Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Jan;74(1):7-14.
Measurement of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Stable Bronchiectasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. dextro@snubh.org
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) can be measured easily, rapidly, and noninvasively for the assessment of airway inflammation, particularly mediated by eosinophil, such as asthma. In bronchiectasis (BE), the pathogenesis has been known as chronic airway inflammation and infection with abnormal airway dilatation; however, there are little studies to evaluate the role of FeNO in BE.
METHODS
From March 2010 to February 2012, 47 patients with BE, diagnosed by high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), performed FeNO, compared with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). All patients carried out a complete blood count including eosinophil count, chemistry, sputum examination, and spirometry, if indicated. A retrospective analysis was performed to elucidate the clinical role of FeNO in BE patients.
RESULTS
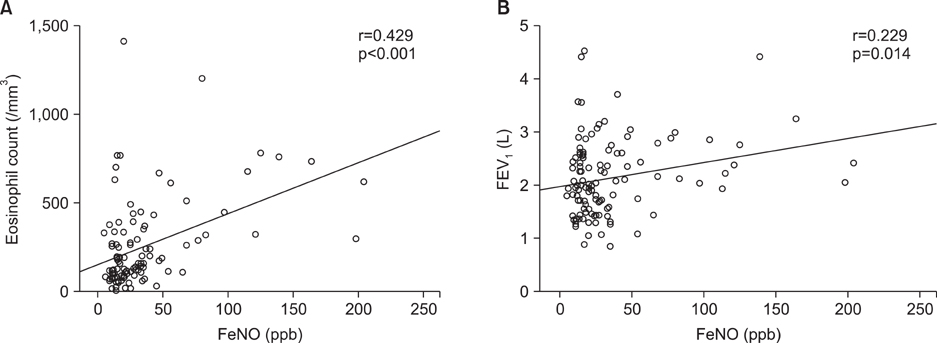
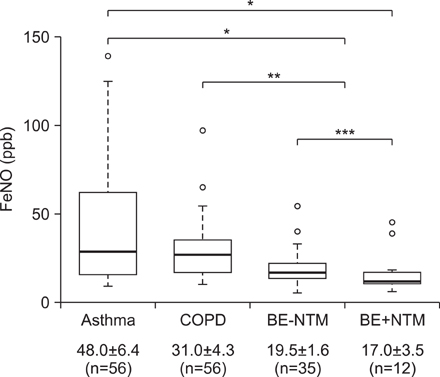
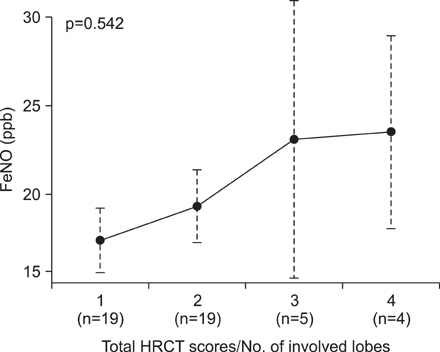
The mean FeNO levels in patients with BE was 18.8+/-1.5 part per billion (ppb), compared to 48.0+/-6.4 and 31.0+/-4.3 in those with asthma and COPD, respectively (p<0.001). The FeNO levels tended to increase along with the disease severity scores by HRCT; however, it was statistically not significant. FeNO in BE with a co-infection of nontuberculous mycobacteria was the lowest at 17.0+/-3.5 ppb among the study population.
CONCLUSION
FeNO in BE was lower than other chronic inflammatory airway diseases, particularly compared with asthma. For clinical application of FeNO in BE, more large-scaled, prospective studies should be considered.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nathan C, Xie QW. Regulation of biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994. 269:13725–13728.2. Kim SH, Yoon HJ. Use of the exhaled nitric oxide for management of asthma and respiratory diseases. Korean J Med. 2008. 74:579–586.3. Barnes PJ, Dweik RA, Gelb AF, Gibson PG, George SC, Grasemann H, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide in pulmonary diseases: a comprehensive review. Chest. 2010. 138:682–692.4. Kharitonov SA, Wells AU, O'Connor BJ, Cole PJ, Hansell DM, Logan-Sinclair RB, et al. Elevated levels of exhaled nitric oxide in bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:1889–1893.5. Wang CH, Liu CY, Lin HC, Yu CT, Chung KF, Kuo HP. Increased exhaled nitric oxide in active pulmonary tuberculosis due to inducible NO synthase upregulation in alveolar macrophages. Eur Respir J. 1998. 11:809–815.6. Dweik RA, Boggs PB, Erzurum SC, Irvin CG, Leigh MW, Lundberg JO, et al. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FENO) for clinical applications. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. 184:602–615.7. Kim C, Kim DG. Bronchiectasis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2012. 73:249–257.8. Kharitonov SA, Barnes PJ. Exhaled biomarkers. Chest. 2006. 130:1541–1546.9. Tsang KW, Leung R, Fung PC, Chan SL, Tipoe GL, Ooi GC, et al. Exhaled and sputum nitric oxide in bronchiectasis: correlation with clinical parameters. Chest. 2002. 121:88–94.10. Ho LP, Innes JA, Greening AP. Exhaled nitric oxide is not elevated in the inflammatory airways diseases of cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis. Eur Respir J. 1998. 12:1290–1294.11. Narang I, Ersu R, Wilson NM, Bush A. Nitric oxide in chronic airway inflammation in children: diagnostic use and pathophysiological significance. Thorax. 2002. 57:586–589.12. Shoemark A, Devaraj A, Meister M, Ozerovitch L, Hansell DM, Wilson R. Elevated peripheral airway nitric oxide in bronchiectasis reflects disease severity. Respir Med. 2011. 105:885–891.13. Van Beek SC, Nhung NV, Sy DN, Sterk PJ, Tiemersma EW, Cobelens FG. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide as a potential screening tool for pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011. 15:185–192.14. Ryoo SW, Shin S, Shim MS, Park YS, Lew WJ, Park SN, et al. Spread of nontuberculous mycobacteria from 1993 to 2006 in Koreans. J Clin Lab Anal. 2008. 22:415–420.15. Oikonomou A, Tsanakas J, Hatziagorou E, Kirvassilis F, Efremidis S, Prassopoulos P. High resolution computed tomography of the chest in cystic fibrosis (CF): is simplification of scoring systems feasible? Eur Radiol. 2008. 18:538–547.16. Idh J, Westman A, Elias D, Moges F, Getachew A, Gelaw A, et al. Nitric oxide production in the exhaled air of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in relation to HIV co-infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2008. 8:146.17. Robroeks CM, Roozeboom MH, de Jong PA, Tiddens HA, Jobsis Q, Hendriks HJ, et al. Structural lung changes, lung function, and non-invasive inflammatory markers in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010. 21:493–500.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement and Interpretation of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide
- Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in the Diagnosis of Asthma and the Assessment of Asthma Control
- Measurements of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric asthma
- Clinical application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric allergic rhinitis
- Erratum: Addition of Acknowledgements. Measurement of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Stable Bronchiectasis