Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Jan;74(1):28-31.
A Case of Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation Infected with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyleemd@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
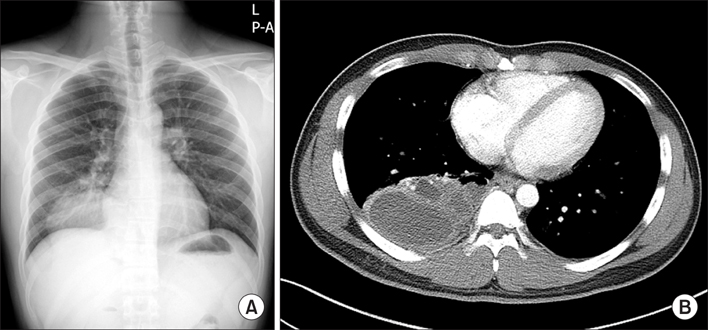
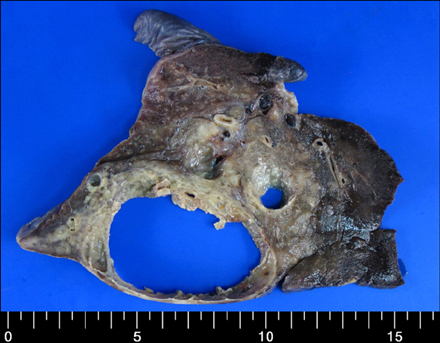
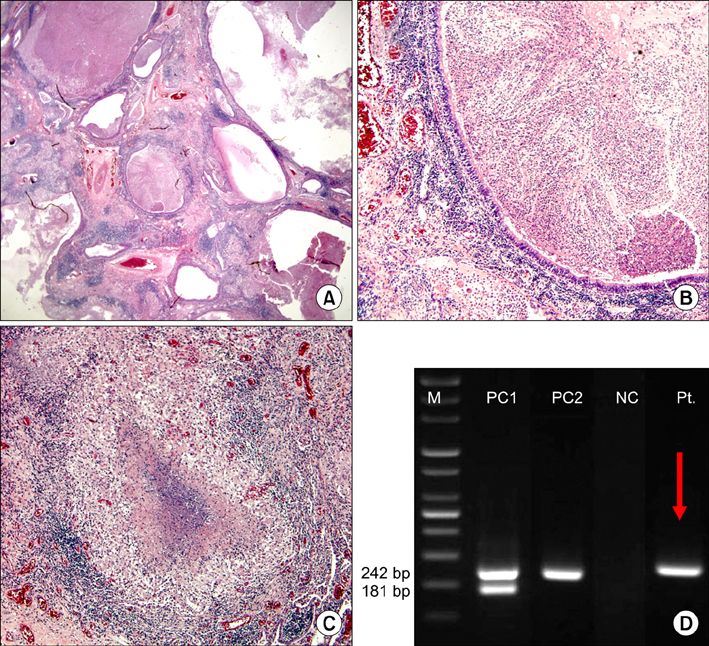
- We present a case of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) in a 25-year-old male who was presented with chronic cough. Chest radiography revealed an abnormal mass-like shadow in the right lower pulmonary zone. A contrast enhanced computed tomography showed an 11 cm solid, cystic mixed mass on the right lower lobe. A right lower lobectomy was performed by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery without complications. The gross specimen showed a massive cavitation with multiloculated cysts of varying size, consistent with CCAM, along with noticeable granulomatous inflammation. Non-tuberculosis mycobacteria were isolated from a bronchial wash specimen, and the resected tissue homogenates were positive for Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex by polymerase chain reaction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Laberge JM, Flageole H, Pugash D, Khalife S, Blair G, Filiatrault D, et al. Outcome of the prenatally diagnosed congenital cystic adenomatoid lung malformation: a Canadian experience. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2001. 16:178–186.2. Ch'In KY, Tang MY. Congenital adenomatoid malformation of one lobe of a lung with general anasarca. Arch Pathol (Chic). 1949. 48:221–229.3. Stocker JT, Madewell JE, Drake RM. Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung: classification and morphologic spectrum. Hum Pathol. 1977. 8:155–171.4. Fromont-Hankard G, Philippe-Chomette P, Delezoide AL, Nessmann C, Aigrain Y, Peuchmaur M. Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor expression in normal human lung and congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002. 126:432–436.5. Kaslovsky RA, Purdy S, Dangman BC, McKenna BJ, Brien T, Ilves R. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma in a child with congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Chest. 1997. 112:548–551.6. Benouaich V, Marcheix B, Begueret H, Brouchet L, Velly JF, Jougon J. Malignancy of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of lung in aged. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2009. 17:634–636.7. Nur S, Badr R, Sandoval C, Brudniki A, Yeh A. Syndromic presentation of a pleuropulmonary blastoma associated with congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation: a case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2007. 42:1772–1775.8. Lin SH, Lee LN, Chang YL, Lee YC, Ding LW, Hsueh PR. Infected bronchogenic cyst due to Mycobacterium avium in an immunocompetent patient. J Infect. 2005. 51:e131–e133.9. Sparks JD, Das BB, Eid NS, Austin EH, Recto M. Atypical mycobacterial infection in sequestrated lung in an infant presenting with chronic pneumonitis and recurrent wheezing. Congenit Heart Dis. 2008. 3:284–287.10. Mooney LR, Brown JW 3rd, Saunders RL Jr. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration infected with a mycobacterium of the Battey-avium complex. Chest. 1975. 68:594–595.11. Shiota Y, Arikita H, Aoyama K, Horita N, Hiyama J, Ono T, et al. Pulmonary sequestration associated by Mycobacterium intracellulare infection. Intern Med. 2002. 41:990–992.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapid identification of mycobacterium avium and mycobacterium intracellulare by the amplification of rRNA sequences
- Vertebral Osteomyelitis due to Mycobacterium intracellulare in an Immunocompetent Elderly Patient After Vertebroplasty
- A Case of Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease in a Patient with Cystic Fibrosis
- A Case of Pulmonary Disease due to Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex
- CONGENITAL CYSTIC ADENOMATOID MALFORMATION TREATED WITH EMERGENCY OPERATION