Tuberc Respir Dis.
2016 Jul;79(3):184-187. 10.4046/trd.2016.79.3.184.
IgG4-Related Lung Disease without Elevation of Serum IgG4 Level: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. casimirus@naver.com
- KMID: 2326687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2016.79.3.184
Abstract
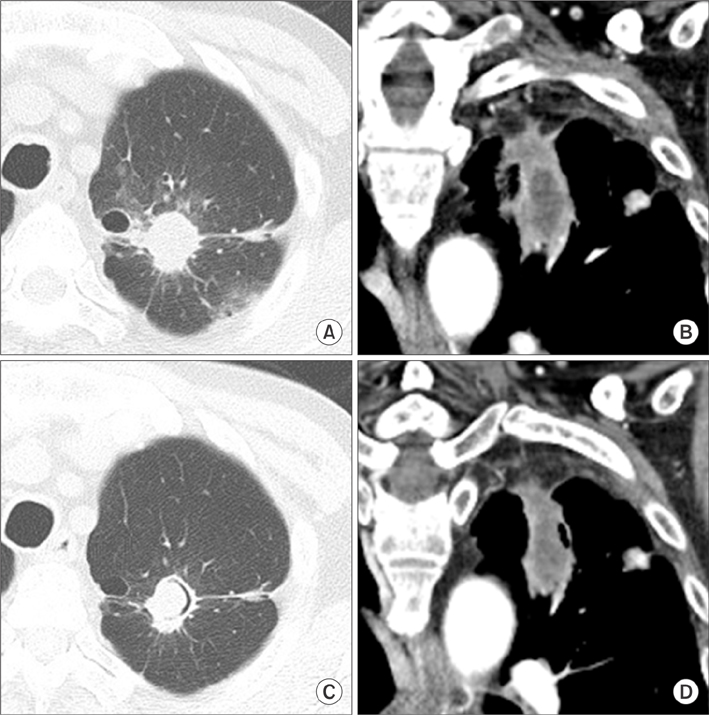
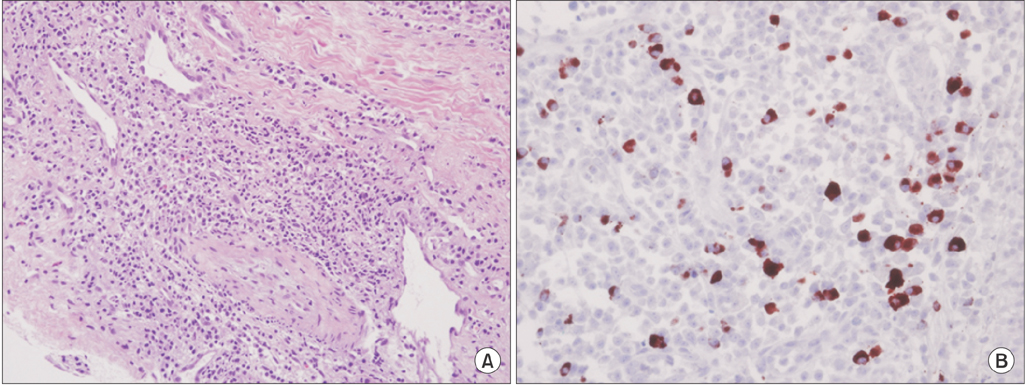
- Since IgG4-related pancreatitis was first reported in 2001, IgG4-related disease has been identified in other organs such as salivary gland, gallbladder, thyroid, retroperitoneum and kidney; but lung invasion is rare. A 63-year-old man presented with hemoptysis at the pulmonary clinic and chest computed tomography revealed about 4.1 cm irregular shaped mass with spiculated margin at the left upper lobe. Despite no elevation of serum IgG4 level, he was finally diagnosed as IgG4-related lung disease by transthoracic needle biopsy. After treatment with oral glucocorticoids, hemoptysis disappeared and the size of lung mass was decreased.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.2. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–984.3. Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A, Onodera M, Abo H, Miyayama S, et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: a clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1886–1893.4. Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Kobayashi T, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology. 2009; 251:260–270.5. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.6. Yoo JW, Roh JH, Lim CM, Lee SD, Kim WS, Kim DS, et al. Two cases of pulmonary involvement of immunoglobulin G4 related autoimmune disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2009; 67:359–363.7. Kwon SH, Lee YK, Shim MS, Lee HI. A case of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease mimicking lung cancer. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2013; 69:53–56.8. Park HY, Han J, Kang G, Yi CA, Chung MP. IgG4-related lung disease presenting as a consolidative mass: a case report. J Lung Cancer. 2010; 9:103–105.9. Kim DH, Koh KH, Oh HS, Kim SJ, Kang SH, Jung BW, et al. A case of immunoglobulin g4-related disease presenting as a pleural mass. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2014; 76:38–41.10. Choi IH, Jang SH, Lee S, Han J, Kim TS, Chung MP. A case report of IgG4-related disease clinically mimicking pleural mesothelioma. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2014; 76:42–45.11. Choi JH, Sim JK, Oh JY, Lee EJ, Hur GY, Lee SH, et al. A case of IgG4-related disease presenting as massive pleural effusion and thrombophlebitis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2014; 76:179–183.12. Ahn JH, Hong SI, Cho DH, Chae EJ, Song JS, Song JW. A case of IgG4-related lung disease presenting as interstitial lung disease. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2014; 77:85–89.13. Kim WJ, Kim YI, Kim JE, Choi YH, Cho HH, Choi YD, et al. Unexplained persistent dyspnea in a young woman with eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis. Respir Care. 2014; 59:e72–e76.14. Ost D, Fein AM, Feinsilver SH. Clinical practice: the solitary pulmonary nodule. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:2535–2542.15. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–1192.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease Mimicking Lung Cancer: Two Case Reports
- Advances in IgG4-related Hepatobiliary Disease
- IgG4-related Skin Disease: Experience with Two Cases
- Clinical Significance of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis and Treatment Response of IgG4-Related Disease in Adults of Southwest China: A Retrospective Study
- A Rare Presentation of IgG4-Related Sinusitis With Chronic Nasal Obstruction and Headache: A Case Report and Literature Review