Korean J Urol.
2012 Nov;53(11):766-773.
Our Experiences with Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy: Orthotopic Neobladder by the Suprapubic Incision Method
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. uroyglee@hallym.or.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report our technique for and experience with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy (RARC) with orthotopic neobladder (ON) formation in a cohort of bladder cancer patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
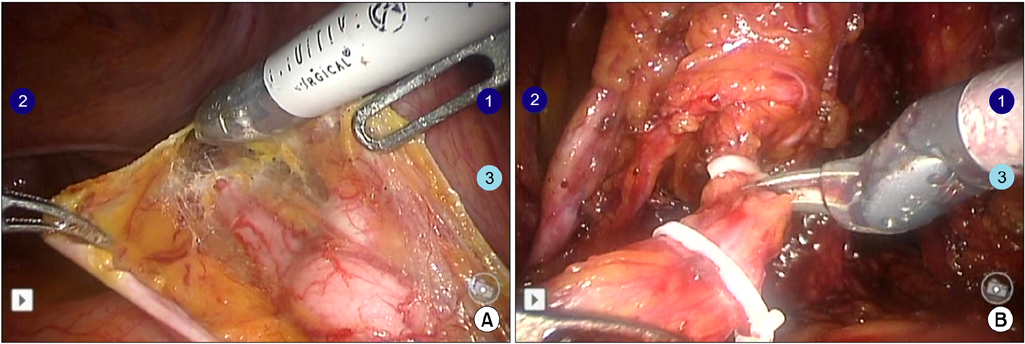
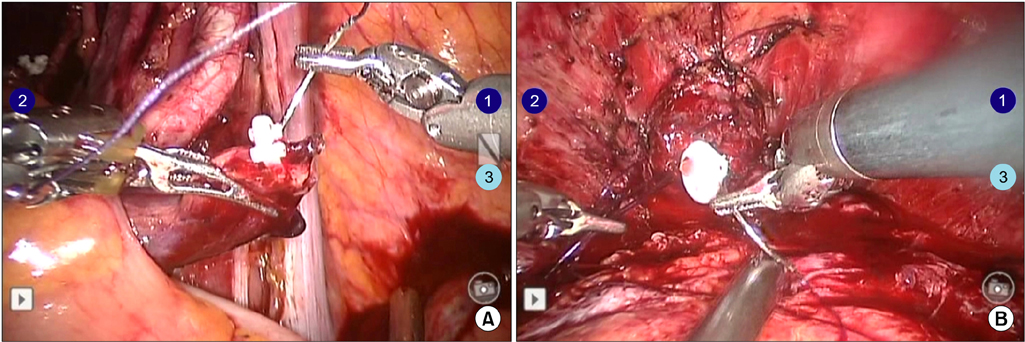
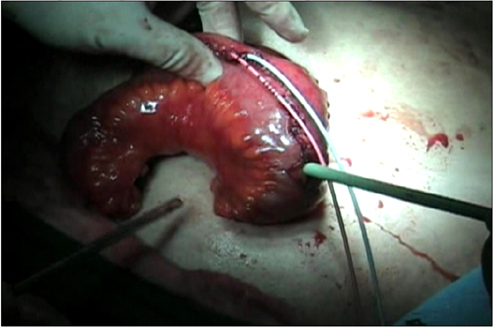
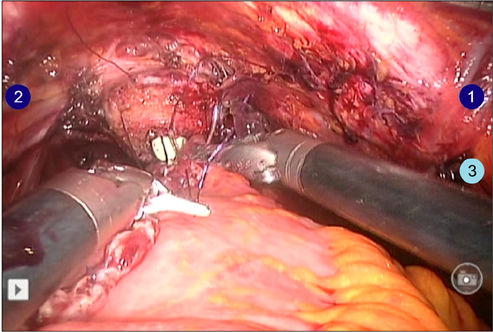
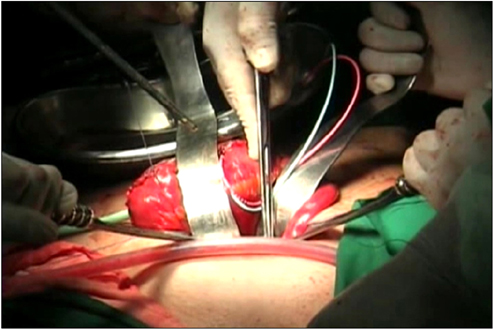
Between December 2007 and December 2011, a total of 35 patients underwent RARC. The patients' mean age was 63.3 years and their mean body mass index was 23.7 kg/m2. Thirty patients had a clinical stage of T2 or higher. Postoperative mean follow-up duration was 25.5 months. In 5 patients, a 4-cm midline infraumbilical skin incision was made for an ileal conduit (IC) and the stoma formation was similar to the open procedure. In 30 patients undergoing the ON procedure, the skin for specimen removal and extracorporeal enterocystoplasty was incised infraumbilically in the early 5 cases with redocking (ON-I) and suprapubically in the latter 25 cases without redocking (ON-S).
RESULTS
The mean operative times of the IC, ON-I, and ON-S groups were 442.5, 646.0, and 531.3 minutes, respectively (p=0.001). Mean console and lymph node dissection time were not significantly different between the groups. Mean urinary diversion times in each group were 68.8, 125.0, and 118.8 minutes, respectively (p=0.001). In the comparison between the ON-I and ON-S group, only operative time was significant. Four patients required a blood transfusion. We had no cases of intraabdominal organ injury or open conversion. Thiry-three patients (94.2%) had a pathologic stage of T2 or higher. Two patients (5.7%) had lymph node-positive disease. Postoperative complications included ileus (n=4), stricture in the uretero-ileal junction (n=2), and vesicovaginal fistula (n=1).
CONCLUSIONS
Our robotic neobladder-suprapubic incision without redocking procedure is easier and more rapid than that of infraumbilical incision with redocking.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herr HW, Bochner BH, Dalbagni G, Donat SM, Reuter VE, Bajorin DF. Impact of the number of lymph nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Urol. 2002. 167:1295–1298.2. Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng AC, Boyd S, et al. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:666–675.3. Konety BR, Allareddy V, Herr H. Complications after radical cystectomy: analysis of population-based data. Urology. 2006. 68:58–64.4. Novotny V, Hakenberg OW, Wiessner D, Heberling U, Litz RJ, Oehlschlaeger S, et al. Perioperative complications of radical cystectomy in a contemporary series. Eur Urol. 2007. 51:397–401.5. Finelli A, Gill IS, Desai MM, Moinzadeh A, Magi-Galluzzi C, Kaouk JH. Laparoscopic extended pelvic lymphadenectomy for bladder cancer: technique and initial outcomes. J Urol. 2004. 172(5 Pt 1):1809–1812.6. Basillote JB, Abdelshehid C, Ahlering TE, Shanberg AM. Laparoscopic assisted radical cystectomy with ileal neobladder: a comparison with the open approach. J Urol. 2004. 172:489–493.7. Haber GP, Colombo JR Jr, Aron M, Ukimura O, Gill IS. Laparoscopic radical cystectomy and urinary diversion: status in 2006. Eur Urol Suppl. 2006. 5:950–955.8. Davis JW, Castle EP, Pruthi RS, Ornstein DK, Guru KA. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy: an expert panel review of the current status and future direction. Urol Oncol. 2010. 28:480–486.9. Kasraeian A, Barret E, Cathelineau X, Rozet F, Galiano M, Sanchez-Salas R, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic cystoprostatectomy with extended pelvic lymphadenectomy, extracorporeal enterocystoplasty, and intracorporeal enterourethral anastomosis: initial Montsouris experience. J Endourol. 2010. 24:409–413.10. Kwon SY, Kim BS, Kim TH, Yoo ES, Kwon TG. Initial experiences with robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy. Korean J Urol. 2010. 51:178–182.11. Park SY, Cho KS, Ham WS, Choi HM, Hong SJ, Rha KH. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy with ileal conduit urinary diversion: initial experience in Korea. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2008. 18:401–404.12. Pruthi RS, Stefaniak H, Hubbard JS, Wallen EM. Robot-assisted laparoscopic anterior pelvic exenteration for bladder cancer in the female patient. J Endourol. 2008. 22:2397–2402.13. Reich DL, Hossain S, Krol M, Baez B, Patel P, Bernstein A, et al. Predictors of hypotension after induction of general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2005. 101:622–628.14. Zmora O, Mahajna A, Bar-Zakai B, Rosin D, Hershko D, Shabtai M, et al. Colon and rectal surgery without mechanical bowel preparation: a randomized prospective trial. Ann Surg. 2003. 237:363–367.15. Brownson P, Jenkins SA, Nott D. Mechanical bowel preparation before colorectal surgery: results of a prospective randomized trial. Br J Surg. 1992. 79:461–462.16. Menon M, Hemal AK, Tewari A, Shrivastava A, Shoma AM, Abol-Ein H, et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy and urinary diversion in female patients: technique with preservation of the uterus and vagina. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. 198:386–393.17. Lee YS, Han WK, Oh YT, Choi YD, Yang SC, Rha KH. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: four cases. Yonsei Med J. 2007. 48:341–346.18. Beecken WD, Wolfram M, Engl T, Bentas W, Probst M, Blaheta R, et al. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy and intra-abdominal formation of an orthotopic ileal neobladder. Eur Urol. 2003. 44:337–339.19. Hemal AK, Abol-Enein H, Tewari A, Shrivastava A, Shoma AM, Ghoneim MA, et al. Robotic radical cystectomy and urinary diversion in the management of bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2004. 31:719–729. viii20. Hemal AK, Kolla SB, Wadhwa P. First case series of robotic radical cystoprostatectomy, bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy and urinary diversion with da vinci-s system. J Robot Surg. 2008. 2:35–40.21. Hall MC, Chang SS, Dalbagni G, Pruthi RS, Seigne JD, Skinner EC, et al. Guideline for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (stages Ta, T1, and Tis): 2007 update. J Urol. 2007. 178:2314–2330.22. Lee KL, Freiha F, Presti JC Jr, Gill HS. Gender differences in radical cystectomy: complications and blood loss. Urology. 2004. 63:1095–1099.23. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004. 240:205–213.24. Pruthi RS, Nielsen ME, Nix J, Smith A, Schultz H, Wallen EM. Robotic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: surgical and pathological outcomes in 100 consecutive cases. J Urol. 2010. 183:510–514.25. Shabsigh A, Korets R, Vora KC, Brooks CM, Cronin AM, Savage C, et al. Defining early morbidity of radical cystectomy for patients with bladder cancer using a standardized reporting methodology. Eur Urol. 2009. 55:164–174.26. Sala LG, Matsunaga GS, Corica FA, Ornstein DK. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystoprostatectomy and totally intracorporeal ileal neobladder. J Endourol. 2006. 20:233–235.27. Cathelineau X, Jaffe J. Laparoscopic radical cystectomy with urinary diversion: what is the optimal technique? Curr Opin Urol. 2007. 17:93–97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy with Orthotopic Ileal W-neobladder
- Comparison of the Complications and Urodynamic Parameters for Orthotopic Bladder Substitution with using Ileocolic or Ileal Segments after Radical Cystectomy
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy
- A Case of Neobladder Rupture Following Blunt Trauma
- Delayed Spontaneous Rupture of an Orthotopic Ileal Neobladder