Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 Sep;69(3):196-200.
A Case of Adult Intussusception Induced by Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdlee@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
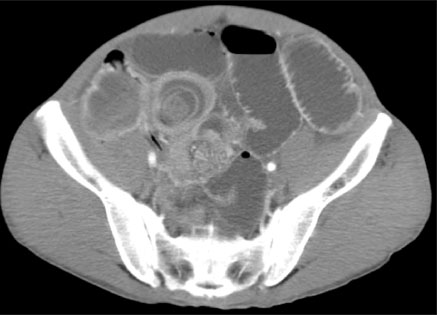
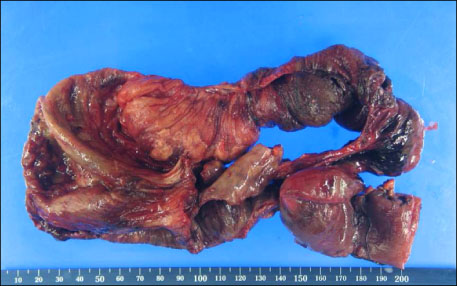
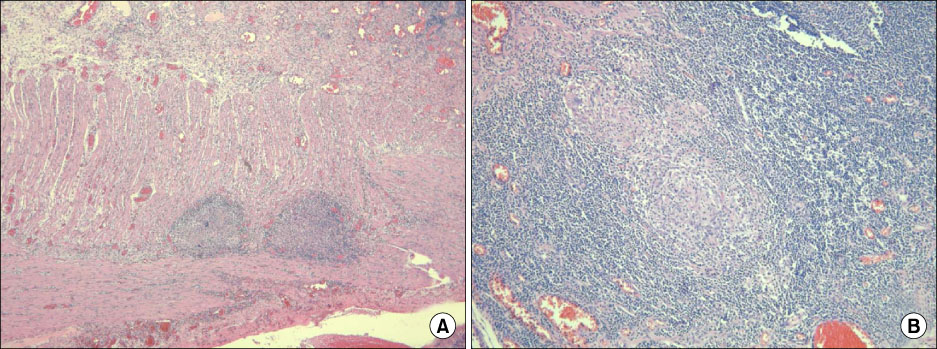
- Intussusception primarily occurs in children and is uncommon in adults. Moreover, intussusception caused by intestinal tuberculosis is very rare. We report a case of intussusception induced by intestinal tuberculosis. A 53-year-old man presented to our hospital with complaints of cough and sputum for 2 weeks. We started anti-tuberculosis medication as the patient's sputum acid-fast staining was positive. After 4 days of treatment, the patient developed abdominal cramping pain. Imaging studies showed ileo-ileal type intussusception. The patient underwent segmental resection of the small bowel and intestinal tuberculosis was confirmed on histological examination. He recovered after surgery and was discharged on anti-tuberculosis medication.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marinis A, Yiallourou A, Samanides L, Dafnios N, Anastasopoulos G, Vassiliou I, et al. Intussusception of the bowel in adults: a review. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:407–411.2. Pollack CV Jr, Pender ES. Unusual cases of intussusception. J Emerg Med. 1991. 9:347–355.3. Nakamura S, Yanagihara K, Izumikawa K, Seki M, Kakeya H, Yamamoto Y, et al. Severe pulmonary tuberculosis complicating Ileocecal intussusception due to intestinal tuberculosis: a case report. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2008. 7:16.4. Wang N, Cui XY, Liu Y, Long J, Xu YH, Guo RX, et al. Adult intussusception: a retrospective review of 41 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:3303–3308.5. Hong ES, Kwon KS, Jeong S, Kim SH, Cho HG, Kim PS, et al. A case of intussusception induced by intestinal tuberculosis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 18:99–105.6. Kim AR, Kim SN, Lee YH, Oh CK. A case of intestinal tuberculosis associated with intussusception. New Med J. 1990. 33:83–86.7. Yang WJ, Yoon DS, Lee JJ, Park CJ, Kim DH. Clinical review of the intussusception in adults. J Korean Surg Soc. 1998. 55:388–393.8. Park SH, Moon HY. Adult intussusception in Korea. J Korean Surg Soc. 1992. 43:829–837.9. Chang CC, Chen YY, Chen YF, Lin CN, Yen HH, Lou HY. Adult intussusception in Asians: clinical presentations, diagnosis, and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:1767–1771.10. McKay R. Ileocecal intussusception in an adult: the laparoscopic approach. JSLS. 2006. 10:250–253.11. Lee YJ, Yang SK, Myung SJ, Byeon JS, Park IG, Kim JS, et al. The usefulness of colonoscopic biopsy in the diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis and pattern of concomitant extra-intestinal tuberculosis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004. 44:153–159.12. Ha HK, Ko GY, Yu ES, Yoon K, Hong WS, Kim HR, et al. Intestinal tuberculosis with abdominal complications: radiologic and pathologic features. Abdom Imaging. 1999. 24:32–38.13. Pettengell KE, Larsen C, Garb M, Mayet FG, Simjee AE, Pirie D. Gastrointestinal tuberculosis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Q J Med. 1990. 74:303–308.14. Sharma MP, Bhatia V. Abdominal tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004. 120:305–315.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intussusception Induced by Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Endoscopic Treatment of Intussusception due to Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Salmonella enteritis: A Rare Cause of Adult Intussusception
- A Case of Lipoma of Terminal Ileum Causing Intussusception of the Transverse Colon
- An Adult Case of Small Bowel Intussusception Caused by Hemangioma Presenting with Intestinal Bleeding