Tuberc Respir Dis.
2015 Jul;78(3):293-296. 10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.293.
Lung Disease Caused by Mycobacterium malmoense in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. heathcliff6800@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2320660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2015.78.3.293
Abstract
- Mycobacterium malmoense is a very rare cause of lung disease in South Korea. We reported the first case of lung disease caused by M. malmoense in an immunocompetent patient. The patient was successfully treated with a 14-month course of antibiotics.
MeSH Terms
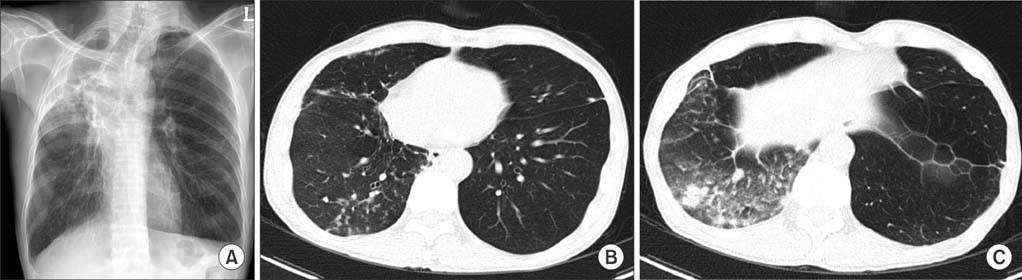
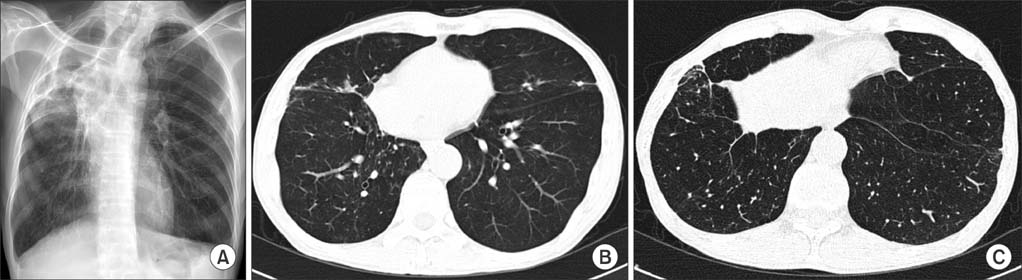
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koh WJ, Kwon OJ, Jeon K, Kim TS, Lee KS, Park YK, et al. Clinical significance of nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated from respiratory specimens in Korea. Chest. 2006; 129:341–348.2. Park YS, Lee CH, Lee SM, Yang SC, Yoo CG, Kim YW, et al. Rapid increase of non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung diseases at a tertiary referral hospital in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010; 14:1069–1071.3. Hoefsloot W, Boeree MJ, van Ingen J, Bendien S, Magis C, de Lange W, et al. The rising incidence and clinical relevance of Mycobacterium malmoense : a review of the literature. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008; 12:987–993.4. Hoefsloot W, van Ingen J, de Lange WC, Dekhuijzen PN, Boeree MJ, van Soolingen D. Clinical relevance of Mycobacterium malmoense isolation in The Netherlands. Eur Respir J. 2009; 34:926–931.5. Buchholz UT, McNeil MM, Keyes LE, Good RC. Mycobacterium malmoense infections in the United States, January 1993 through June 1995. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27:551–558.6. Ryoo SW, Shin S, Shim MS, Park YS, Lew WJ, Park SN, et al. Spread of nontuberculous mycobacteria from 1993 to 2006 in Koreans. J Clin Lab Anal. 2008; 22:415–420.7. Aksamit TR. Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary disease in patients with pre-existing lung disease. Clin Chest Med. 2002; 23:643–653.8. Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:367–416.9. Jenkins PA, Campbell IA, Banks J, Gelder CM, Prescott RJ, Smith AP. Clarithromycin vs ciprofloxacin as adjuncts to rifampicin and ethambutol in treating opportunist mycobacterial lung diseases and an assessment of Mycobacterium vaccae immunotherapy. Thorax. 2008; 63:627–634.10. Pulmonary disease caused by M. malmoense in HIV negative patients: 5-yr follow-up of patients receiving standardised treatment. Eur Respir J. 2003; 21:478–482.11. Sano C, Tatano Y, Shimizu T, Yamabe S, Sato K, Tomioka H. Comparative in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activities of sitafloxacin, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin against Mycobacterium avium. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011; 37:296–301.12. Fouad M, Gallagher JC. Moxifloxacin as an alternative or additive therapy for treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Pharmacother. 2011; 45:1439–1444.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pulmonary and Endobronchial Mycobacterium avium Infection Presenting as an Acute Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Mycobacterium avium Infection Presenting as Endobronchial Lesions in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Vertebral Osteomyelitis due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in an Immunocompetent Elderly Patient After Vertebroplasty
- Vertebral Osteomyelitis caused by Mycobacterium abscessus in an Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease in a Patient with Cystic Fibrosis