J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2002 Jun;9(2):148-156.
Surgical Treatment of Post-Traumatic Kyphosis with Neurologic Compromised Osteoporotic Fracture: Comparison between Anterior-Posterior Surgery versus Posterior Egg-Shell Procedure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul Spine Institute, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Korea. dragon@sanggyepaik.ac.kr
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To compare the surgical results between anterior-posterior surgery and posterior eggshell procedures in post-traumatic kyphosis with neurologic compromised osteoporotic fracture. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Combined anterior-posterior surgery is usually recommended in cases of kyphotic deformities with neurologic deficit secondary to osteoporosis. However, it is associated with significant morbidity in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
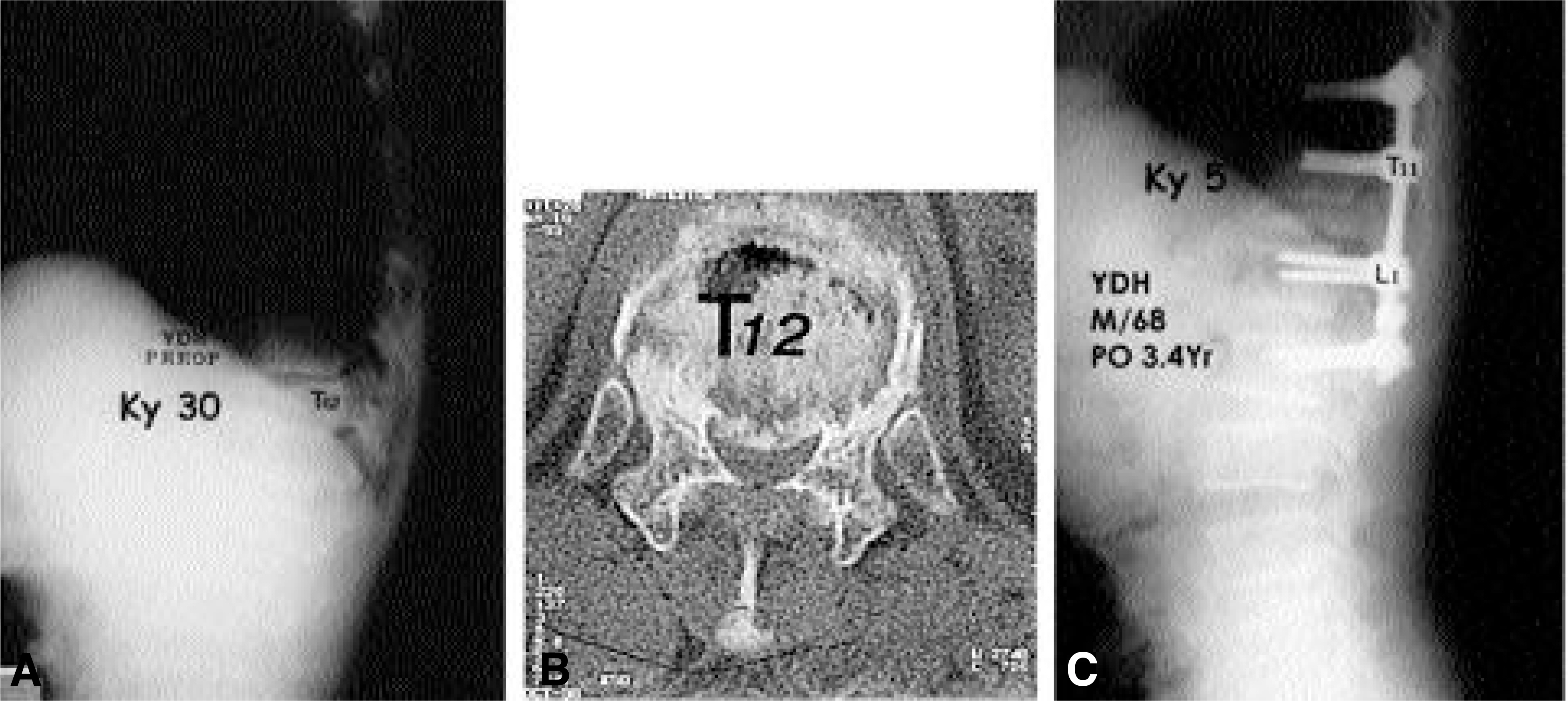
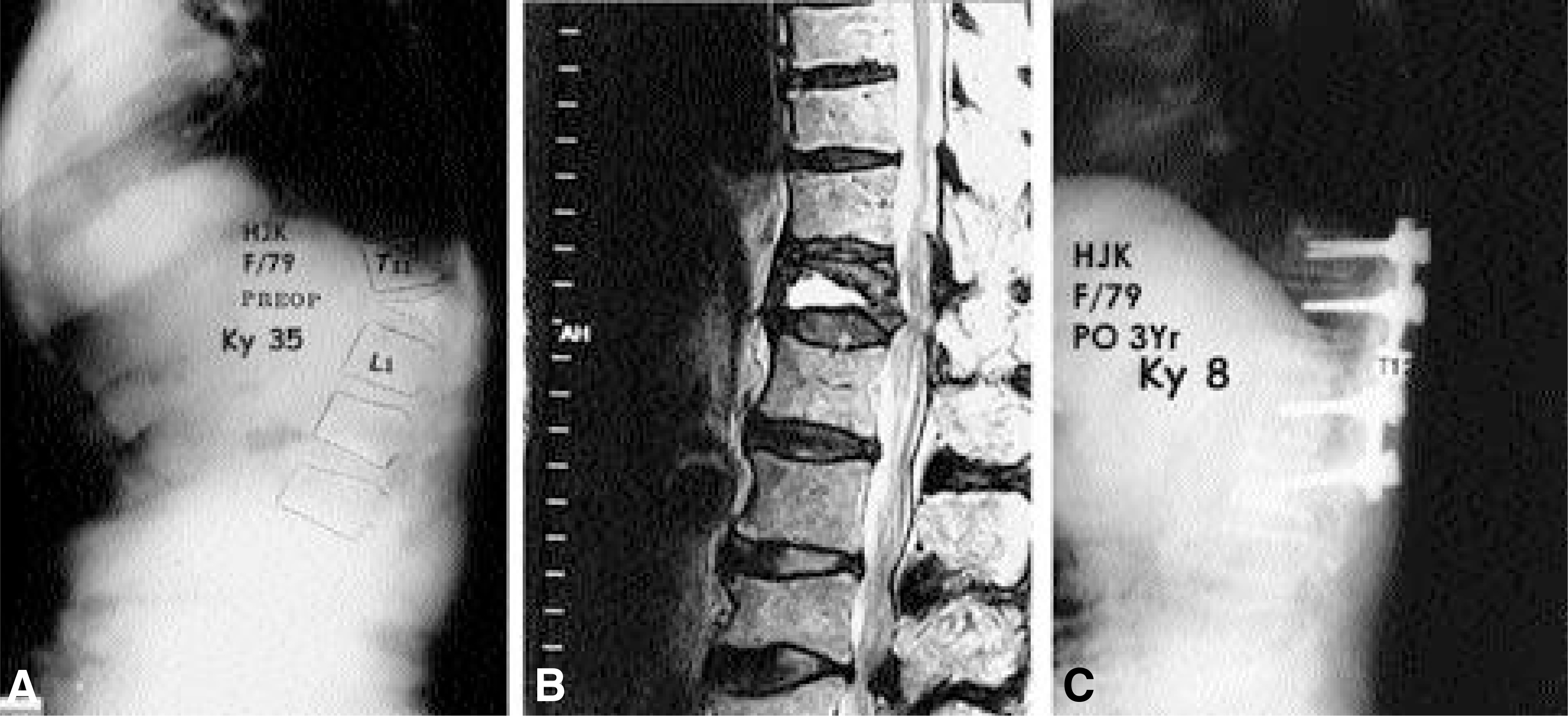
Twenty-six post-traumatic kyphosis with neurologic compromised osteoporotic fracture patients subjected to either anterior-posterior surgery (n=11) or posterior egg-shell procedure (n=15) were analyzed. The average age at the operation was 62.6 years (range: 50-82), male : female ratio was 12 : 14, and the average follow up was 2.9 years (range:2.0-4.9). Preoperative interval from injury to operation was 15.4 months (range: 1-36). Thoracolumbar (T12-L1) fracture was in 20 and lumbar fracture was in 6.
RESULTS
There was no significant difference in age, sex, preoperative and postoperative Frankel grade, and preoperative vertebral collapse between two groups(p<0.05). In anterior-posterior group, the mean operation time was 351 minutes with a mean blood loss of 2892 ml, and preoperative kyphosis of 22 degrees was corrected to 11 degrees at latest follow-up with 7 cases of neurologic improvement. In the eggshell group, the mean operative time was 215 minutes with blood loss of 1930 ml, and preoperative kyphosis of 34 degrees was corrected to 8 degrees at latest follow-up with 11 cases of neurologic improvement. Egg-shell group showed significantly less operation time and blood loss with beter kyphosis correction. In anterior-posterior group, postoperative pneumonia was developed in 2 and superficial infection in 1. Distal screw loosening was detected in 4, 2 in anterior-posterior group and 2 in posterior eggshell group. One of them was treated by revision and others were treated by brace more than 6 months.
CONCLUSIONS
Posterior eggshell procedure showed a better kyphosis correction with significantly less operation time and blood loss. It is a preferable alternative to anterior-posterior surgery in post-traumatic kyphosis with neurologic compromised osteoporotic fracture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Eysel P, Schwitalle M, Oberstein A, Rompe JD, Hopf C, Kullmer K. Preoperative estimation of screw fixation strength in vertebral bodies. Spine15;. 23(2):174–180. 1998.
Article2). Gertzbein SD, Harris MB. Wedge osteotomy for the correction of post-traumatic kyphosis. Spine;. 17(3):374–379. 1992.
Article3). Ha KY, Kim KW, Park SJ, Paek DH, Ha JH. The surgical treatment of osteoporotic vertebral collapse caused by minor trauma. J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 33(1):105–112. 1998.
Article4). Heinig CF, Boyd BM. One stage vertebrectomy or eggshell procedure. Orthop Trans. 9:130. 1985.5). Jahng JS, Kang KS, Yang KH, Park HW, Lee SB. A clinical study on osteoporosis and back pain. J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 24(4):1210–1216. 1989.6). Kaneda K, Asano S, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M. The treatment of osteoporotic-posttraumatic vertebral collapse using the Kaneda device and a bioactive ceramic vertebral prosthesis. Spine;. 17:S295–303. 1992.
Article7). Kempinsky WH, Morgan PP, Boniface WR. Osteoporotic kyphosis with paraplegia. Neurology. 8:181–186. 1958.
Article8). Kostuik JP, Matsusaki H. Anterior stabilization, instrumentation, and decompression for post-traumatic kyphosis. Spine;. 14(4):379–386. 1989.
Article9). Kumpan W, Salomonowitz E, Seidl G, Wittich GR. The intravertebral vacuum phenomenon. Skeletal Radiol;. 15(6):444–447. 1986.
Article10). Lane JM, Russell L, Khan SN. Osteoporosis. Clin Orthop;. 372:139–150. 2000.
Article11). Lee KY, Kim CH, Shin SH. Osteoporotic vertebral fracture with myelopathy. J of Korean Spine Surg. 8(3):242–247. 2001.
Article12). Malcolm BW, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Chou SN. Post-traumatic kyphosis. A review of forty-eight surgically treated patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am;. 63(6):891–899. 1981.
Article13). McAfee PC, Bohlman HH, Yuan HA. An te r ior decompression of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures with incomplete neurological deficit using a retroperitoneal approach. J Bone Joint Surg Am;. 67(1):89–104. 1985.14). Mochida J, Toh E, Chiba M, Nishimura K. Treatment of osteoporotic late collapse of a vertebral body of thoracic and lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord. 14(5):393–398. 2001.
Article15). Roberson JR, Whitesides TE Jr. Surgical reconstruction of late post-traumatic thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine;. 10(4):307–312. 1985.
Article16). Saita K, Hoshino Y, Kikkawa I, Nakamura H. Posterior spinal shortening for paraplegia after vertebral collapse caused by osteoporosis. Spine;. 25(21):2832–2835. 2000.
Article17). Saville PD. A quantitative approach to simple radiographic diagnosis of osteoporosis: its application to the osteoporosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum;. 10(5):416–422. 1967.
Article18). Shikata J, Yamamuro T, Iida H, Shimizu K, Yoshi-kawa J. Surgical treatment for paraplegia resulting from vertebral fractures in senile osteoporosis. Spine;. 15(6):485–489. 1990.
Article19). Suk SI, Lee CK, Kang HS, Lee JH, Min HJ, Cha SH, Chung YJ. Vertebral fracture in osteoporosis. J of Korean Orthop Assoc. 28(3):980–987. 1993.
Article20). Sutherland CJ, Miller F, Wang GJ. Early progres -sive kyphosis following compression fractures. Two case reports from a series of “ stable” thoracolumbar compression fractures. Clin Orthop. 173:216–220. 1983.21). Tanaka S, Kubota M, Fujimoto Y, Hayashi J, Nishikawa K. Conus medullaris syndrome secondary to an L1 burst fracture in osteoporosis. A case report. Spine. 15(14):2131–2134. 1993.22). Thiranont N, Netrawichien P. Transpedicular decancellation closed wedge vertebral osteotomy for treatment of fixed flexion deformity of spine in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine;. 18(16):2517–2522. 1993.
Article23). Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop. 194:142–152. 1985.
Article24). Whitesides TE Jr. Traumatic kyphosis of the thoracolumbar spine. Clin Orthop. 128:78–92. 1977.
Article25). Wu SS, Hwa SY, Lin LC, Pai WM, Chen PQ, Au MK. Management of rigid post-traumatic kyphosis. Spine. 1(19):2260–2266. 1996.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture with Neurologic Deficits in Thoracolumbar Junction: Comparative Analysis of the Results According to the Surgical Methods
- Posterior Surgery of Neurologically Compromised Osteoporotic Kyphosis: Posterolateral Decompression and Stabilization using Titanium Mesh
- Major Surgical Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Elderly: A Comparison of Anterior Spinal Fusion, Anterior-Posterior Combined Surgery and Posterior Closing Wedge Osteotomy
- Analysis for Etiology of Correction Loss after Surgical Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture with Neurologic Deficits
- Surgical Treatment of Post - traumatic Kyphosis