Prog Med Phys.
2016 Jun;27(2):64-71. 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.64.
Efficacy and Accuracy of Patient Specific Customize Bolus Using a 3-Dimensional Printer for Electron Beam Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sg.ju@samsung.com
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Physics, Kyonggi University, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2328190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.2.64
Abstract
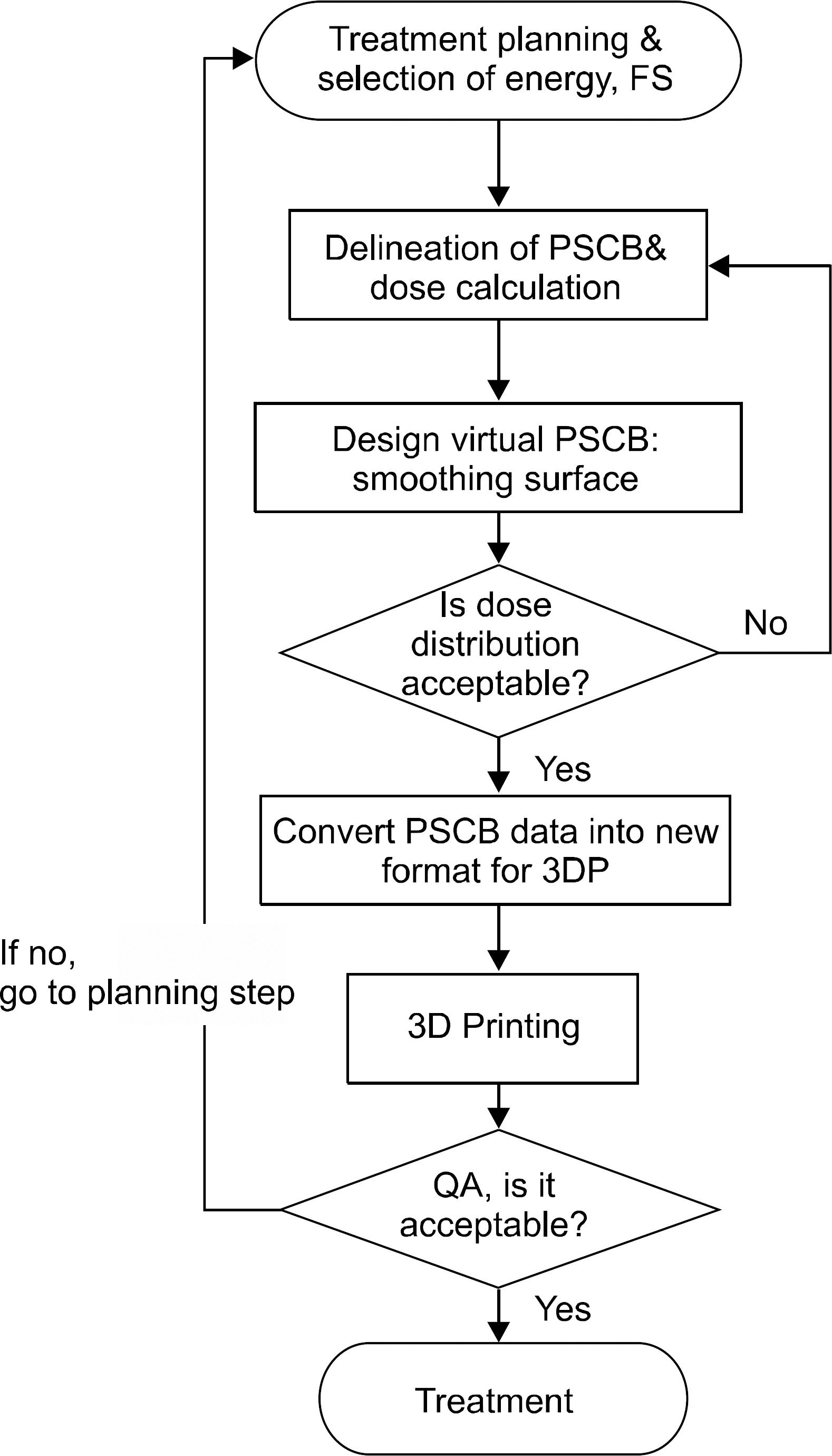
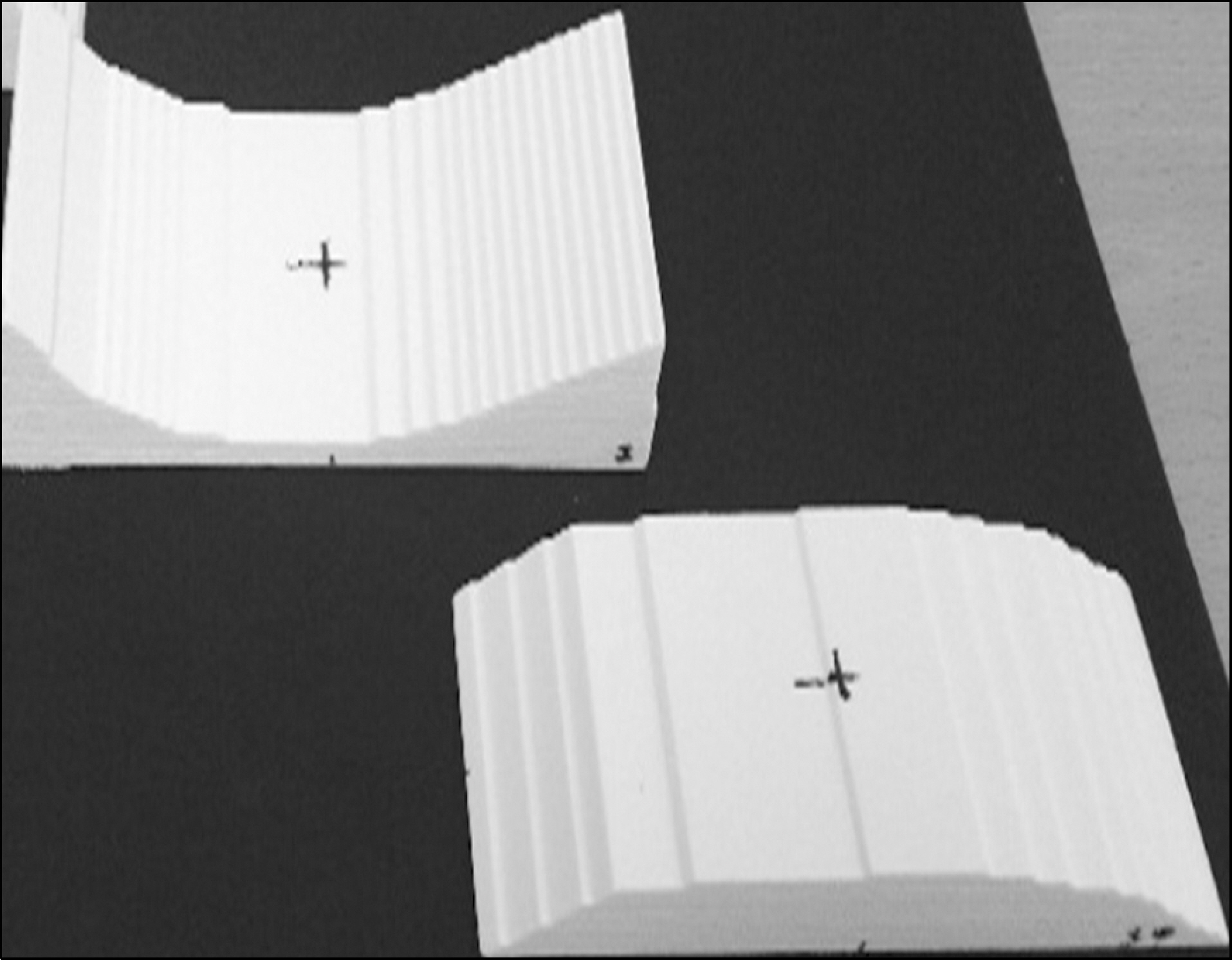
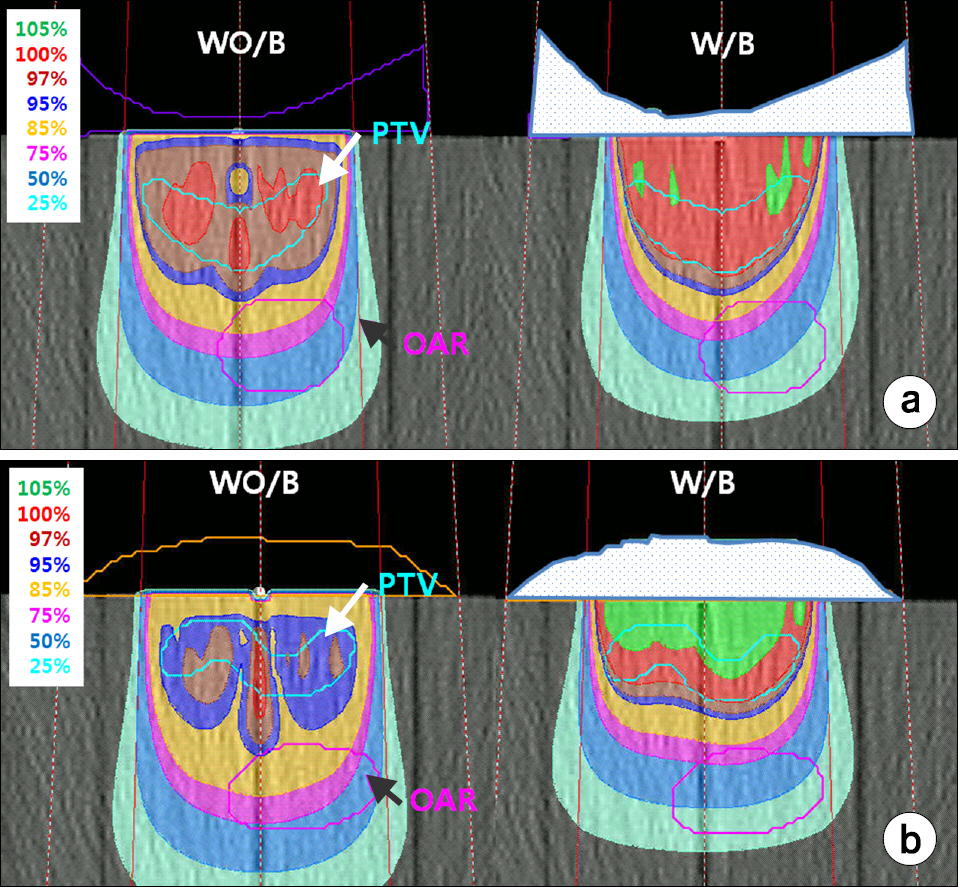
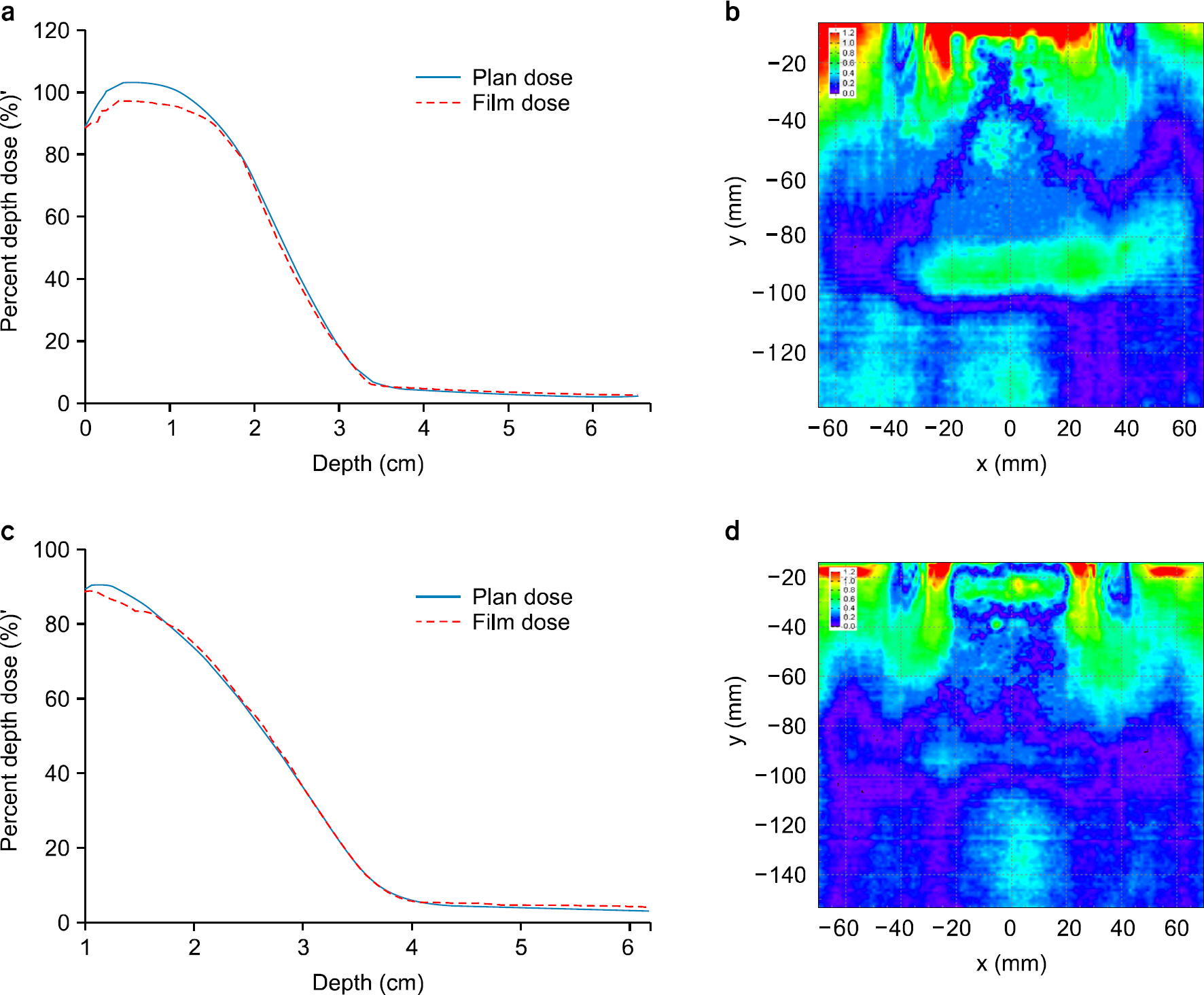
- We develop a manufacture procedure for the production of a patient specific customized bolus (PSCB) using a 3D printer (3DP). The dosimetric accuracy of the 3D-PSCB is evaluated for electron beam therapy. In order to cover the required planning target volume (PTV), we select the proper electron beam energy and the field size through initial dose calculation using a treatment planning system. The PSCB is delineated based on the initial dose distribution. The dose calculation is repeated after applying the PSCB. We iteratively fine-tune the PSCB shape until the plan quality is sufficient to meet the required clinical criteria. Then the contour data of the PSCB is transferred to an in-house conversion software through the DICOMRT protocol. This contour data is converted into the 3DP data format, STereoLithography data format and then printed using a 3DP. Two virtual patients, having concave and convex shapes, were generated with a virtual PTV and an organ at risk (OAR). Then, two corresponding electron treatment plans with and without a PSCB were generated to evaluate the dosimetric effect of the PSCB. The dosimetric characteristics and dose volume histograms for the PTV and OAR are compared in both plans. Film dosimetry is performed to verify the dosimetric accuracy of the 3D-PSCB. The calculated planar dose distribution is compared to that measured using film dosimetry taken from the beam central axis. We compare the percent depth dose curve and gamma analysis (the dose difference is 3%, and the distance to agreement is 3 mm) results. No significant difference in the PTV dose is observed in the plan with the PSCB compared to that without the PSCB. The maximum, minimum, and mean doses of the OAR in the plan with the PSCB were significantly reduced by 9.7%, 36.6%, and 28.3%, respectively, compared to those in the plan without the PSCB. By applying the PSCB, the OAR volumes receiving 90% and 80% of the prescribed dose were reduced from 14.40 cm³ to 0.1 cm³ and from 42.6 cm³ to 3.7 cm³, respectively, in comparison to that without using the PSCB. The gamma pass rates of the concave and convex plans were 95% and 98%, respectively. A new procedure of the fabrication of a PSCB is developed using a 3DP. We confirm the usefulness and dosimetric accuracy of the 3D-PSCB for the clinical use. Thus, rapidly advancing 3DP technology is able to ease and expand clinical implementation of the PSCB.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Khan FM, Doppke KP, Hogstrom KR, et al. Clinical electron-beam dosimetry: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 25. Med Phys. 18(1):73–109. 1991.2. Kirova YM, Campana F, Fournier-Bidoz N, et al. Postmastectomy electron beam chest wall irradiation in women with breast cancer: a clinical step toward conformal electron therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 69(4):1139–1144. 2007.3. Perkins GH, McNeese MD, Antolak JA, Buchholz TA, Strom EA, Hogstrom KR. A custom three-dimensional electron bolus technique for optimization of postmastectomy irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 51(4):1142–1151. 2001.
Article4. Low DA, Starkschall G, Bujnowski SW, Wang LL, Hogstrom KR. Electron bolus design for radiotherapy treatment planning: bolus design algorithms. Med Phys. 19(1):115–124. 1992.
Article5. Zablow AI, Eanelli TR, Sanfilippo LJ. Electron beam therapy for skin cancer of the head and neck. Head Neck. 14(3):188–195. 1992.
Article6. Hogstrom KR. Treatment planning in electron beam therapy. Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 25:30–52. ; discussion 61–33 (. 1991.
Article7. Lief EP, Lo YC, Humm JL. Electron wedges for radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 40(1):233–243. 1998.
Article8. Ma CM, Pawlicki T, Lee MC, et al. Energy-and intensitymodulated electron beams for radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 45(8):2293–2311. 2000.9. Kudchadker RJ, Hogstrom KR, Garden AS, McNeese MD, Boyd RA, Antolak JA. Electron conformal radiotherapy using bolus and intensity modulation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 53(4):1023–1037. 2002.
Article10. Archambeau JO, Forell B, Doria R, Findley DO, Jurisch R, Jackson R. Use of variable thickness bolus to control electron beam penetration in chest wall irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 7(6):835–842. 1981.
Article11. Beach JL, Coffey CW, Wade JS. Individualized chest wall compensating bolus for electron irradiation following mastectomy: an ultrasound approach. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 7(11):1607–1611. 1981.12. Kesner SB, Howe RD. Design Principles for Rapid Prototyping Forces Sensors using 3D Printing. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron PP(99): 1–5 (. 2011.13. Ju SG, Kim MK, Hong CS, et al. New technique for developing a proton range compensator with use of a 3-dimensional printer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88(2):453–458. 2014.
Article14. Burleson S, Baker J, Hsia AT, Xu Z. Use of 3D printers to create a patient-specific 3D bolus for external beam therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 16(3):5247. 2015.
Article15. Harris BD, Nilsson S, Poole CM. A feasibility study for using ABS plastic and a low-cost 3D printer for patient-specific brachytherapy mould design. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 38(3):399–412. 2015.
Article16. Lindsay C, Kumlin J, Jirasek A, et al. 3D printed plastics for beam modulation in proton therapy. Phys Med Biol. 60(11):N231–240. 2015.
Article17. Zarghami N, Jensen MD, Talluri S, et al. Technical Note: Immunohistochemical evaluation of mouse brain irradiation targeting accuracy with 3D-printed immobilization device. Med Phys. 42(11):6507–6513. 2015.
Article18. Zou W, Fisher T, Zhang M, et al. Potential of 3D printing technologies for fabrication of electron bolus and proton compensators. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 16(3):4959. 2015.
Article19. Kim M, Ju SG, Chung K, et al. Development of a 3D optical scanning-based automatic quality assurance system for proton range compensators. Med Phys. 42(2):1071–1079. 2015.
Article20. Alexa M, Behr J, Cohen-Or D, Fleishman S, Levin D, Silva CT. Computing and rendering point set surfaces. Ieee Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics. 9(1):3–15. 2003.
Article21. Wikipedia. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereolithography.22. Hogstrom KR, Mills MD, Meyer JA, et al. Dosimetric evaluation of a pencil-beam algorithm for electrons employing a two-dimensional heterogeneity correction. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 10(4):561–569. 1984.
Article23. Low DA, Harms WB, Mutic S, Purdy JA. A technique for the quantitative evaluation of dose distributions. Med Phys. 25(5):656–661. 1998.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Implementation of 3D Printing in the Construction of Patient Specific Bolus for Photon Beam Radiotherapy for Mycosis Fungoides
- Fabrication of a Patient-Customized Helmet with a Three-Dimensional Printer for Radiation Therapy of Scalp
- Fabrication and Characterization of a One-dimensional Fiber-optic Dosimeter for Electron Beam Therapy Dosimetry
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Geometric Evaluation of Patient-Specific 3D Bolus from 3D Printed Mold and Casting Method for Radiation Therapy