Restor Dent Endod.
2012 May;37(2):110-113.
Re-establishment of occlusion after unilateral condylar fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. operatys16@yuhs.ac
Abstract
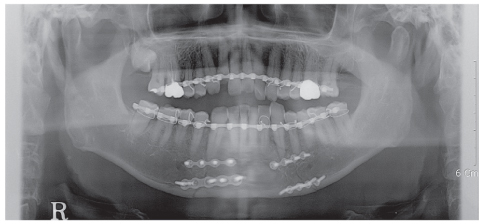
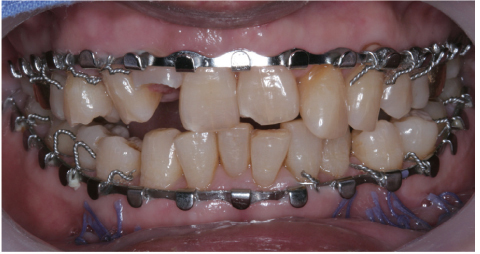
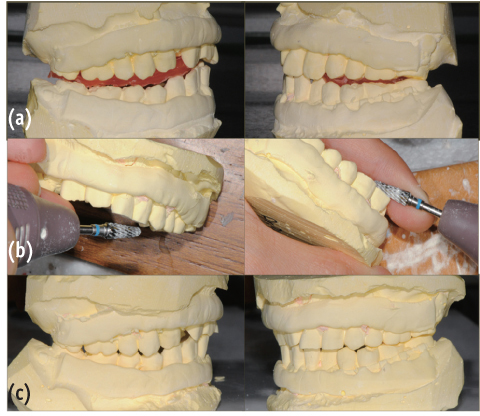
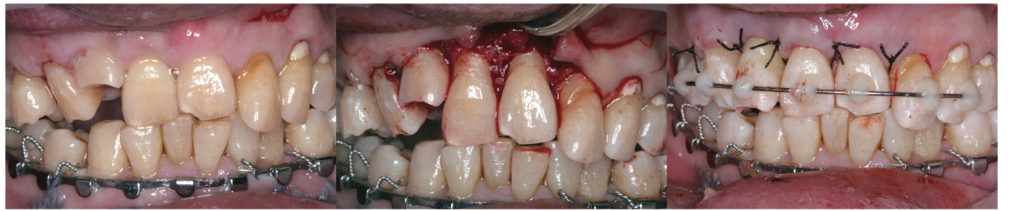
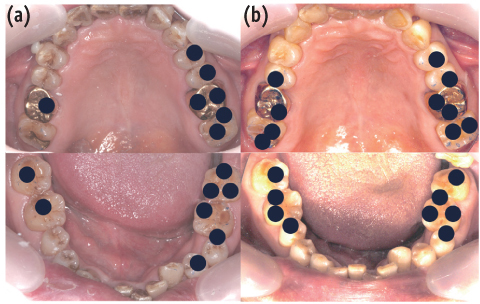
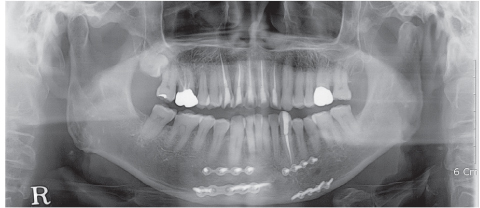
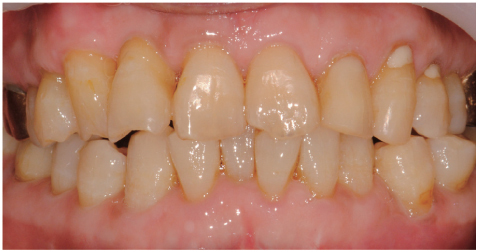
- Complications resulting from condylar fracture include occlusal disturbance due to loss of leverage from temporomandibular joint (TMJ). In general, closed reduction with active physical training has been performed, and under favorable circumstances, adaptation occurs in attempt to restore the articulation. The patient in this case report had unilateral condylar fracture accompanied with multiple teeth injuries, but he was left without any dental treatment for 1 mon which led to unrestorable occlusal collapse. Fortunately, delayed surgical repositioning of dislocated maxillary anterior teeth followed by consistent long-term physical training has been proved successful. Normal occlusion and satisfactory remodeling of condyle were obtained on 10 mon follow-up.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Medina AC. Functional appliance treatment for bilateral condylar fracture in a pediatric patient. Pediatr Dent. 2009. 31:432–437.2. Ellis E, Throckmorton GS. Treatment of mandibular condylar process fractures: biological considerations. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005. 63:115–134.
Article3. Talwar RM, Ellis E 3rd, Throckmorton GS. Adaptations of the masticatory system after bilateral fractures of the mandibular condylar process. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998. 56:430–439.
Article4. Villarreal PM, Monje F, Junquera LM, Mateo J, Morillo AJ, González C. Mandibular condyle fractures: determinants of treatment and outcome. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004. 62:155–163.
Article5. Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM, Skeie A, Hjørting-Hansen E, Schwartz O. Effect of treatment delay upon pulp and periodontal healing of traumatic dental injuries - a review article. Dent Traumatol. 2002. 18:116–128.
Article6. Miyashin M, Kato J, Takagi Y. Tissue reactions after experimental luxation injuries in immature rat teeth. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1991. 7:26–35.
Article7. Trombelli L, Farina R, Marzola A, Bozzi L, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J. Modeling and remodeling of human extraction sockets. J Clin Periodontol. 2008. 35:630–639.
Article8. Murakami K, Yamamoto K, Sugiura T, Yamanaka Y, Kirita T. Changes in mandibular movement and occlusal condition after conservative treatment for condylar fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. 67:83–91.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Modified high-submandibular appraoch for open reduction and internal fixation of condylar fracture: case series report
- T-Condylar Fracture of Distal Humerus in a Child: A Case Report
- Intracorporeal reduction of condylar fracture using both pedicled condylar and seperated ramal fragments after vertical ramal osteotomy
- A Case Report Of Facial Asymmetry From Unilateral Condylar Hyperplasia
- Condylar ankylosis: Unilateral posttraumatic condylar pseudoankylosis