Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Dec;63(6):491-496.
The Effect of Repeated Education using a Computerized Scoring System for the Proper Use of Inhalation Medicine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. ghlee@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pharmacy, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Elderly Welfare, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The best way of delivering drugs for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is via the inhaled route of administration. However, many patients use inhaler devices incorrectly. To augment the proper use of inhalation medicine and to improve knowledge of the disease and compliance, we have developed a "Computerized Respiratory Service Program" and applied the use of this program to educate patients.
METHODS
Prospectively, this study was performed in 164 patients with asthma or COPD prescribed with inhaled medication. When inhalation medication was first prescribed, education using a drug model was conducted two times and thereafter every month. In addition, education using a drug model was conducted and the ability of the patient to use inhalation medicine properly was evaluated.
RESULTS
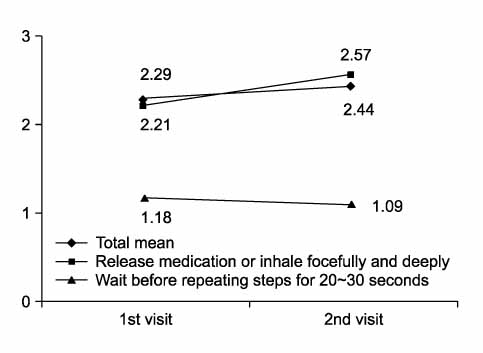
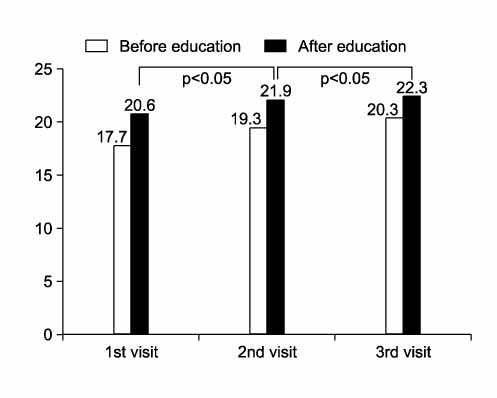
A total of 164 patients participated in the sessions more than two times and received education. Fifty-seven patients participated in three sesions. After the patients received education one time, the ability of these patients to use an inhaler had an average score of 20.6. After the patients received education two times, the average score was 21.9. After the patients received education three times, the average score was 22.3, a further increase. The compliance of using the inhaler was 70.1% at the second session and increased to 81.8% at the third session.
CONCLUSION
Feedback education using the "Computerized Respiratory Service Program" will increase the ability of the patient to use an inhaler and consistent education can maintain patient compliance with inhaler use.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cochrane MG, Bala MV, Downs KE, Mauskopf J, Ben-Joseph RH. Inhaled corticosteroids for asthma therapy: patient compliance, devices, and inhalation technique. Chest. 2000. 117:542–550.2. Molimard M, Raherison C, Lignot S, Depont F, Abouelfath A, Moore N. Assessment of handling of inhaler devices in real life: an observational study in 3,811 patients in primary care. J Aerosol Med. 2003. 16:249–254.3. Hesselink AE, Penninx BW, Wijnhoven HA, Kriegsman DM, van Eijk JT. Determinants of an incorrect inhalation technique in patients with asthma or COPD. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2001. 19:255–260.4. Hanania NA, Wittman R, Kesten S, Chapman KR. Medical personnel's knowledge of and ability to use inhaling devices. Metered-dose inhalers, spacing chambers, and breath-actuated dry powder inhalers. Chest. 1994. 105:111–116.5. Cochrane GM. Therapeutic compliance in asthma: its magnitude and implications. Eur Respir J. 1992. 5:122–124.6. Giraud V, Roche N. Misuse of corticosteroid metered-dose inhaler is associated with decreased asthma stability. Eur Respir J. 2002. 19:246–251.7. Newman SP, Weisz AW, Talaee N, Clarke SW. Improvement of drug delivery with a breath actuated pressurised aerosol for patients with poor inhaler technique. Thorax. 1991. 46:712–716.8. van Beerendonk I, Mesters I, Mudde AN, Tan TD. Assessment of the inhalation technique in outpatients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using a metered-dose inhaler or dry powder device. J Asthma. 1998. 35:273–279.9. Horsley MG, Bailie GR. Risk factors for inadequate use of pressurized aerosol inhalers. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1988. 13:139–143.10. Kamps AW, Brand PL, Roorda RJ. Determinants of correct inhalation technique in children attending a hospital-based asthma clinic. Acta Paediatr. 2002. 91:159–163.11. Tsang KW, Lam WK, Ip M, Kou M, Yam L, Lam B, et al. Inability of physicians to use metered-dose inhaler. J Asthma. 1997. 34:493–498.12. Gallefoss F, Bakke PS. How does patient education and self-management among asthmatics and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affect medication? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:2000–2005.13. van der Palen J, Klein J, Rovers M. Compliance with inhaled medication and self-treatment guidelines following a self-management programme in adult asthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1997. 10:652–657.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the inhalation performance in patients with asthma
- New Scoring System for Jebsen Hand Function Test
- Electrocardiographic Diagnosis of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy by Scoring System
- New Inhalation Anesthetics
- A new scoring system for differentiation between benign and malignant ovarian masses