World J Mens Health.
2014 Aug;32(2):69-75. 10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.2.69.
The Prescribing and Dispensing of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in South Korea: A Questionnaire Survey of Patient Discomfort
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dgmoon@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2320795
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.2.69
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was performed to investigate the discomfort reported by patients taking phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is) in clinical practice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From September 2011 to March 2012, we surveyed patients who were prescribed PDE5Is for erectile dysfunction (ED). The questionnaire elicited information concerning: patient characteristics, medication counseling received and inconveniences experienced in hospitals and at pharmacies, effects of PDE5Is, and the separation of the prescribing and the dispensing of PDE5Is.
RESULTS
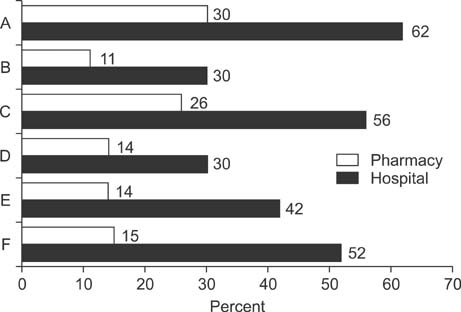
A total of 237 patients completed the questionnaire (mean age: 58.81+/-9.14 years). Among the 62 patients (26.0%) who reported having encountered some inconveniences in hospitals, the most frequently expressed concerns 'assistant staff,' including nurses (38.7%), 'testing procedures' (27.4%), and 'the issuing of prescriptions' (22.6%). Of the 137 patients (57.8%) who noted inconveniences in obtaining medications from pharmacies, 60.6% cited 'self-consciousness' as the most common reason, followed by 'insufficient medication counseling' (22.6%), and 'absence of consultation' (11.6%). In contrast, 82% of the patients were satisfied with the medication counseling that they had received in hospitals, covering drug usage, side effects, and precautions regarding PDE5Is; this proportion was only 30% for pharmacies. Further, most patients (89%) indicated that they preferred to obtain their prescriptions and medications for ED from the hospital at the same time.
CONCLUSIONS
Treatment of ED is a highly private matter. According to the survey, ED patients more often felt that obtaining medication from pharmacies was inconvenient. The sociocultural aspects of ED necessitate that exceptions to separating the prescribing and the dispensing of medication be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Impotence: NIH consensus development panel on impotence. JAMA. 1993; 270:83–90.2. Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the 'Cologne Male Survey'. Int J Impot Res. 2000; 12:305–311.
Article3. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994; 151:54–61.
Article4. Giuliano F, Chevret-Measson M, Tsatsaris A, Reitz C, Murino M, Thonneau P. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in France: results of an epidemiological survey of a representative sample of 1004 men. Eur Urol. 2002; 42:382–389.
Article5. Goldstein I, Lue TF, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen RC, Steers WD, Wicker PA. Sildenafil Study Group. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1397–1404.
Article6. Martin-Morales A, Sanchez-Cruz JJ, Saenz de Tejada I, Rodriguez-Vela L, Jimenez-Cruz JF, Burgos-Rodriguez R. Prevalence and independent risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Spain: results of the Epidemiologia de la Disfuncion Erectil Masculina Study. J Urol. 2001; 166:569–574.
Article7. Sung HH, Woo KJ, Jeong JY, Han DH, Lee SW. The refill rate and reasons for abandonment of phosphodiesterase5 inhibitors in erectile dysfunction patients. Korean J Urol. 2007; 48:646–651.
Article8. Huang SS, Lin CH, Chan CH, Loh el-W, Lan TH. Newly diagnosed major depressive disorder and the risk of erectile dysfunction: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Psychiatry Res. 2013; 210:601–606.
Article9. Lee EK, Malone DC. Comparison of peptic-ulcer drug use and expenditures before and after the implementation of a government policy to separate prescribing and dispensing practices in South Korea. Clin Ther. 2003; 25:578–592.
Article10. Kang HY, Park CY, Joong Kim HJ. Public attitude and knowledge on a new health policy for pharmaceutical care in Korea. Health Policy. 2002; 62:195–209.
Article11. Kim HJ, Chung W, Lee SG. Lessons from Korea's pharmaceutical policy reform: the separation of medical institutions and pharmacies for outpatient care. Health Policy. 2004; 68:267–275.
Article12. Jeong HS. Health care reform and change in public-private mix of financing: a Korean case. Health Policy. 2005; 74:133–145.
Article13. Park NC, Kim TN, Park HJ. Treatment strategy for non-responders to PDE5 inhibitors. World J Mens Health. 2013; 31:31–35.
Article14. Nicolosi A, Glasser DB, Kim SC, Marumo K, Laumann EO. GSSAB Investigators' Group. Sexual behaviour and dysfunction and help-seeking patterns in adults aged 40-80 years in the urban population of Asian countries. BJU Int. 2005; 95:609–614.
Article15. Ahn TY, Park JK, Lee SW, Hong JH, Park NC, Kim JJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Korean men: results of an epidemiological study. J Sex Med. 2007; 4:1269–1276.
Article16. Cho BL, Kim YS, Choi YS, Hong MH, Seo HG, Lee SY, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in primary care: results of a Korean study. Int J Impot Res. 2003; 15:323–328.17. Hatzichristou D, Haro JM, Martin-Morales A, von Keitz A, Riley A, Bertsch J, et al. EDOS Group. Patterns of switching phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: results from the Erectile Dysfunction Observational Study. Int J Clin Pract. 2007; 61:1850–1862.
Article18. Kell PD, Hvidsten K, Morant SV, Harnett JP, Bridge S. Factors that predict changing the type of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor medication among men in the UK. BJU Int. 2007; 99:860–863.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utilization, Safety, and Related Factors of Illegal Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in South Korean Men
- A Survey on the Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Separation of Prescribing and Dispensing Medicine: Among Patients of Family Medicine Clinic in an University Hospital
- Chronic Low Dosing of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor for Erectile Dysfunction
- Treatment Strategy for Non-Responders to PDE5 Inhibitors
- Recreational Use of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors and Its Associated Factors among Undergraduate Male Students in an Ethiopian University: A Cross-Sectional Study