Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Aug;65(2):142-146.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome after Topotecan Therapy in a Patient with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jinhwalee@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
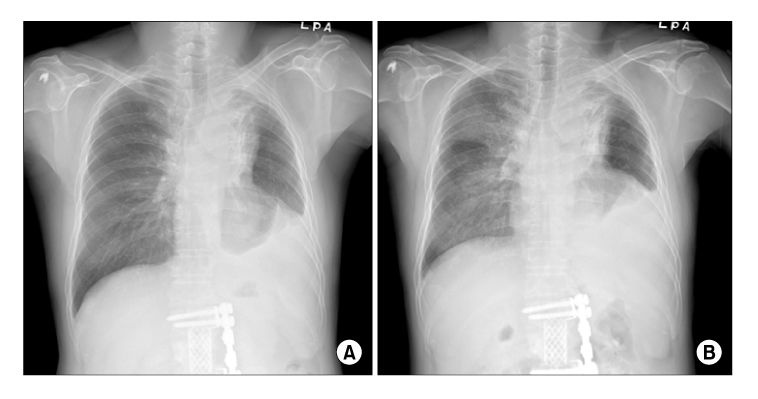
- Small cell lung cancer is characterized by an aggressive clinical course and a high tendency for early dissemination in spite of a good chemotherapy response. Topotecan is a topoisomerase I inhibitor, and it is used as second-line treatment for small cell lung cancer. The reported dose-limiting adverse reactions to topotecan are mainly hematologic. Yet pulmonary toxicity associated with topotecan is known to be rare. We report here on a case that showed the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome during the 3rd cycle of topotecan chemotherapy in a patient with small cell lung cancer. He developed dyspnea and respiratory failure, and the chest CT scan revealed diffuse ground-glass opacity that was probably due to chemotherapy-related pulmonary toxicity. He finally died of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cooper S, Spiro SG. Small cell lung cancer: treatment review. Respirology. 2006. 11:241–248.2. MacCallum C, Gillenwater HH. Second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2006. 8:258–264.3. Ardizzoni A, Hansen H, Dombernowsky P, Gamucci T, Kaplan S, Postmus P, et al. Topotecan, a new active drug in the second-line treatment of small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study in patients with refractory and sensitive disease. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Early Clinical Studies Group and New Drug Development Office, and the Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:2090–2096.4. Eckardt JR, von Pawel J, Pujol JL, Papai Z, Quoix E, Ardizzoni A, et al. Phase III study of oral compared with intravenous topotecan as second-line therapy in small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:2086–2092.5. Maksymiuk AW, Marschke RF Jr, Tazelaar HD, Grill J, Nair S, Marks RS, et al. Phase II trial of topotecan for the treatment of mesothelioma. Am J Clin Oncol. 1998. 21:610–613.6. Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Sporn TA, Goodman PC. Pulmonary drug toxicity: radiologic and pathologic manifestations. Radiographics. 2000. 20:1245–1259.7. Maitland ML, Wilcox R, Hogarth DK, Desai AA, Caligiuri P, Abrahams C, et al. Diffuse alveolar damage after a single dose of topotecan in a patient with pulmonary fibrosis and small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2006. 54:243–245.8. Edgerton CC, Gilman M, Roth BJ. Topotecan-induced bronchiolitis. South Med J. 2004. 97:699–701.9. Masuda N, Fukuoka M, Kusunoki Y, Matsui K, Takifuji N, Kudoh S, et al. CPT-11: a new derivative of camptothecin for the treatment of refractory or relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992. 10:1225–1229.10. Limper AH. Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Murray JF, Nadel JA, editors. Drug-induced pulmonary disease. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders;1888–1912.11. Limper AH. Chemotherapy-induced lung disease. Clin Chest Med. 2004. 25:53–64.12. Malik SW, Myers JL, DeRemee RA, Specks U. Lung toxicity associated with cyclophosphamide use: two distinct patterns. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. 154:1851–1856.13. Fukuoka M, Niitani H, Suzuki A, Motomiya M, Hasegawa K, Nishiwaki Y, et al. A phase II study of CPT-11, a new derivative of camptothecin, for previously untreated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992. 10:16–20.14. Madarnas Y, Webster P, Shorter AM, Bjarnason GA. Irinotecan-associated pulmonary toxicity. Anticancer Drugs. 2000. 11:709–713.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chemotherapy in Lung Cancer
- Clinical Study of Topotecan as Second-Line Treatment in Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Clinical Response to Etoposide Plus Carboplatin and Topotecan Chemotherapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Efficacy of Topotecan as a Second-Line Treatment of Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Patients with Refractory and Sensitive Disease: Retrospective Study
- A case of advanced ovarian cancer which was treated with topotecan after taxol-cisplatin treatment failed