J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2006 Dec;13(4):327-331.
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Associated with Dysphonia and Dysphagia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hsh@nph.go.kr
Abstract
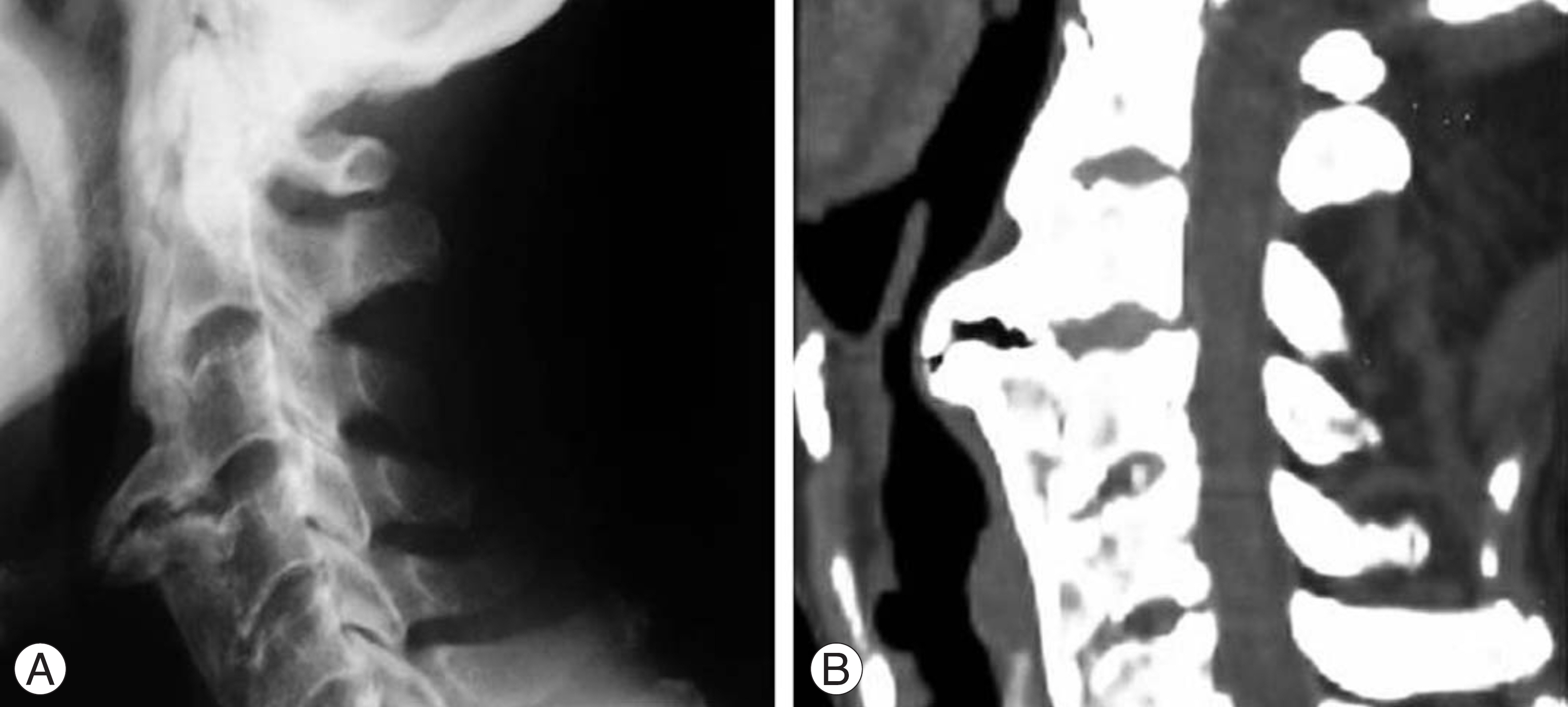
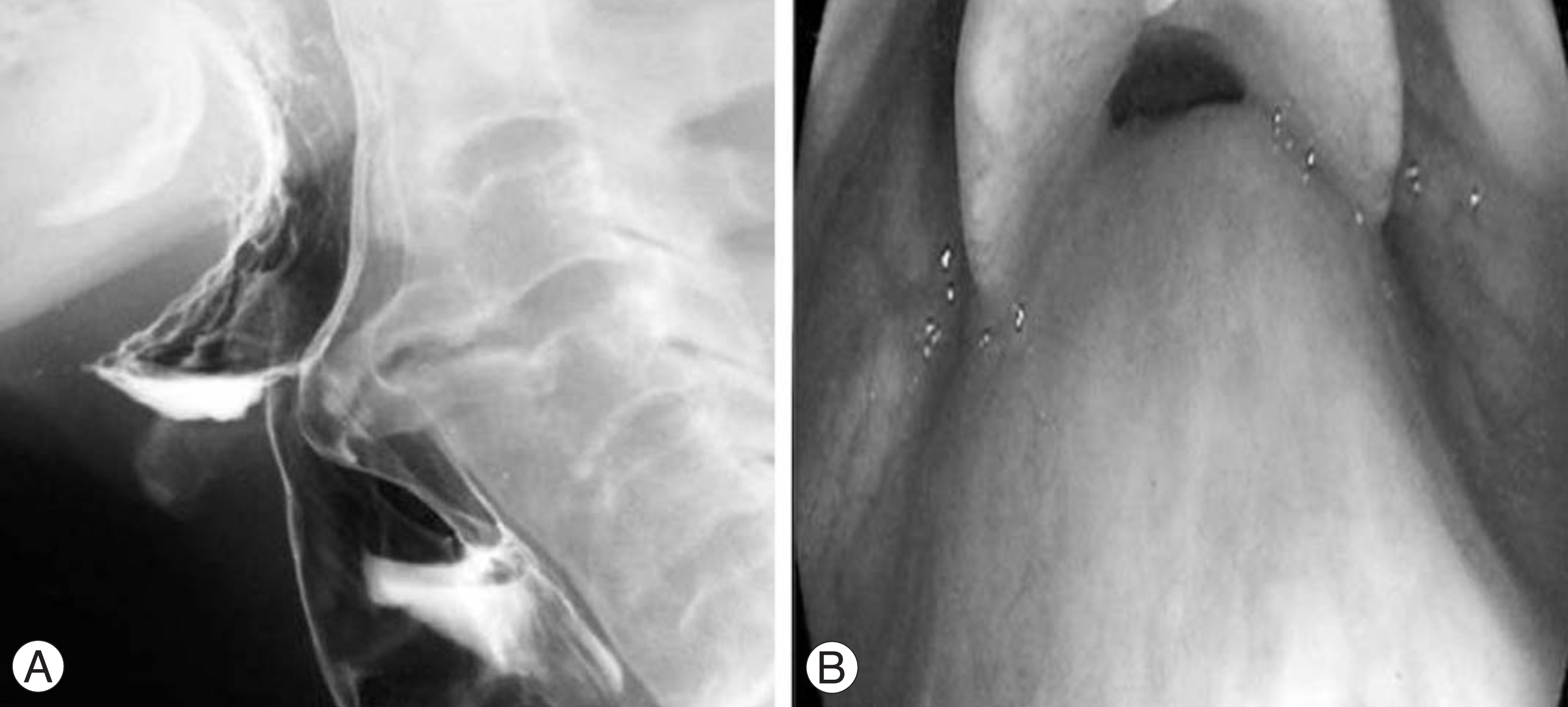
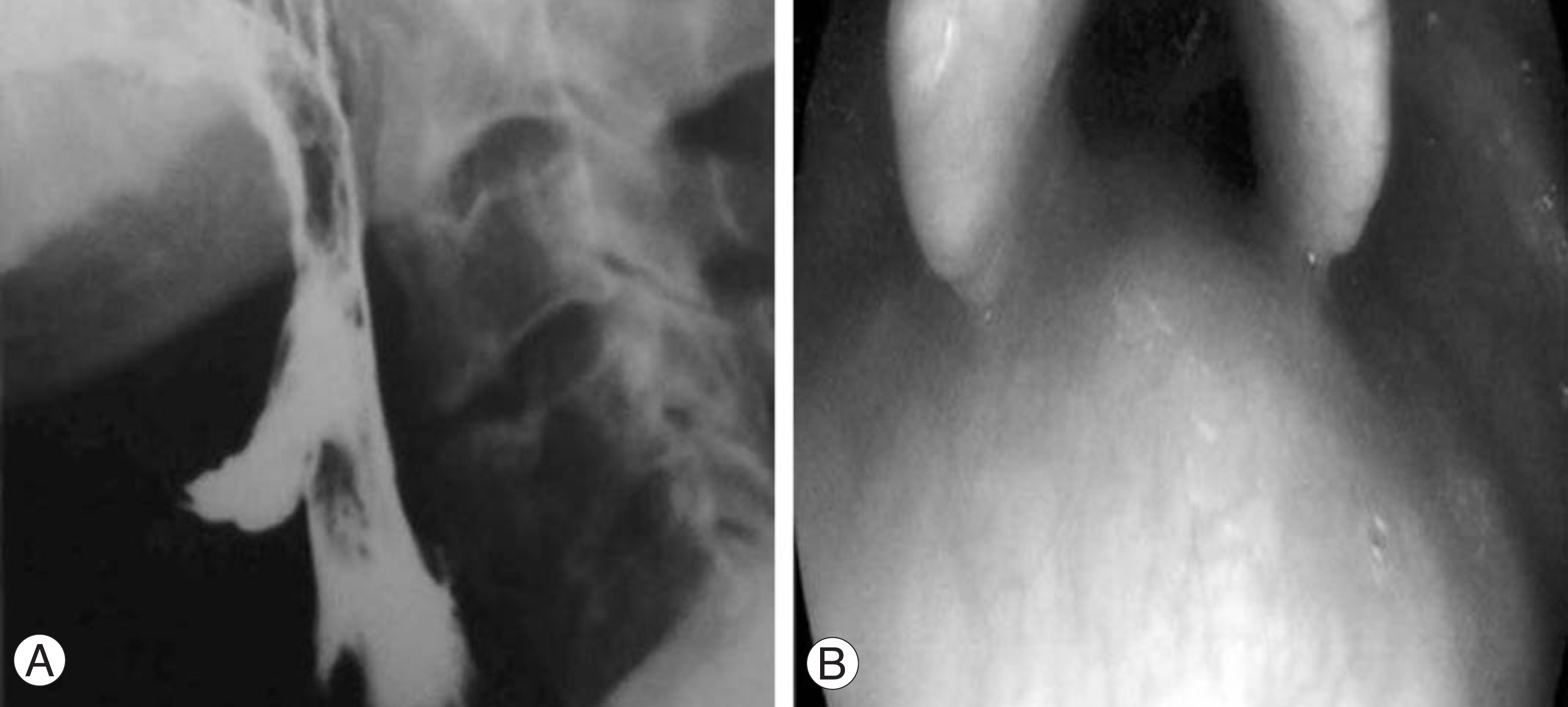
- We encountered a rare case of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) associated with dysphonia and dysphagia. An 80 year-old man developed progressive dysphonia and dysphagia. The radiology study, esophagogram and nasopharyngoscopic exam revealed the esophagus and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx to be severely compressed by the unfused osteophyte of the 3rd and 4th cervical intervertebral space. It was thought that the osteophyte formation was caused by not merely DISH but degenerative changes due to a concentration of stress around the unfused hyperostosis. A resection of the osteophyte was performed, which resolved the clinical symptoms. The follow-up radiology study, esophagogram and nasopharyngoscopic exam showed that the osteophyte had disappeared.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Resnick D, Shapiro RF, Wiesner KB, Niwayama G, Utsinger PD, Shaul SR. Diffuse idiopathic hyperostosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1978; 7:153–187.2). Forestier J, Rotes-Querol J. Senile ankylosing hyperostosis of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1950; 9:321–330.
Article3). Resnick D, Shaul SR, Robins JM. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Forestier's disease with extraspinal manifestations. Diagnostic Radiology. 1975; 115:513–524.
Article4). Weinfeld RM, Olson PN, Maki DD, Griffiths HJ. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) in two large American Midwest metropolitan hospital populations. Skeletal Radiol. 1997; 26:222–225.
Article5). Kim SK, Choi BR, Kim CG, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Korea. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:2032–2035.6). Gamach FW, Voorhies RM. Hypertrophic cervical osteophytes causing dysphagia. A review. J Neurosurgery. 1980; 53:338–343.7). Kim YW, Jang HG, Jung JC, Lee KB. Dysphagia due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine. J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 2003; 10:335–339.8). Papakostas K, Thakar A, Nandapalan V, O'Sullivan G. An unusual case of stridor due to osteophytes of the cervical spine (Forestier's disease). J Laryngol Otol. 1999; 113:65–67.
Article9). Karlins NL, Yagan R. Dyspnea and hoarseness: A complication of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Spine. 1991; 16:235–237.
Article10). Eviatar E, Harell M. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis with dysphagia (A review). J Laryngol Otol. 1987; 101:627–632.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dysphagia due to Cervical Osteophytes: Case Report
- Dysphagia Due to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis of The Cervical Spine: A Case Report
- A Case of Dysphagia due to Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction and Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
- A Case of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis with Dysphagia
- A Case of Forestier's Disease with Dyspnea