J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2009 Jul;47(3):312-319.
A study on the shear bond strengths of veneering ceramics to the colored zirconia core
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, Graduate School, Pusan National University, Korea. jeonyc@paran.com
Abstract
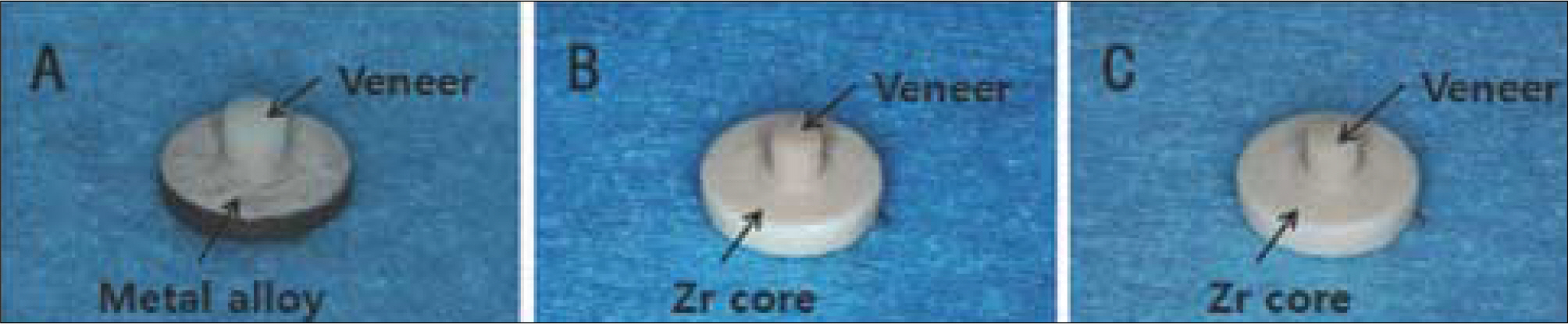
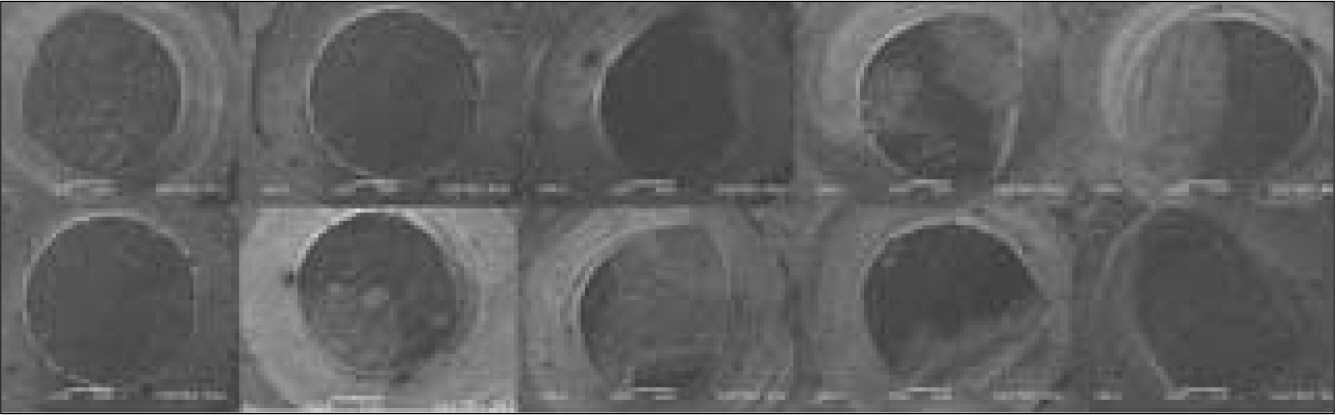
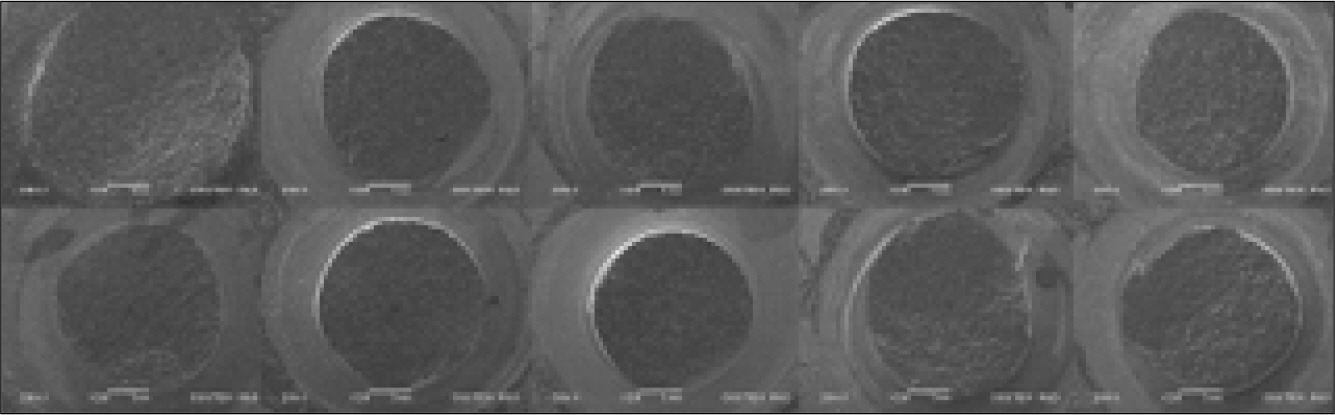
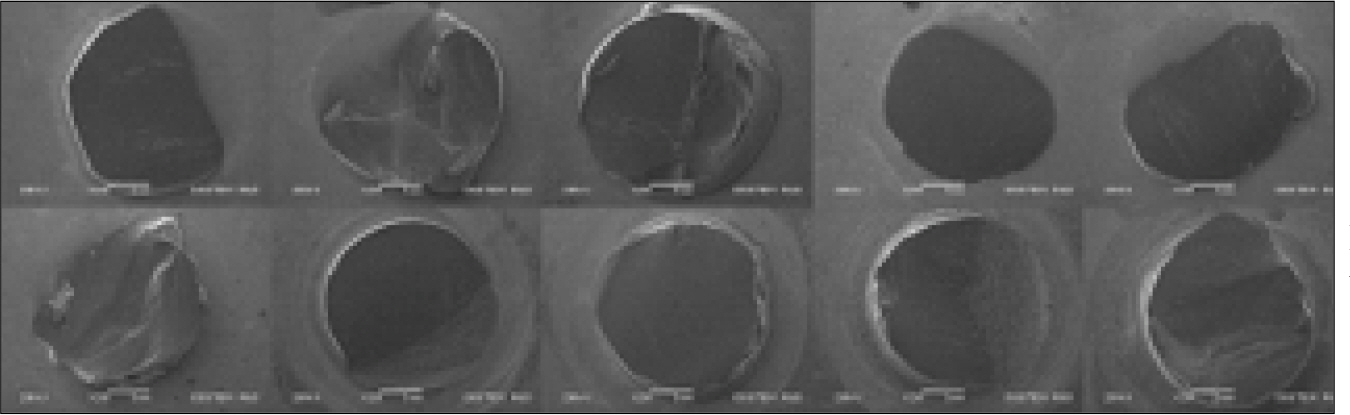
- STATEMENT OF PROBLEM: Delamination of veneering porcelain from underlying ceramic substructures has been reported for zirconia-ceramic restorations. Colored zirconia cores for esthetics have been reported that their bond strength with veneered porcelain is weaker compared to white zirconia cores. PURPOSE: This study aimed to investigate the shear bond strength by manufacturing the veneering porcelain on the colored zirconia core, using the layering technique and heat-pressing technique, and to evaluate the clinical stability by comparing the result of this with that of conventional metal ceramic system. MATERIAL AND METHODS: A Metal ceramic (MC) system was tested as a control group. The tested systems were Katana zirconia with CZR (ZB) and Katana Zirconia with NobelRondo Press (ZP). Thirty specimens, 10 for each system and control, were fabricated. Specimen disks, 3 mm high and 12 mm diameter, were fabricated with the lost-wax technique (MC) and the CAD-CAM (ZB and ZP). MC and ZB specimens were prepared using opaque and dentin veneering ceramics, veneered, 3 mm high and 2.8 mm in diameter, over the cores. ZP specimens were prepared using heat pressing ingots, 3 mm high and 2.8mm in diameter. The shear bond strength test was performed in a Shear bond test machine. Load was applied at a cross-head speed of 0.50 mm/min until failure. Mean shear bond strengths (MPa) were analyzed with the One-way ANOVA. After the shear bond test, fracture surfaces were examined by SEM. RESULTS: The mean shear bond strengths (SD) in MPa were MC control 29.14 (2.26); ZB 29.48 (2.30); and ZP 29.51 (2.32). The shear bond strengths of the tested systems were not significantly different (P > .05). All groups presented cohesive and adhesive failures, and showed predominance of cohesive failures in ceramic veneers. CONCLUSION: 1. The shear bond strengths of the tested groups were not significantly different from the control group (P > .05). 2. There was no significant different between the layering technique and the heat pressing technique in the veneering methods on the colored zirconia core. 3. All groups presented cohesive and adhesive failures, and showed predominance of cohesive failures in ceramic veneers.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Guazzato M., Albakry M., Ringer SP., Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:449–56.
Article2.Guazzato M., Albakry M., Swain MV., Ironside J. Mechanical properties of In-Ceram Alumina and In-Ceram Zirconia. Int J Prosthodont. 2002. 15:339–46.3.Jeoung HC. Fracture strength of zirconia monolithic crowns. J Korean Acad Prosthdont. 2006. 44:157–64.4.Isabelle Denry., Kelly JR. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:299–307.5.Aboushelib MN., Kleverlaan CJ., Feilzer AJ. Microtensile bond strength of different components of core veneered all-ceramic restorations. Part II: Zirconia veneering ceramics. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:857–63.6.Aboushelib MN., Kleverlaan CJ., Feilzer AJ. Effect of zirconia type on its bond strength with different veneer ceramics. J Prosthodont. 2008. 17:401–8.
Article7.Potiket N., Chiche G., Finger IM. In vitro fracture strength of teeth restored with different all-ceramic crown systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 92:491–5.8.Strub JR., Beschnidt SM. Fracture strength of 5 different all-ceramic crown systems. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:602–9.9.Gorman CM., Hill RG. Heat-pressed ionomer glass-ceramics. Part I: an investigation of flow and microstructure. Dent Mater. 2003. 19:320–6.
Article10.Gorman CM., Hill RG. Heat-pressed ionomer glass-ceramics. Part II. Mechanical property evaluation. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:252–61.
Article11.Kim CH., Jeon YC., Joeng CM., Lim JS. Effect of surface treatments of zirconia ceramic on the bond strength of resin cements. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2004. 42:386–96.12.Piconi C., Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999. 20:1–25.
Article13.Vult von Steyern P., Carlson P., Nilner K. All-ceramic fixed partial dentures designed according to the DC-Zirkon technique. A 2-year clinical study. J Oral Rehabil. 2005. 32:180–7.14.Du ¨ndar M., Ozcan M., Go ¨kec¸B., Co ¨mlekog ̌lu E., Leite F., Valandro LF. Comparison of two bond strength testing methodologies for bilayered all-ceramics. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:630–6.15.Guess PC., Kulis A., Witkowski S., Wolkewitz M., Zhang Y., Strub JR. Shear bond strengths between different zirconia cores and veneering ceramics and their susceptibility to thermocycling. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:1556–67.
Article16.Du ¨ndar M., Ozcan M., Co ¨mlekoglu E., Gu ¨ngo ¨r MA., Artunc¸ C. Bond strengths of veneering ceramics to reinforced ceramic core materials. Int J Prosthodont. 2005. 18:71–2.17.Al-Dohan HM., Yaman P., Dennison JB., Razzoog ME., Lang BR. Shear strength of core-veneer interface in bilayered ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 91:349–55.
Article18.Aboushelib MN., Kler M., Feilzer AJ. Effect of veneering method on the fracture and bond strength of bilayered zirconia restoration. Int J Prosthodont. 2008. 21:237–40.19.Hara AT., Pimenta LA., Rodrigues AL Jr. Influence of crosshead speed on resin-dentin shear bond strength. Dent Mater. 2001. 17:165–9.
Article20.ISO 9693. Metal-ceramic bond characterization (Schwickerath crack initiation test). Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for standardization;1999.21.Devigus A., Lombardi G. Shading Vita In-ceram YZ substructures: influence on value and chroma, part II. Int J Comput Dent. 2004. 7:379–88.22.Shah K., Holloway JA., Denry IL. Effect of coloring with various metal oxides on the microstructure, color, and flexural strength of 3Y-TZP. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008. 87:329–37.
Article23.Chevalier J., Deville S., Mu ¨nch E., Jullian R., Lair F. Critical effect of cubic phase on aging in 3mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics for hip replacement prosthesis. Biomaterials. 2004. 25:5539–45.
Article24.Peterson IM., Wuttiphan S., Lawn BR., Chyung K. Role of microstructure on contact damage and strength degradation of micaceous glass-ceramics. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:80–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Shear bond strength of veneer ceramic and colored zirconia by using aqueous metal chloride solutions
- Effect of surface treatmet on the shear bond strength of a zirconia core to veneering ceramic
- Effects of coloring procedures on zirconia/veneer ceramics bond strength
- Shear bond strength of veneering ceramic to coping materials with different pre-surface treatments
- Evaluation of shear bond strengths of gingiva-colored composite resin to porcelain, metal and zirconia substrates