J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2013 Jun;19(3):414-426.
Process of Overcoming Turnover Intention in Career Nurses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Nursing, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 2Neurological Care Unit, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University, Korea. nsicu01@cmcnu.or.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to identify the process of overcoming the intention toward turnover experienced by career nurses.
METHODS
Data were collected from 10 career nurses though in-depth interviews about their experiences. The main question was "How do you describe your experience of the process of overcoming intention to turnover as a career nurse?" Qualitative data from field and transcribed notes were analyzed using Strauss & Corbin's grounded theory methodology.
RESULTS
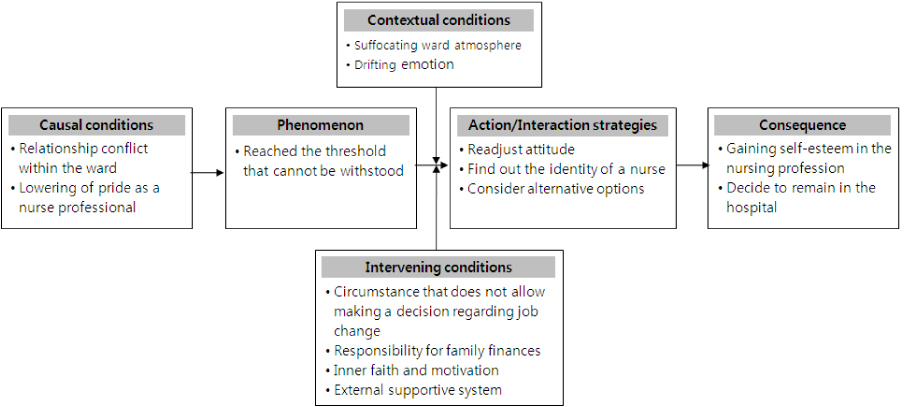
From the participants' statement, 127 concepts, 34 subcategories and 13 categories were extracted through the open coding process. The core category was discovered to be 'back to the original place'. Phenomenon was identified as 'reached the threshold that cannot be withstood' and this series of process was categorized as having four stages: 'conflict', 'meditation', 'discovery' and 'conquest'. There were three types of overcoming turnover intention in career nurses, 'adjustment', 'compromise', 'self-led'.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study produced useful information about the needs of career nurses during the process of overcoming turnover intention based on their stage and overcoming types of turnover intension. Ultimately this study may help decrease the turnover intention of career nurses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cavanagh SJ, Coffin DA. Staff turnover among hosp ital nurses. J Adv Nurs. 1992. 17(11):1369–1376. http://dx.doir.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.1992.tb01861.x.2. Cho YA, Kim GS, Kim ES, Park HM, Yoo MS, Lim EO, et al. A correlational study on ICU nurses' job stress, the way of coping, and the turnover intention. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2009. 15(3):129–141.3. Coomber B, Barriball KL. Impact of job satisfactioncomponents on intent to leave and turnover for hospital-based nurse: A review of the research literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2007. 44(2):297–314. http://dx.doir.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2006.02.004.4. Curran CR, Miller N. The impact of corporate culture on nurse retention. Nurs Clin North Am. 1990. 25(3):537–549.5. Glaser BG. Theoretical sensitivity. 1978. Mill Valley: Sociology Press.6. Hayes LJ, O'Brien-Pallas L, Duffield C, Shamian J, Buchan J, Hughes F, et al. Nurse turnover: A literature review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2006. 43(2):237–263. http://dx.doir.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2005.02.007.7. Jones CB. Calculating and updating nursing turnover costs. Nurs Econ. 1992. 10(1):39–45.8. Kang HS, Cho KJ, Choe NH, Kim WO. Reconstruction of professional identity in clinical nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2002. 32(4):470–481.9. Kim BS, Ryu ES, Kim KH, Chung HK, Song MS, Choi KS. A study on the experience of nurses' socialization process in the hospital setting. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1999. 29(2):393–404.10. Kim CH, Yang SS, Kim YJ, Son YJ, You MA, Song JE. A structural equation model of nurses' turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2009. 15:550–562.11. Kim JK, Kim MJ. A review of research on hospital nurses' turnover intention. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2011. 17:538–550.12. Kim MA, Park KO, You SJ, Kim MJ, Kim ES. A survey of nursing activities in small and medium-size hospitals: Reasons for turnover. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2009. 15(1):149–165.13. Kim MJ, Park SA. Experiences of hospital nurses` turnover: Determinants of factors affecting turnover intention. J Mil Nurs Res. 2010. 28(1):56–69.14. Kim MR. Clinical nurses' professionalism, nursing performance and intention of retention. 2008. Seoul, Korea: Hanyang University;Unpublished master's thesis.15. Kim MY. A study of factors influencing turnover solution in hospital nurses. Korean Nurse. 1995. 34(4):54–69.16. Kim YR. A study on the turnover intention of the oncology nurse. 2007. Gwangju, Korea: Chonnam National University;Unpublished master's thesis.17. Larrabee JH, Janney MA, Ostrow CI. Predicting registered nurse job satisfaction and intend to leave. J Nurs Adm. 2003. 33(5):271–283.18. Lee YJ, Kim KB. Experiences of nurse turnover. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008. 38:248–257. http://dx.doir.org/10.4040/jkan.2008.38.2.248.19. Lincoln YS, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. 1985. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.20. Liou SR. Nurses' intention to leave: Critically analyse the theory of reasoned action and organizational commitment model. J Nurs Manag. 2009. 17(1):92–99. http://dx.doir.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2008.00873.x.21. Park KO. The system and policy related to nursing personnel. Korean J Nurs Query. 2006. 15(2):5–17.22. Rambur B, Palumbo MV, Mongeon J. A statewide a nalysis of RN's intention to leave their position. Nurs Outlook. 2003. 51(4):182–188. http://dx.doir.org/10.1016/S0029-6554(03)00115-5.23. Son HM, Koh MH, Kim CM, Moon JH. The clinical experiences of adaptation as a new nursing staff. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2001. 31:988–997.24. Son IS, Kim HS, Kwon JS, Park DL, Han YH, Han SS. Development of an instrument to measure organizational socialization of new clinical nurses. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2008. 14(1):85–97.25. Strauss AL, Corbin J. Basics of qualitative research:Techniques and procedures for developing ground theory. 1998. London: Sage.26. Winter-Collins A, McDaniel AM. Sense of belonging and new graduate job satisfaction. J Nurses Staff Dev. 2000. 16(3):103–111.27. Yoon GS, Kim SY. Influences of job stress and burnout on turnover intention of nurses. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2010. 16:507–516.28. Yoon SH. A study on new graduate nurses' clinical experience of adaptation. J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2002. 8:55–72.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Influencing Turnover Intention of Nurses in Small-medium sized Hospitals
- Moderating Effects of Work-family Conflict between Job . Organizational . Career Characteristics and Turnover Intention among Nurses in Small and Medium-sized Hospitals
- The Experiences of Overcoming Turnover Intention among Experienced Nurses
- The Mediating Role of Career Calling in the Relationship Between Family-Supportive Supervisor Behaviors and Turnover Intention Among Public Hospital Nurses in China
- Effect of the Nursing Work Environment on Turnover Intention: Serial Mediation Effects of Career Motivation and Job Satisfaction