J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2015 Jun;22(2):43-49. 10.4184/jkss.2015.22.2.43.
Clinical Value of Visualized Prediction of Corrective Osteotomy of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2322951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2015.22.2.43
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the clinical value of preoperative planning via computer simulation by comparing preoperative and postoperative measurements of a patient with ankylosing spondylitis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Ankylosing spondylitis is a disorder that results in a spinal deformity because chronic inflammation at the ligament attachment sites triggers ossification; it causes round fixed kyphosis. This causes limitations in not only everyday life but also social interaction because it is impossible for patients to face forward. Therefore, surgical correction is necessary.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
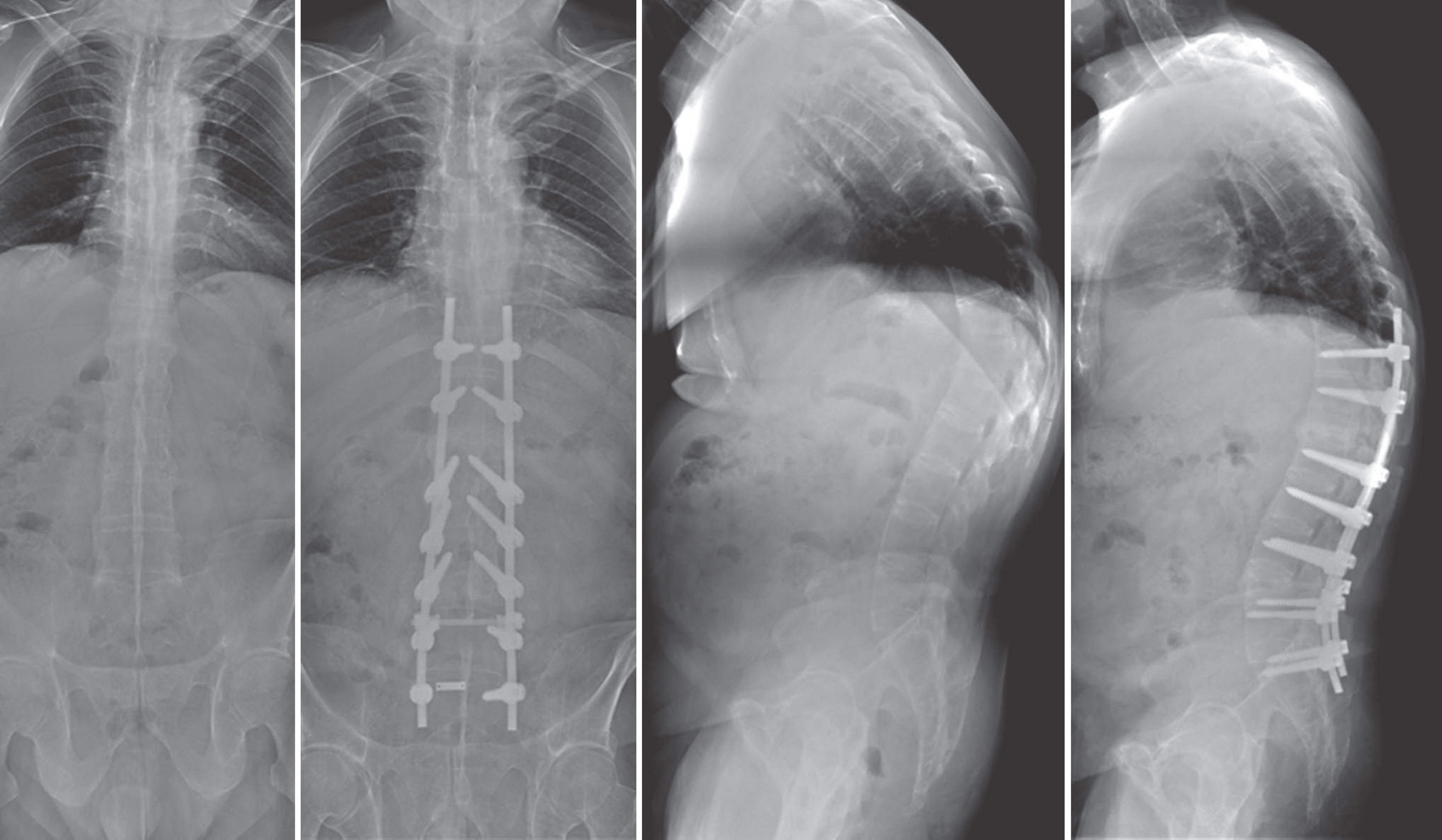
We analyzed 38 patients (41 instances) who underwent correctional osteotomy between June 2007 and March 2014 to treat kyphosis caused by ankylosing spondylitis. We chose the appropriate operation site on the basis of preoperative simulations of osteotomy and the site for pre- and postoperative radiological evaluations conducted from the lateral view in a standing position. For the clinical evaluation, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Function Index (BASFI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Survey (HADS), and Health Locus of Control Form C Questionnaire (HLC-C) were used.
RESULTS
The mean sagittal vertical axis (SVA) was improved from 123.4 mm to 66.1 mm, the mean thoracic kyphosis angle (TKA) changed from 42.2degrees to 40.1degrees, and the mean lumbar lordosis angle (LLA) improved from 16.0degrees to 28.5degrees. The correlation coefficients between the preoperative predictive value and the postoperative radiographic measurement were 0.43, 0.93, and 0.87, which were all statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS
By comparing the preoperative measurement with the postoperative radiologic score, we found that the two were correlated and that the clinical assessment improved on the basis of the visualization. Therefore, preoperative simulation of patients with ankylosing spondylitis along with a kyphotic deformity is thought to be clinically effective.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim TJ, Kim TH. Clinical spectrum of ankylosing spondylitis in Korea. Joint Bone Spine. 2010; 77:235–40.
Article2. McMaster MJ. A technique for lumbar spinal osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67:204–10.
Article3. Pham T. Pathophysiology of ankylosing spondylitis: what's new? Joint Bone Spine. 2008; 75:656–60.
Article4. Kim KT, Suk KS, Cho YJ, et al. Clinical outcome results of pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with kyphotic deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:612–8.
Article5. Smith-Petersen MN, Larson CB, Aufranc OE. Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheuma-toid arthritis. Clin Orthop Retat Res. 1969; 66:6–9.
Article6. Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop. 1985; 194:142–52.
Article7. Bridwell KH. Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs. vertebral column resection for spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:S171–8.
Article8. Suk KS, Kim KT, Lee SH, et al. Significance of chin-brow vertical angle in correction of kyphotic deformity of ankylosing spondylitis patients. Spine. 2003; 28:2001–5.
Article9. Ondra SL, Marzouk S, Koski T, et al. Mathematical calcu-lation of pedicle subtraction osteotomy size to allow precision correction of fixed sagittal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:E973–9.
Article10. Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, et al. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:2281–5.11. Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, et al. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:2286–91.12. Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983; 67:361–70.
Article13. Wallston KA, Stein MJ, Smith CA. Form C of the MHLC scales: a condition-specific measure of locus of control. J Pers Assess. 1994; 63:534–53.
Article14. Meunier PJ1, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al. Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: clinical guidelines. International Committee for Osteoporosis Clinical Guidelines. Clin Ther. 1999; 21:1025–44.15. Park YS, Kim JH, Ryu JA, et al. The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis: distinguishing between the inflammatory and traumatic subtypes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:961–6.16. Sciubba DM, Nelson C, Hsieh P, et al. Perioperative chal-lenges in the surgical management of ankylosing spondylitis. Neurosurg Focus. 24:2008; E10.
Article17. Gertzbein SD, Harris MB. Wedge osteotomy for the correction of post-traumatic kyphosis. A new technique and a report of three cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992; 17:374–9.18. Ondra SL, Mazouk S, Koski T, et al. Mathematical calcu-lation of pedicle subtraction osteotomy size to allow precision correction of fixed sagittal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:E973–9.
Article19. Suk KS, Kim KT, Lee SH, et al. Significance of chin-brow vertical angle in correction of kyphotic deformity of ankylosing spondylitis patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2001–5.
Article20. Min K, Hahn F, Leonardi M. Lumbar spinal osteotomy for kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis: the significance of the whole body kyphosis angle. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20:149–53.21. Lafage V, Bharucha NJ, Schwab F, et al. Multicenter validation of a formula predicting postoperative spinopelvic alignment. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 16:15–21.
Article22. Park YS, Kim HS, Baek SW, et al. Preoperative com-puter-based simulations for the correction of kyphotic deformities in ankylosing spondylitis patients. Spine J. 2014; 14:2420–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of the Halo Sign and the Grafted Bone according to the Usage of Teriparatide for the Correction Loss due to Screw Loosening after Corrective Osteotomy
- Effect of the Corrective Osteotomy in Ankylosing Spondylitis to Quality of Life(QOL)
- Re-stooping after Corrective Osteotomy in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Computer Simulation for Surgical Correction of Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Narrative Review
- Multisegmental Osteotomy for Kyphotic Deformity in Ankylosing Spondylitis