Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Jun;64(6):439-444.
Diagnostic Approach to a Patient with a Pleural Effusion Including Ultrasound-guided Paracentesis Performed by a Medical Resident
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea. 0021yu@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Radiology, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
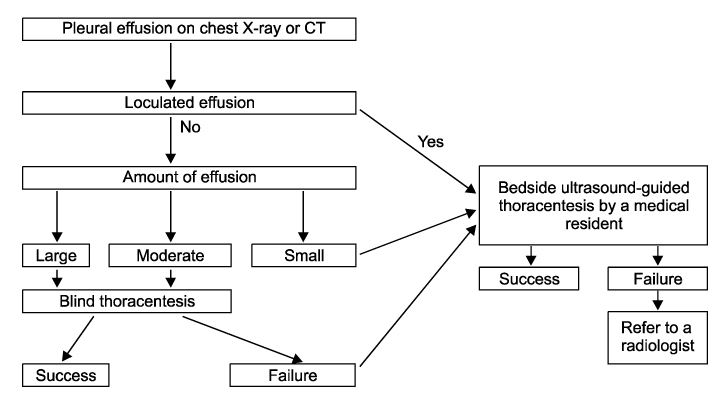
A patient with a pleural effusion that is difficult to safely drain by a "blind" thoracentesis procedure is generally referred to a radiologist for ultrasound-guided thoracentesis. But such a referral increases the cost and the patient's inconvenience, and it causes delay in the diagnostic procedures. If ultrasound-guided thoracentesis is performed as a bedside procedure by a medical resident, then this will reduce the previously mentioned problems. So these patients with pleural effusions were treated by medical residents at our medical center, and the procedures included bedside ultrasound-guided thoracenteses.
METHODS
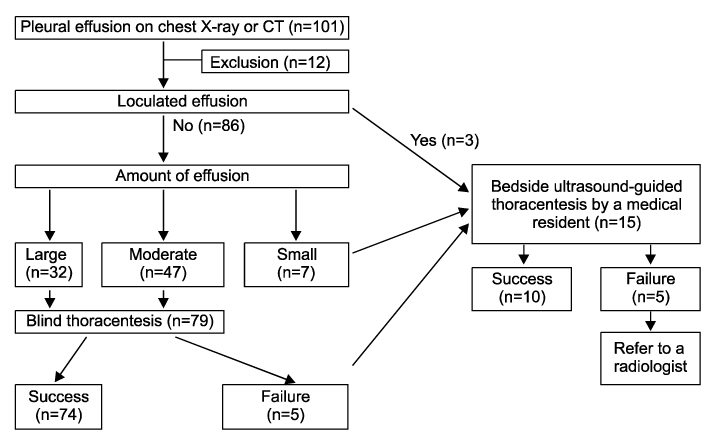
We studied 89 cases of pleural effusions from March 2003 to June 2005. A "blind" thoracentesis was performed if the amount of pleural effusion was moderate or large. Bedside ultrasound-guided thoracentesis was performed for small or loculated effusions or for the cases that failed with performing a "blind" thoracentesis.
RESULTS
"Blind" thoracenteses were performed in 79 cases that had a moderate or large amount of uncomplicated pleural effusions and the success rate was 93.7% (74/79 cases). Ultrasound-guided thoracentesis by the medical residents was performed in 15 cases and the success rate was 66.7% (10/15 cases). The 5 failedcases included all 3 cases with loculated effusions and 2 cases with a small amount of pleural effusion. All the failed cases were referred to one radiologist and they were then successfully treated. If we exclude the 3 cases with loculated pleural effusions, the success rate of ultrasound-guided thoracentesis by the medical residents increased up to 83% (10/12 cases). Two cases of complications (1 pneumothorax, 1 hydrohemothorax) occurred during ultrasound-guided thoracentesis.
CONCLUSION
Ultrasound-guided thoracentesis performed as a bedside procedure by a medical resident may be relatively effective and safe. If a patient has a loculated effusion, then it would be better to first refer the patient to a radiologist.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Light RW. Light RW, editor. Thoracocentesis and pleural biopsy. Pleural diseases. 2001. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;358–377.2. Grogan DR, Irwin RS, Channick R, Raptopoulos V, Curley FJ, Bartter T, et al. Complications associated with thoracentesis. A prospective, randomized study comparing three different methods. Arch Intern Med. 1990. 150:873–877.3. Seneff MG, Corwin RW, Gold LH, Irwin RS. Complications associated with thoracocentesis. Chest. 1986. 90:97–100.4. Aleman C, Alegre J, Armadans L, Andreu J, Falco V, Recio J, et al. The value of chest roentgenography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax after thoracentesis. Am J Med. 1999. 107:340–343.5. Collins TR, Sahn SA. Thoracocentesis. Clinical value, complications, technical problems, and patient experience. Chest. 1987. 91:817–822.6. Raptopoulos V, Davis LM, Lee G, Umali C, Lew R, Irwin RS. Factors affecting the development of pneumothorax associated with thoracentesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. 156:917–920.7. Lipscomb DJ, Flower CD, Hadfield JW. Ultrasound of the pleura: an assessment of its clinical value. Clin Radiol. 1981. 32:289–290.8. O'Moore PV, Mueller PR, Simeone JF, Saini S, Butch RJ, Hahn PF, et al. Sonographic guidance in diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the pleural space. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 149:1–5.9. Roth BJ, Cragun WH, Grathwohl KW. Complications associated with thoracentesis. Arch Intern Med. 1991. 151:2095–2096.10. Hirsch JH, Rogers JV, Mack LA. Real-time sonography of pleural opacities. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981. 136:297–301.11. Rozycki GS, Pennington SD, Feliciano DV. Surgeon-performed ultrasound in the critical care setting: its use as an extension of the physical examination to detect pleural effusion. J Trauma. 2001. 50:636–642.12. Weingardt JP, Guico RR, Nemcek AA Jr, Li YP, Chiu ST. Ultrasound findings following failed, clinically directed thoracenteses. J Clin Ultrasound. 1994. 22:419–426.13. Kohan JM, Poe RH, Israel RH, Kennedy JD, Benazzi RB, Kallay MC, et al. Value of chest ultrasonography versus decubitus roentgenography for thoracentesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986. 133:1124–1126.14. Diacon AH, Brutsche MH, Soler M. Accuracy of pleural puncture sites: a prospective comparison of clinical examination with ultrasound. Chest. 2003. 123:436–441.15. Jones PW, Moyers JP, Rogers JT, Rodriguez RM, Lee YC, Light RW. Ultrasound-guided thoracentesis: is it a safer method? Chest. 2003. 123:418–423.16. Feller-Kopman D. Ultrasound-guided thoracentesis. Chest. 2006. 129:1709–1714.17. Fishman AP, Elias JA, Fishman JA, Grippi MA, Kaiser LR, Senior RM. Fishman's pulmonary diseases and disorders. 1998. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc..18. Mason RJ, Broaddus VC, Murray JF, Nadel JA. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders.19. Park SR, Kim JH, Ha NR, Lee JH, Kim SH, Sohn JW, et al. Etiology and characteristics of massive pleural effusions investigated at one university hospital in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006. 61:456–462.20. Shin IC, Na MJ, Lee SW, Kim YJ, Park IW, Choi BW, et al. A Study on the relationship between number of thoracentesis and complication after thoracentesis in tuberculous pleurisy. Korean J Med. 1992. 42:290–296.21. Mayo PH, Doelken P. Pleural ultrasonography. Clin Chest Med. 2006. 27:215–227.22. Tu CY, Hsu WH, Hsia TC, Chen HJ, Tsai KD, Hung CW, et al. Pleural effusions in febrile medical ICU patients: chest ultrasound study. Chest. 2004. 126:1274–1280.23. Bartlett JG, Finegold SM. Anaerobic infections of the lung and pleural space. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974. 110:56–77.24. Bartter T, Mayo PD, Pratter MR, Santarelli RJ, Leeds WM, Akers SM. Lower risk and higher yield for thoracentesis when performed by experienced operators. Chest. 1993. 103:1873–1876.25. Petersen WG, Zimmerman R. Limited utility of chest radiograph after thoracentesis. Chest. 2000. 117:1038–1042.26. Brandstetter RD, Karetzky M, Rastogi R, Lolis JD. Pneumothorax after thoracentesis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Heart Lung. 1994. 23:67–70.