World J Mens Health.
2014 Dec;32(3):167-175. 10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.3.167.
Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between CXCR4 Expression and Metastasis in Prostate Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Severance Hospital, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Yangpyeong Health Center, Yangpyeong, Korea.
- 3Division of Epidemic Intelligence Service, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kscho99@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2320781
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2014.32.3.167
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Experimental studies have suggested that the stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis is associated with tumor aggressiveness and metastasis in several malignancies. We performed a meta-analysis to elucidate the relationship between CXCR4 expression and the clinicopathological features of prostate cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data were collected from studies comparing Gleason score, T stage, and the presence of metastasis with CXCR4 levels in human prostate cancer samples. The studies were pooled, and the odds ratio (OR) of CXCR4 expression for clinical and pathological variables was calculated.
RESULTS
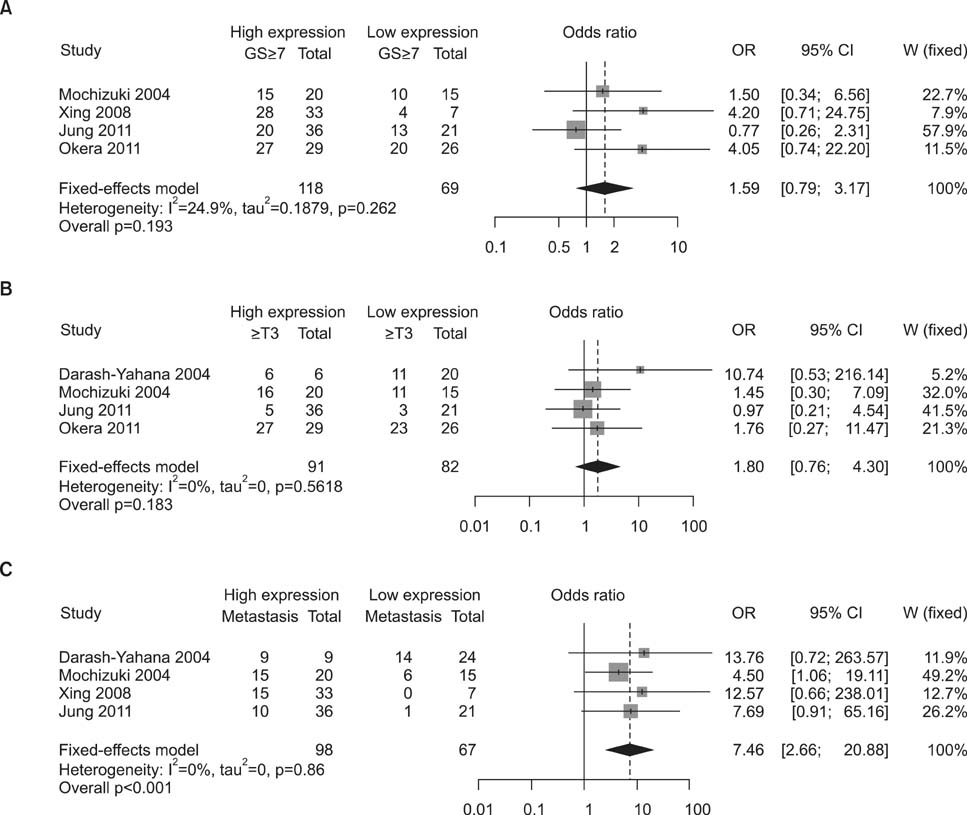
Five articles were eligible for the current meta-analysis. We found no relationship between CXCR4 expression and Gleason score (<7 vs. > or =7). The forest plot using the fixed-effects model indicated an OR of 1.585 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.793~3.171; p=0.193). Further, CXCR4 expression was not associated with the T stage (or =T3), and the relevant meta-analysis showed OR=1.803 (95% CI: 0.756~4.297, p=0.183). However, increased CXCR4 expression was strongly associated with metastatic disease with a fixed-effects pooled OR of 7.459 (95% CI: 2.665~20.878, p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Our meta-analysis showed that the higher CXCR4 protein expression in prostate cancer specimens is significantly associated with the presence of metastatic disease. This supports previous experimental data supporting the role played by the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in metastasis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee JY, Lee DH, Cho NH, Rha KH, Choi YD, Hong SJ, et al. Charlson comorbidity index is an important prognostic factor for long-term survival outcomes in Korean men with prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:316–323.
Article2. The Leuprolide Study Group. Leuprolide versus diethylstilbestrol for metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1984; 311:1281–1286.3. Gittes RF. Carcinoma of the prostate. N Engl J Med. 1991; 324:236–245.
Article4. Briganti A, Suardi N, Gallina A, Abdollah F, Novara G, Ficarra V, et al. Predicting the risk of bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014; 40:3–11.
Article5. Wells TN, Power CA, Lusti-Narasimhan M, Hoogewerf AJ, Cooke RM, Chung CW, et al. Selectivity and antagonism of chemokine receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1996; 59:53–60.
Article6. Furusato B, Mohamed A, Uhlén M, Rhim JS. CXCR4 and cancer. Pathol Int. 2010; 60:497–505.
Article7. Wang J, Wang J, Sun Y, Song W, Nor JE, Wang CY, et al. Diverse signaling pathways through the SDF-1/CXCR4 chemokine axis in prostate cancer cell lines leads to altered patterns of cytokine secretion and angiogenesis. Cell Signal. 2005; 17:1578–1592.8. Chinni SR, Sivalogan S, Dong Z, Filho JC, Deng X, Bonfil RD, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling activates Akt-1 and MMP-9 expression in prostate cancer cells: the role of bone microenvironment-associated CXCL12. Prostate. 2006; 66:32–48.
Article9. Singh S, Singh UP, Grizzle WE, Lillard JW Jr. CXCL12-CXCR4 interactions modulate prostate cancer cell migration, metalloproteinase expression and invasion. Lab Invest. 2004; 84:1666–1676.
Article10. Kukreja P, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D, Liu K, Agrawal KC. Up-regulation of CXCR4 expression in PC-3 cells by stromal-derived factor-1alpha (CXCL12) increases endothelial adhesion and transendothelial migration: role of MEK/ERK signaling pathway-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:9891–9898.11. Wang Q, Diao X, Sun J, Chen Z. Regulation of VEGF, MMP-9 and metastasis by CXCR4 in a prostate cancer cell line. Cell Biol Int. 2011; 35:897–904.
Article12. Darash-Yahana M, Pikarsky E, Abramovitch R, Zeira E, Pal B, Karplus R, et al. Role of high expression levels of CXCR4 in tumor growth, vascularization, and metastasis. FASEB J. 2004; 18:1240–1242.
Article13. Mochizuki H, Matsubara A, Teishima J, Mutaguchi K, Yasumoto H, Dahiya R, et al. Interaction of ligand-receptor system between stromal-cell-derived factor-1 and CXC chemokine receptor 4 in human prostate cancer: a possible predictor of metastasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 320:656–663.
Article14. Xing Y, Liu M, Du Y, Qu F, Li Y, Zhang Q, et al. Tumor cell-specific blockade of CXCR4/SDF-1 interactions in prostate cancer cells by hTERT promoter induced CXCR4 knockdown: A possible metastasis preventing and minimizing approach. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008; 7:1839–1848.
Article15. Jung SJ, Kim CI, Park CH, Chang HS, Kim BH, Choi MS, et al. Correlation between chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and prognostic factors in patients with prostate cancer. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52:607–611.
Article16. Okera M, Bae K, Bernstein E, Cheng L, Lawton C, Wolkov H, et al. Evaluation of nuclear factor κB and chemokine receptor CXCR4 co-expression in patients with prostate cancer in the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 8610. BJU Int. 2011; 108:E51–E58.
Article17. Akashi T, Koizumi K, Tsuneyama K, Saiki I, Takano Y, Fuse H. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and prognosis in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008; 99:539–542.
Article18. de Muga S, Hernández S, Salido M, Lorenzo M, Agell L, Juanpere N, et al. CXCR4 mRNA overexpression in high grade prostate tumors: lack of association with TMPRSS2-ERG rearrangement. Cancer Biomark. 2012-2013; 12:21–30.
Article19. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article20. Keaney M, Lorimer AR. Auditing the implementation of SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) clinical guidelines. Int J Health Care Qual Assur Inc Leadersh Health Serv. 1999; 12:314–317.21. Flay BR, Biglan A, Boruch RF, Castro FG, Gottfredson D, Kellam S, et al. Standards of evidence: criteria for efficacy, effectiveness and dissemination. Prev Sci. 2005; 6:151–175.
Article22. Kumpfer KL, Alvarado R. Family-strengthening approaches for the prevention of youth problem behaviors. Am Psychol. 2003; 58:457–465.
Article23. Bröning S, Kumpfer K, Kruse K, Sack PM, Schaunig-Busch I, Ruths S, et al. Selective prevention programs for children from substance-affected families: a comprehensive systematic review. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2012; 7:23.
Article24. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560.
Article25. Fleiss JL. Analysis of data from multiclinic trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:267–275.
Article26. DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials. 2007; 28:105–114.
Article27. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994; 50:1088–1101.
Article28. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article29. Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, Wanzeck J, Wojakowski W, Janowska-Wieczorek A, et al. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005; 23:879–894.
Article30. Wirth MP. Hormone-refractory prostate cancer: what have we learned? BJU Int. 2007; 100:Suppl 2. 56–59.
Article31. Cereda V, Formica V, Massimiani G, Tosetto L, Roselli M. Targeting metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: mechanisms of progression and novel early therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014; 23:469–487.
Article32. Domanska UM, Timmer-Bosscha H, Nagengast WB, Oude Munnink TH, Kruizinga RC, Ananias HJ, et al. CXCR4 inhibition with AMD3100 sensitizes prostate cancer to docetaxel chemotherapy. Neoplasia. 2012; 14:709–718.
Article33. Cho KS, Yoon SJ, Lee JY, Cho NH, Choi YD, Song YS, et al. Inhibition of tumor growth and histopathological changes following treatment with a chemokine receptor CXCR4 antagonist in a prostate cancer xenograft model. Oncol Lett. 2013; 6:933–938.
Article34. Debnath B, Xu S, Grande F, Garofalo A, Neamati N. Small molecule inhibitors of CXCR4. Theranostics. 2013; 3:47–75.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Expression and Prognostic Factors in Patients with Prostate Cancer
- Association of CXCR4 Expression with Metastasis and Survival among Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Differential Expression of CXCR4 in Conventional High-grade and Low-grade Central Osteosarcoma and Its Prognostic Implications
- Clinical Significance of C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 4 and Integrin αvβ6 Expression in Breast Cancer
- Expression of CXCR4 and SDF-1alpha in Primary Breast Cancers and Metastatic Lymph Nodes