Restor Dent Endod.
2013 Aug;38(3):146-153.
The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Restorative Science, University of Minnesota School of Dentistry, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
- 2Department of Conservative Dentistry, Pusan National University School of Dentistry and Institute of Translational Dental Sciences, Yangsan, Korea. golddent@pusan.ac.kr
- 3Process Development Team, Memory Division R&D Center, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Yongin, Korea.
- 4Department of Diagnostic and Biological Sciences, University of Minnesota School of Dentistry, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
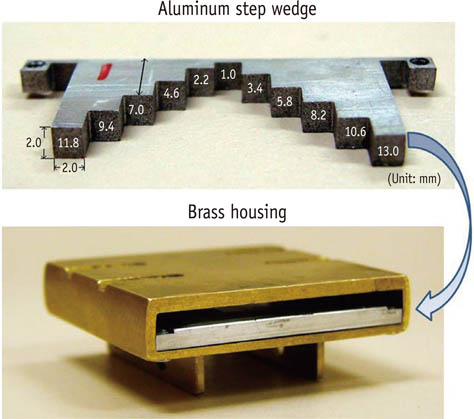
Aluminum step wedge (ASW) equivalent radiodensity (eRD) has been used to quantify restorative material's radiodensity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of image acquisition control (IAC) of a digital X-ray system on the radiodensity quantification under different exposure time settings.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
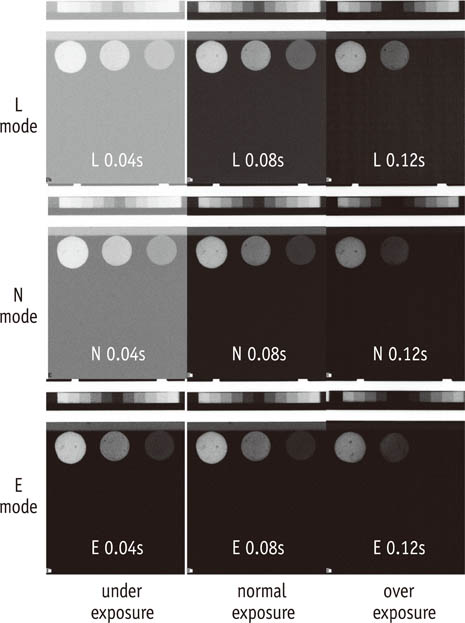
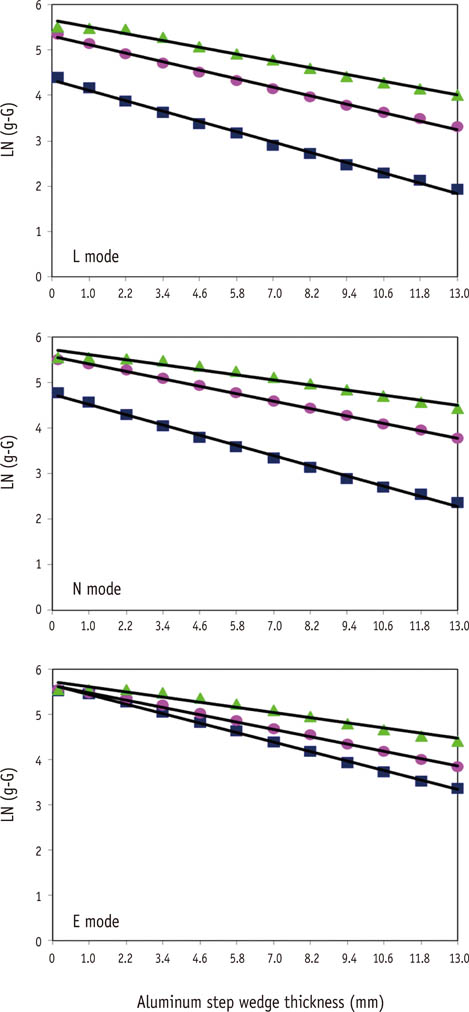
Three 1-mm thick restorative material samples with various opacities were prepared. Samples were radiographed alongside an ASW using one of three digital radiographic modes (linear mapping (L), nonlinear mapping (N), and nonlinear mapping and automatic exposure control activated (E)) under 3 exposure time settings (underexposure, normal-exposure, and overexposure). The ASW eRD of restorative materials, attenuation coefficients and contrasts of ASW, and the correlation coefficient of linear relationship between logarithms of gray-scale value and thicknesses of ASW were compared under 9 conditions.
RESULTS
The ASW eRD measurements of restorative materials by three digital radiographic modes were statistically different (p = 0.049) but clinically similar. The relationship between logarithms of background corrected grey scale value and thickness of ASW was highly linear but attenuation coefficients and contrasts varied significantly among 3 radiographic modes. Varying exposure times did not affect ASW eRD significantly.
CONCLUSIONS
Even though different digital radiographic modes induced large variation on attenuation of coefficient and contrast of ASW, E mode improved diagnostic quality of the image significantly under the under-exposure condition by improving contrasts, while maintaining ASW eRDs of restorative materials similar. Under the condition of this study, underexposure time may be acceptable clinically with digital X-ray system using automatic gain control that reduces radiation exposure for patient.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wenzel A, Gröndahl HG. Direct digital radiography in the dental office. Int Dent J. 1995; 45:27–34.2. Nomoto R, Mishima A, Kobayashi K, McCabe JF, Darvell BW, Watts DC, Momoi Y, Hirano S. Quantitative determination of radio-opacity: equivalence of digital and film X-ray systems. Dent Mater. 2008; 24:141–147.
Article3. Schick Technologies. CDR DICOM quick start guide. Long Island City: Schick Technologies, Inc.;2004.4. Uffmann M, Schaefer-Prokop C. Digital radiography: the balance between image quality and required radiation dose. Eur J Radiol. 2009; 72:202–208.
Article5. ISO 4049 Dentistry - polymer-based filling, restorative and luting materials. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization;1998.6. ISO-Standards ISO 9917 Dentistry-water-based cements. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization;1998. p. 1–23.7. Nickoloff EL, Dutta AK, Lu ZF. Influence of phantom diameter, kVp and scan mode upon computed tomography dose index. Med Phys. 2003; 30:395–402.
Article8. Rasimick BJ, Shah RP, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. Radiopacity of endodontic materials on film and a digital sensor. J Endod. 2007; 33:1098–1101.
Article9. Sabbagh J, Vreven J, Leloup G. Radiopacity of resin based materials in film radiographs and storage phosphor plate (Diagora). Oper Dent. 2004; 29:677–684.10. Baksi BG, Sen BH, Eyuboglu TF. Differences in aluminum equivalent values of endodontic sealers: conventional versus digital radiography. J Endod. 2008; 34:1101–1104.
Article11. Gu S, Rasimick BJ, Deutsch AS, Musikant BL. Radiopacity of dental materials using a digital X-ray system. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:765–770.
Article12. Rasimick BJ, Gu S, Deutsch AS, Musikant BL. Measuring the radiopacity of luting cements, dowels, and core build-up materials with a digital radiography system using a CCD sensor. J Prosthodont. 2007; 16:357–364.
Article13. Yang J, Chiou R, Ruprecht A, Vicario J, MacPhail LA, Rams TE. A new device for measuring density of jaw bones. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2002; 31:313–316.
Article14. Southard TE, Wunderle DM, Southard KA, Jakobsen JR. Geometric and densitometric standardization of intraoral radiography through use of a modified XCP system. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999; 87:253–257.
Article15. Kitagawa H, Scheetz JP, Farman AG. Comparison of complementary metal oxide semiconductor and charge-coupled device intraoral X-ray detectors using subjective image quality. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2003; 32:408–411.
Article16. Schulze D, Rother UJ, Fuhrmann AW, Tietke M. A comparison of two intraoral CCD sensor systems in terms of image quality and interobserver agreement. Int J Comput Dent. 2003; 6:141–150.17. Benediktsdottir IS, Hintze H, Petersen JK, Wenzel A. Image quality of two solid-state and three photostimulable phosphor plate digital panoramic systems, and treatment planning of mandibular third molar removal. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2003; 32:39–44.
Article18. Walsh C, Gorman D, Byrne P, Larkin A, Dowling A, Malone JF. Quality assurance of computed and digital radiography systems. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2008; 129:271–275.
Article19. Chantler CT, Olsen K, Dragoset RA, Chang J, Kishore AR, Kotochigova SA, Zucker DS. X-Ray Form Factor, Attenuation and Scattering Tables (version 2.1). [Online]. Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology;Available: http://physics.nist.gov/ffast [Monday, 29-Jul-2013 23:22:42 EDT]. Originally published as Chantler CT. J Phys Chem Ref Data 2000;29:597-1048.20. Brooks RA, Di Chiro G. Beam hardening in x-ray reconstructive tomography. Phys Med Biol. 1976; 21:390–398.
Article21. Cho JY, Han WJ. The reduction methods of operator's radiation dose for portable dental X-ray machines. Restor Dent Endod. 2012; 37:160–164.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Digital X-ray Imaging in Dentistry
- The ability of panoramic radiography in assessing maxillary sinus inflammatory diseases
- The Predictability of Stone Composition According to the Radiodensity of Urinary Stone on KUB Film
- Applications of Artificial Intelligence in MR Image Acquisition and Reconstruction
- Nuclear Medical Physics – A Review of an Advanced Technology