Korean J Pain.
2016 Jul;29(3):197-201. 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.197.
Clinical Effectiveness of Ultrasound-guided Costotransverse Joint Injection in Thoracic Back Pain Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kbyoon@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2327643
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.197
Abstract
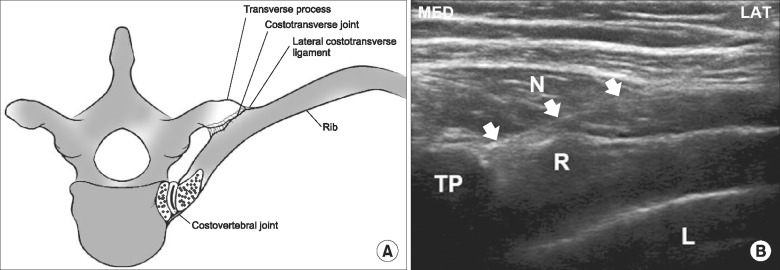
- Because of its anatomical location and function, the costotransverse (CTRV) joint can be a source of thoracic back pain. In this retrospective observational study, we evaluated the clinical effectiveness of the CTRV joint injection in thoracic back pain patients with suspected CTRV joint problems. We enrolled 20 thoracic back pain patients with localized tenderness that was provoked by the application of pressure on the affected CTRV joints. We injected it with 0.5 ml of a ropivacaine and triamcinolone mixture at each level. The mean pre-injection pain score decreased by 37.9% (7.2 ± 1.5 to 4.5 ± 1.7, P < 0.001) two weeks after CTRV joint injection. In addition, 70% of patients reported an excellent or good level of satisfaction. We demonstrated that an ultrasound-guided injection of the CTRV joint reduced patients' pain scores and led to a high level of satisfaction at short-term follow-ups in patients with suspected CTRV joint problems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fruth SJ. Differential diagnosis and treatment in a patient with posterior upper thoracic pain. Phys Ther. 2006; 86:254–268. PMID: 16445339.
Article2. Atluri S, Datta S, Falco FJ, Lee M. Systematic review of diagnostic utility and therapeutic effectiveness of thoracic facet joint interventions. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:611–629. PMID: 18850026.3. Singh V, Manchikanti L, Shah RV, Dunbar EE, Glaser SE. Systematic review of thoracic discography as a diagnostic test for chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:631–642. PMID: 18850027.4. Kim D. Bipolar intra-articular radiofrequency thermocoagulation of the thoracic facet joints: a case series of a new technique. Korean J Pain. 2014; 27:43–48. PMID: 24478900.
Article5. Lau LS, Littlejohn GO. Costotransverse joint injection description of technique. Australas Radiol. 1987; 31:47–49. PMID: 2956942.
Article6. Takeuchi T, Abumi K, Shono Y, Oda I, Kaneda K. Biomechanical role of the intervertebral disc and costovertebral joint in stability of the thoracic spine. A canine model study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1414–1420. PMID: 10423785.
Article7. Oda I, Abumi K, Lü D, Shono Y, Kaneda K. Biomechanical role of the posterior elements, costovertebral joints, and rib cage in the stability of the thoracic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:1423–1429. PMID: 8792518.
Article8. Sanzhang C, Rothschild BM. Zygapophyseal and costovertebral/costotransverse joints: an anatomic assessment of arthritis impact. Br J Rheumatol. 1993; 32:1066–1071. PMID: 8252316.
Article9. Young BA, Gill HE, Wainner RS, Flynn TW. Thoracic costotransverse joint pain patterns: a study in normal volunteers. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008; 9:140. PMID: 18922181.
Article10. Deimel GW, Hurdle MF, Murthy N, Cartwright JA, Smith J, Pingree MJ. Sonographically guided costotransverse joint injections: a computed tomographically controlled cadaveric feasibility study. J Ultrasound Med. 2013; 32:2083–2089. PMID: 24277889.11. Dedrick GS, Sizer PS, Sawyer BG, Brismeè JM, Smith MP. Immunohistochemical study of human costotransverse joints: a preliminary investigation. Clin Anat. 2011; 24:741–747. PMID: 21400610.
Article12. Dreyfuss P, Tibiletti C, Dreyer SJ. Thoracic zygapophyseal joint pain patterns. A study in normal volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:807–811. PMID: 8202799.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided interventions for controlling the thoracic spine and chest wall pain: a narrative review
- Ultrasound Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Space Block for Chronic Intractable Upper Back Pain
- Ultrasound-guided Injection in the Pathology around Wrist Joint
- Injections for Pelvic or Sacral Pain
- Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Medial Branch Block for the Facet Joint Pain