J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2004 Dec;11(4):202-209.
Optimal Trajectories of C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2 Pars-Pedicle Screws
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bschang@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
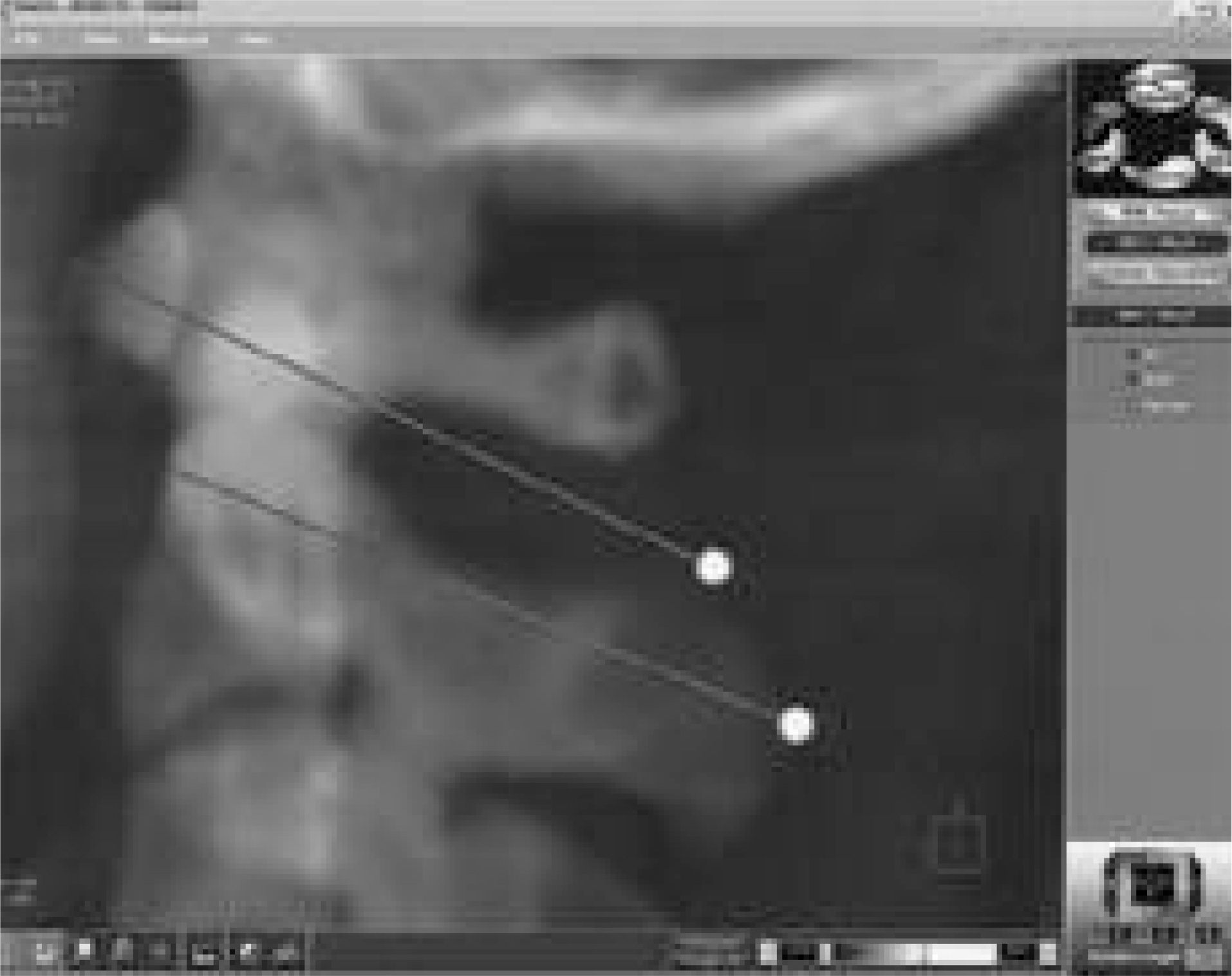
- STUDY DESIGN: Surgical simulation using CT images of the cervical spine and computers.
OBJECTIVES
The optimal trajectories for C1 lateral mass screws and C2 pars-pedicle screws were sought, and their accuracy evaluated. LITERATURE REVIEW SUMMARY: There have been a few suggestions for the trajectories of the screws listed above, but these are somewhat vague or impractical.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Using 1 mm-sliced CT scan images of 128 patients, and a V-works spine surgery simulator 4.0 (Cybermed, Inc., Korea), the optimal trajectories with which 4.0 mm screws can be inserted without breaching bone cortices were determined. The anatomical characteristics of the cases having a cortical perforation were analyzed.
RESULTS
The insertion point suggested for a C1 screw was 1 mm lateral to the middle of the junction of the posterior arch and posterior inferior part of the lateral mass. The screw was directed 15 degrees medially and toward the junction of the superior 2/3 and inferior 1/3 of the anterior tubercle in the lateral fluoroscopic view. The C2 screw was directed 30 degrees medially, and toward the anterior end of the superior articular process, in the lateral fluoroscopic view. The insertion point was one where the screw was inserted close to the superomedial border of the pedicle. Using these trajectories, all (256/256) of the C1 screws were inserted safely. However, 6.3% (16/256) of the C2 screws breached the inferolateral cortices of the pedicles, due to the pedicles being either too narrow or too medially angulated.
CONCLUSIONS
Herein, more practical and safe screw trajectories have been suggested. Using these trajectories, all the C1 and most of the C2 screws were able to be inserted safely. However, there were some cases in which the C2 screws could not be inserted without breaching the vertebral artery groove. Therefore, preoperative thin-slice CT scanning, with three-dimensional reconstruction and/or three-dimensional CT-angiography, is recommended for these cases.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Abumi K, Kaneda K. Pedicle screw fixation for nontrau -matic lesions of the cervical spine. Spine. 1997; 22:1853–1863.2). Ebraheim NA, Mission JR, Xu R, Yeasting RA. The optimal transarticular C1-2 screw length and the location of the hypoglossal nerve. Surg Neurol. 2000; 53:208–210.
Article3). Ebraheim N, Rollins JR Jr, Xu R, Jackson WT. Anatomic consideration of C2 pedicle screw placement. Spine. 1996; 21:691–695.
Article4). Goel A, Desai KI, Muzumdar DP. Atlantoaxial fixation using plate and screw method: A report of 160 treated patients. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:1351–1357.
Article5). Harms J, Melcher RP. Posterior C1-C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine. 2001; 26:2467–2471.
Article6). Hong X, Dong Y, Yunbing C, Qingshui Y, Shizheng Z, Jingfa L. Posterior screw placement on the lateral mass of atlas.: An anatomic study. Spine. 2004; 29:500–503.7). Howington JU, Kruse JJ, Awasthi D. Surgical anatomy of the C-2 pedicle. J Neurosurg Spine. 2001; 95:88–92.
Article8). Resnick DK, Lapsiwala S, Trost GR. Anatomic suitability of the C1-C2 complex for pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 2002; 27:1494–1498.
Article9). Wang MY, Samudrala S. Cadaveric morphometric analysis for atlantal lateral mass screw placement. Neurosurgery. 2004; 54:1436–40.
Article10). Xu R, Ebraheim NA, Missoon JR, Yeasting RA. The reliability of the lateral radiograph in determination of the optimal transarticular C1-C2 screw length. Spine. 1998; 23:2190–2194.
Article11). Xu R, Nadaud MC, Ebraheim NA, Yeasting RA. Morphology of the Second cervical vertebra and the posterior projection or the C2 pedicle axis. Spine. 1995; 20:259–263.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterior Atlantoaxial Fixation with Lateral Mass Screw in the Atlas and Pedicle Screw in the Axis
- Atlantoaxial Fixation using C2 Subarticular Screws and C1 Lateral Mass Screws : A Technical Report
- Old Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation Associated with High-riding Vertebral Arteries: Arthrodesis Using C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2 Laminar Screws: A Case Report
- Atlantoaxial Stabilization Using C1 Lateral Mass and C2 Pedicle/Translaminar Screw Fixation by Intraoperative C1- and C2-Direct-Captured Navigation with Preoperative Computed Tomography Images
- Posterior Atlantoaxial Fixation with a Combination of Pedicle Screws and a Laminar Screw in the Axis for a Unilateral High-riding Vertebral Artery