Tuberc Respir Dis.
2009 Sep;67(3):239-243.
Delftia acidovorans Isolated from the Drainage in an Immunocompetent Patient with Empyema
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. doc4u@hanmail.net
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- 4Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
Abstract
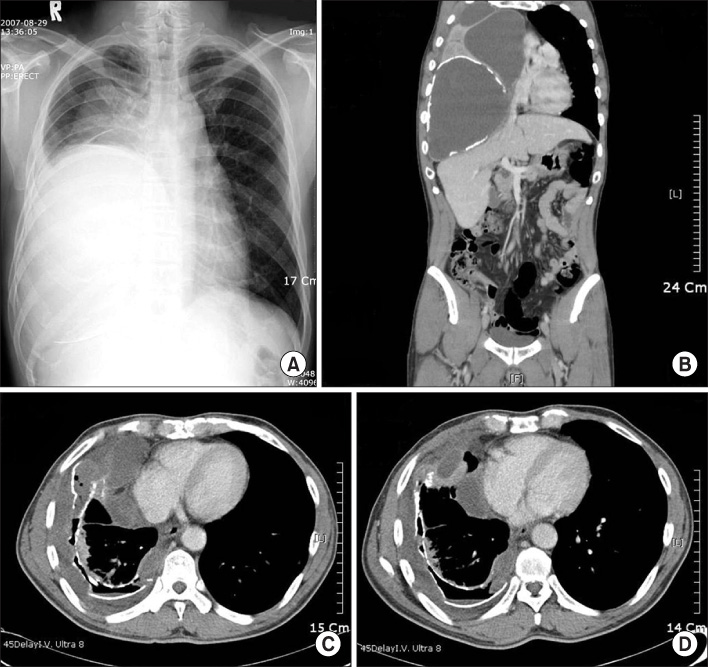
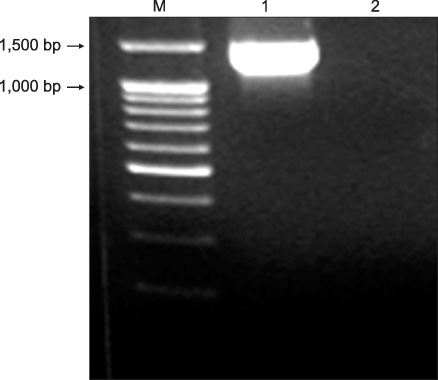
- Delftia acidovorans is a gram-negative motile rod found ubiquitously in soil and in water. Confirmed isolation from clinical infections is rare, and has been documented mostly in immunocompromised patients or those with indwelling catheters. A 53-year-old man was referred for the evaluation of a huge mass-like lesion found incidentally by chest X-ray. The lesion occupied more than half of the right lung and was diagnosed as a large loculated pleural effusion by CT scan. Bloody pus was drained through a percutaneous catheter, and D. acidovorans, identified by the Vitek GN card and confirmed by amplification of 16S ribosomal RNA and sequencing analysis, was isolated repeatedly from the drained pus. The patient was treated with imipenem/cilastatin to which the organism was sensitive. This is a rare report of chronic empyema associated with D. acidovorans in the respiratory system of an immunocompetent patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bergogne-Bérézin E. Cohen J, Powderly W, editors. Pseudomonas and miscellaneous gram-negative bacilli. Infectious disease. 2004. 2nd ed. St Louis: Mosby;2203–2217.2. Castagnola E, Conte M, Venzano P, Garaventa A, Viscoli C, Barretta MA, et al. Broviac catheter-related bacteraemias due to unusual pathogens in children with cancer: case reports with literature review. J Infect. 1997. 34:215–218.3. Ender PT, Dooley DP, Moore RH. Vascular catheter-related Comamonas acidovorans bacteremia managed with preservation of the catheter. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996. 15:918–920.4. López-Menchero R, Sigüenza F, Caridad A, Alonso JC, Ferreruela RM. Peritonitis due to Comamonas acidovorans in a CAPD patient. Perit Dial Int. 1998. 18:445–446.5. Stonecipher KG, Jensen HG, Kastl PR, Faulkner A, Rowsey JJ. Ocular infections associated with Comamonas acidovorans. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991. 112:46–49.6. Horowitz H, Gilroy S, Feinstein S, Gilardi G. Endocarditis associated with Comamonas acidovorans. J Clin Microbiol. 1990. 28:143–145.7. Franzetti F, Cernuschi M, Esposito R, Moroni M. Pseudomonas infections in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. J Intern Med. 1992. 231:437–443.8. Henry D, Campbell M, LiPuma J, Speert D. Identification of Burkholderia cepacia isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis and use of a simple new selective medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1997. 35:614–619.9. Massol-Deya A, Odelson D, Hickey R, Tiedje J. Akkermans ADL, Van Elsas JD, De Bruijn FJ, editors. Bacterial community fingerprinting of amplified 16S and 16-23S ribosomal DNA gene sequences and restriction endonuclease analysis. Molecular microbial ecology manual. 1995. Boston: Kluwer Academic;1–8.10. Daur AV, Klimak F Jr, Cogo LL, Botao GD, Monteiro CL, Dalla Costa LM. Enrichment methodology to increase the positivity of cultures from body fluids. Braz J Infect Dis. 2006. 10:372–373.11. Perla R, Knutson E. Delftia acidovorans bacteremia in an intravenous drug abuser. Am J Infect Dis. 2005. 1:73–74.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Delftia acidovorans Peritonitis in a Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Managed with Preserving the Dialysis Catheter
- A Case of Comamonas Acidovorans Corneal Ulcer
- Treatment of Huge Chronic Tuberculous Empyema with Cardiopulmonary Dysfunction: 1 case report
- Experience of Comamonas Acidovorans Keratitis with Delayed Onset and Treatment Response in Immunocompromised Cornea
- Comamonas Acidovorans Peritonitis in a CAPD Patient Managed with Preservation of the Catheter