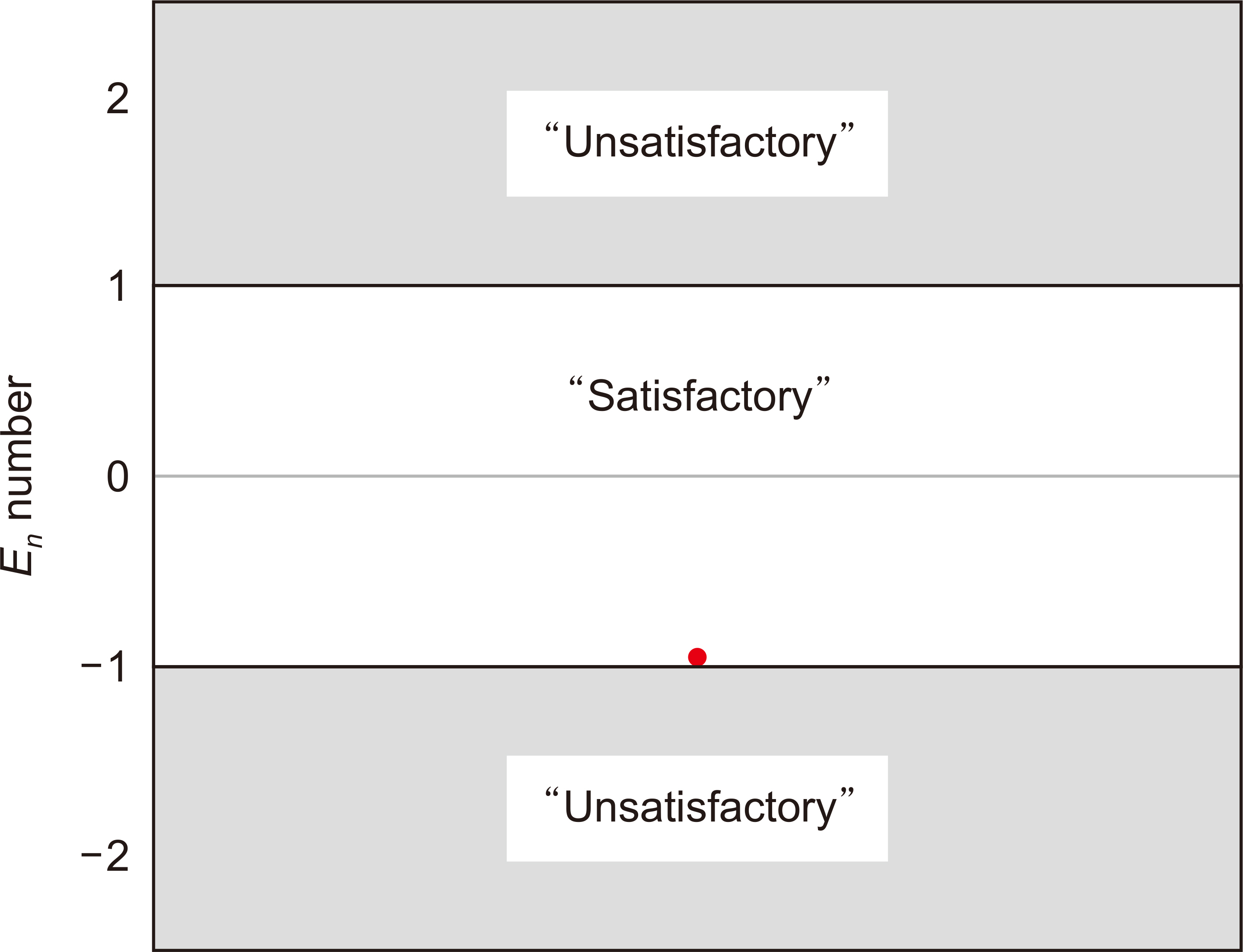
A certain amount of the absorbed dose to water for the high-energy X-ray from the medical linear accelerator (LINAC) installed in the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) was delivered to the postal dose audit package given by the dosimetry audit service provider, in which the radio-photoluminescence (RPL) glass dosimeters were mounted. The dosimetry audit service provider read the RPL glass dosimeters and sent the readout dose value with its uncertainty to KRISS. The performance of the dosimetry audit service provider was evaluated based on the En number given in ISO/IEC 17043:2010.
Results
The evaluated En number was −0.954. Based on the ISO/IEC 17043, the performance of the dosimetry service provider is “satisfactory.”
Conclusions
As part of the conformity assessment, the KRISS performed the proficiency test over the postal dose audit practice run by the dosimetry audit service provider. The proficiency test is in line with confirming the traceability of the medical institutions to the primary standard of absorbed dose to the water of the KRISS and ensuring the confidence of the dosimetry audit service provider.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Formulation of a New
En Score in the Proficiency Test
Chul-Young Yi, In Jung Kim, Jong In Park, Yun Ho Kim, Young Min Seong
Prog Med Phys. 2024;35(1):16-19. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2024.35.1.16.
Reference
-
References
1. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). 2006. IAEA TRS-398. Absorbed dose determination in external beam radiotherapy: an international code of practice for dosimetry based on standards of absorbed dose to water. IAEA;Vienna: DOI: 10.1016/s0167-8140(01)80920-8.2. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2017. Reference number ISO/IEC 17025. General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. ISO;Geneva:3. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). 2010. Reference number ISO/IEC 17043. Conformity assessment- general requirements for proficiency testing. ISO;Geneva:4. Kim IJ, Kim BC, Kim JH, Chung JP, Kim HM, Yi CY. 2017; Building a graphite calorimetry system for the dosimetry of therapeutic X-ray beams. Nucl Eng Technol. 49:810–816. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2017.01.015.
Article5. Kim YH, Yi CY, Kim IJ, Kim BC, Kim JH, Seong YM, et al. 2020; Monte Carlo studies on dose conversion factors from graphite to water for high energy X-ray beams. Radiat Phys Chem. 171:108760. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.108760.
Article6. Kim IJ, Kim BC, Yi CY, Shimizu M, Morishita Y, Saito N. 2020; Bilateral comparison of the absorbed dose to water in high energy X-ray beams between the KRISS and the NMIJ. Nucl Eng Technol. 52:1511–1516. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2019.12.011.
Article7. Thomas C. 2005. Rapport BIPM-05/07. The BIPM key comparison database (KCDB): technical aspects and data management. Bureau International des Poids et Mesures;Sèvres:
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Formulation of a New En Score in the Proficiency Test
- Analysis of the Service Quality Provided by Foodserice Workers in Restaurants
- Comparision of Priorities in Health Center Nutrition Service Needs between Provider and Consumer
- Report of the Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service on General and Specialized Coagulation Tests in Korea (2016–2019)
- Postal Dosimetry Audits for the Domestic Medical Linear Accelerator