J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Sep;79(3):173-179.
Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. lovebreast@naver.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) has had poor prognosis compared with the luminal subtype. And there has been no benefit from doxorubicin. However, the addition of paclitaxel is known to improve both disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). The aim of our study was to assess the effect of the addition of paclitaxel after adjuvant chemotherapy with doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide in TNBC.
METHODS
We randomly selected 87 women from 104 women with TNBC who had been randomly assigned to receive doxorubicin (60 mg per square meter of body-surface area) plus cyclophosphamide (600 mg per square meter) for four cycles, followed by four cycles of paclitaxel (175 mg per square meter) or two more cycles of doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide. Due to predictions of clinical outcomes in women who receive adjuvant paclitaxel based chemotherapy, immunohistochemical analyses of these tissue specimens for CK5/6 were used.
RESULTS
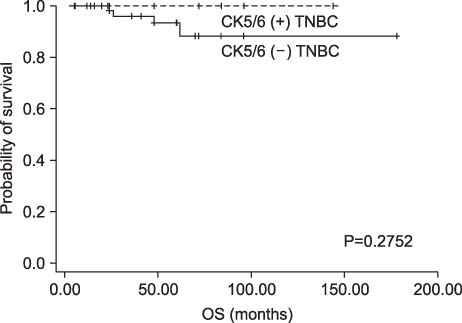
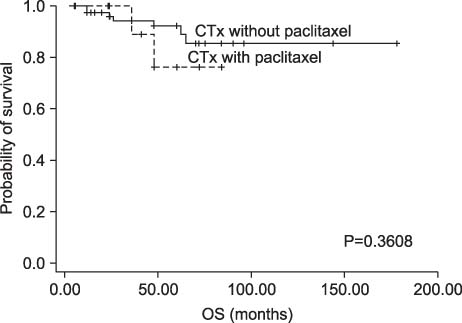
Among patients with TNBC, 24 patients (27.6%) were classified as CK5/6-positive triple negative type. Twelve patients were classified as paclitaxel chemotherapy group and 75 patients were classified as no paclitaxel group. No interaction was observed between DFS or OS and paclitaxel regimens. CK5/6 was, however, not associated with a significant benefit from paclitaxel in our study.
CONCLUSION
In our study, the addition of paclitaxel after adjuvant treatment with doxorubicin (<60 mg per square meter) is not associated with DFS or OS in TNBC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol. 2007. 18:1133–1144.2. Kim MJ, Ro JY, Ahn SH, Kim HH, Kim SB, Gong G. Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer: a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neuoverexpressing phenotypes. Hum Pathol. 2006. 37:1217–1226.3. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005. 365:1687–1717.4. Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000. 406:747–752.5. Smith I, Chua S. Medical treatment of early breast cancer. I: adjuvant treatment. BMJ. 2006. 332:34–37.6. Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:10869–10874.7. Wood WC, Budman DR, Korzun AH, Cooper MR, Younger J, Hart RD, et al. Dose and dose intensity of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II, node-positive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1994. 330:1253–1259.8. Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:5367–5374.9. Budman DR, Berry DA, Cirrincione CT, Henderson IC, Wood WC, Weiss RB, et al. The Cancer and Leukemia Group B. Dose and dose intensity as determinants of outcome in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998. 90:1205–1211.10. Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, et al. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:8418–8423.11. Umemura S, Kurosumi M, Moriya T, Oyama T, Arihiro K, Yamashita H, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation for hormone receptors in breast cancer: a practically useful evaluation system and handling protocol. Breast Cancer. 2006. 13:232–235.12. Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, Cirrincione CT, Goldstein LJ, Martino S, et al. Improved outcomes from adding sequential paclitaxel but not from escalating doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003. 21:976–983.13. Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 1998. 11:155–168.14. Mass RD, Press MF, Anderson S, Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Dybdal N, et al. Evaluation of clinical outcomes according to HER2 detection by fluorescence in situ hybridization in women with metastatic breast cancer treated with trastuzumab. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005. 6:240–246.15. Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:1474–1481.16. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:118–145.17. Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008. 52:108–118.18. Laakso M, Loman N, Borg A, Isola J. Cytokeratin 5/14-positive breast cancer: true basal phenotype confined to BRCA1 tumors. Mod Pathol. 2005. 18:1321–1328.19. Li H, Cherukuri P, Li N, Cowling V, Spinella M, Cole M, et al. Nestin is expressed in the basal/myoepithelial layer of the mammary gland and is a selective marker of basal epithelial breast tumors. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:501–510.20. Lakhani SR, Reis-Filho JS, Fulford L, Penault-Llorca F, van der Vijver M, Parry S, et al. Prediction of BRCA1 status in patients with breast cancer using estrogen receptor and basal phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:5175–5180.21. Savage K, Lambros MB, Robertson D, Jones RL, Jones C, Mackay A, et al. Caveolin 1 is overexpressed and amplified in a subset of basal-like and metaplastic breast carcinomas: a morphologic, ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and in situ hybridization analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13:90–101.22. Reis-Filho JS, Steele D, Di Palma S, Jones RL, Savage K, James M, et al. Distribution and significance of nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR/p75NTR) in normal, benign and malignant breast tissue. Mod Pathol. 2006. 19:307–319.23. Herschkowitz JI, He X, Fan C, Perou CM. The functional loss of the retinoblastoma tumour suppressor is a common event in basal-like and luminal B breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. 2008. 10:R75.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment Outcomes of Weakly Positive Hormone Receptor Breast Cancer and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Comment on “Histomorphological Factors Predicting the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancerâ€
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Early Stage Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Comparison with Non-triple Negative Group
- Fear of Cancer Recurrence and Unmet Needs in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Survivors
- Therapeutic Effects of Paclitaxel (Taxol ) in Metastatic Breast Cancer