Korean J Urol.
2013 Jan;54(1):15-21.
Impact of Prostate Volume on Oncological and Functional Outcomes After Radical Prostatectomy: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Versus Open Retropubic
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. mdrafael@snu.ac.kr
- 2Departement of Urology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We compared the impact of prostate volume on oncological and functional outcomes 2 years after robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) and open radical retropubic prostatectomy (ORP).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between 2003 and 2010, 253 consecutive patients who had undergone prostatectomy by a single surgeon were serially followed over 2 years postoperatively. RALP was performed on 77 patients and ORP on 176. The patients were divided into two subgroups according to prostate volume as measured by transrectal ultrasound: less than 40 g and 40 g or larger. Recoveries of potency and continence were checked serially by interview 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months postoperatively.
RESULTS
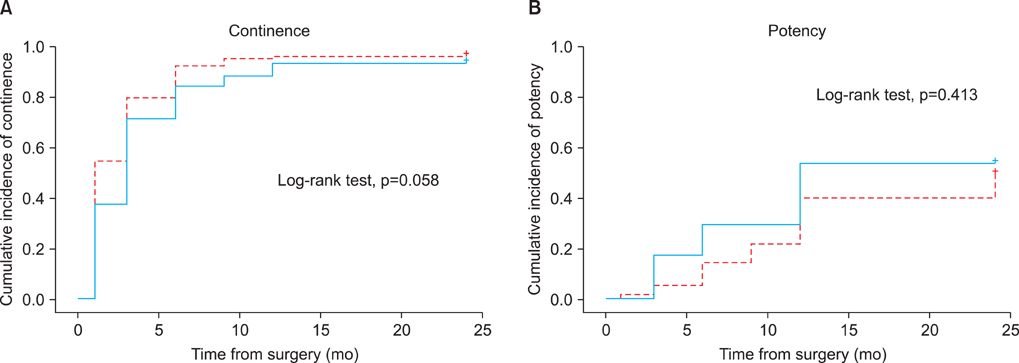
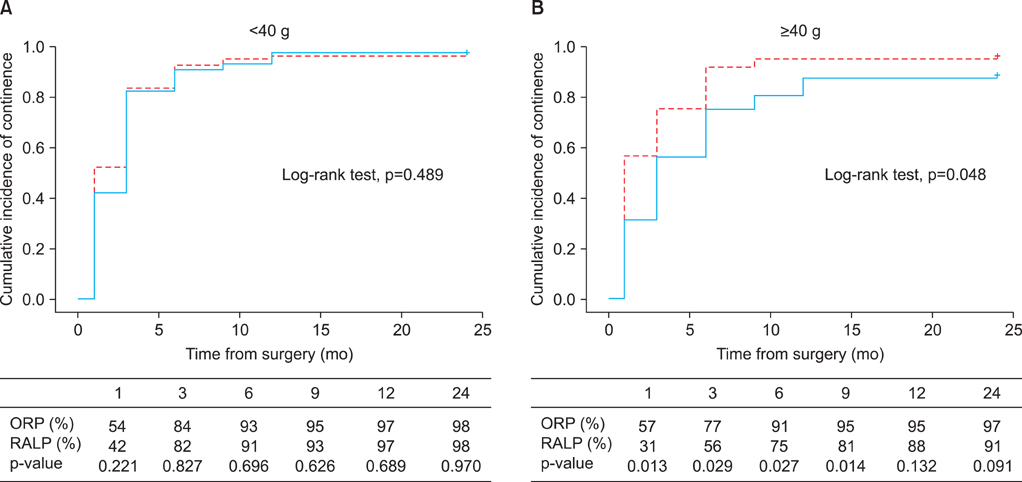
RALP was associated with less blood loss (ORP vs. RALP: 910 mL vs. 640 mL, p<0.001) but a longer operation time (150 minutes vs. 220 minutes, p<0.001) than was ORP. No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups for oncological outcomes, such as positive surgical margin (40% vs. 39%, p=0.911) or biochemical recurrence (12% vs. 7%, p=0.155). The overall functional outcomes showed no statistically significant differences at 2 years of follow-up (continence: 97% vs. 94%, p=0.103; potency: 51% vs. 56%, p=0.614). In the results of an inter-subgroup analysis, potency recovery was more rapid in patients who underwent RALP in a small-volume prostate than in those who underwent ORP in a small-volume prostate (3 months: 24% vs. 0%, p=0.005; 6 months: 36% vs. 10%, p=0.024). However, patients who underwent RALP in a large-volume prostate were less likely to recover continence than were patients who underwent ORP in a large-volume prostate (97% vs. 88%, p=0.025).
CONCLUSIONS
Patients can be expected to recover erectile function more quickly after RALP than after ORP, especially in cases of a small prostate volume.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Cancer Information Center [Internet]. c2011. cited 2012 May 2. Goyang (KR): National Cancer Information Center;Available from: http://www.cancer.go.kr/ncic/.2. Fracalanza S, Ficarra V, Cavalleri S, Galfano A, Novara G, Mangano A, et al. Is robotically assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy less invasive than retropubic radical prostatectomy? Results from a prospective, unrandomized, comparative study. BJU Int. 2008. 101:1145–1149.3. Finkelstein J, Eckersberger E, Sadri H, Taneja SS, Lepor H, Djavan B. Open versus laparoscopic versus robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: the European and US experience. Rev Urol. 2010. 12:35–43.4. Duffey B, Varda B, Konety B. Quality of evidence to compare outcomes of open and robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Curr Urol Rep. 2011. 12:229–236.5. Tewari A, Srivasatava A, Menon M. Members of the VIP Team. A prospective comparison of radical retropubic and robot-assisted prostatectomy: experience in one institution. BJU Int. 2003. 92:205–210.6. Ficarra V, Cavalleri S, Novara G, Aragona M, Artibani W. Evidence from robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2007. 51:45–55.7. Ficarra V, Novara G, Fracalanza S, D'Elia C, Secco S, Iafrate M, et al. A prospective, non-randomized trial comparing robot-assisted laparoscopic and retropubic radical prostatectomy in one European institution. BJU Int. 2009. 104:534–539.8. Hu JC, Gu X, Lipsitz SR, Barry MJ, D'Amico AV, Weinberg AC, et al. Comparative effectiveness of minimally invasive vs open radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 2009. 302:1557–1564.9. Hsu EI, Hong EK, Lepor H. Influence of body weight and prostate volume on intraoperative, perioperative, and postoperative outcomes after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Urology. 2003. 61:601–606.10. D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Tomaszewski JE, Wein A. A prostate gland volume of more than 75 cm3 predicts for a favorable outcome after radical prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer. Urology. 1998. 52:631–636.11. Ahlering TE, Kaplan AG, Yee DS, Skarecky DW. Prostate weight and early potency in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2008. 72:1263–1268.12. Ficarra V, Novara G, Artibani W, Cestari A, Galfano A, Graefen M, et al. Retropubic, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and cumulative analysis of comparative studies. Eur Urol. 2009. 55:1037–1063.13. Schroeck FR, Sun L, Freedland SJ, Albala DM, Mouraviev V, Polascik TJ, et al. Comparison of prostate-specific antigen recurrence-free survival in a contemporary cohort of patients undergoing either radical retropubic or robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2008. 102:28–32.14. Krambeck AE, DiMarco DS, Rangel LJ, Bergstralh EJ, Myers RP, Blute ML, et al. Radical prostatectomy for prostatic adenocarcinoma: a matched comparison of open retropubic and robot-assisted techniques. BJU Int. 2009. 103:448–453.15. Sooriakumaran P, Haendler L, Nyberg T, Gronberg H, Nilsson A, Carlsson S, et al. Biochemical recurrence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in a European single-centre cohort with a minimum follow-up time of 5 years. Eur Urol. 2012. 62:768–774.16. Rozet F, Jaffe J, Braud G, Harmon J, Cathelineau X, Barret E, et al. A direct comparison of robotic assisted versus pure laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a single institution experience. J Urol. 2007. 178:478–482.17. Rocco B, Matei DV, Melegari S, Ospina JC, Mazzoleni F, Errico G, et al. Robotic vs open prostatectomy in a laparoscopically naive centre: a matched-pair analysis. BJU Int. 2009. 104:991–995.18. Tewari A, Peabody JO, Fischer M, Sarle R, Vallancien G, Delmas V, et al. An operative and anatomic study to help in nerve sparing during laparoscopic and robotic radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:444–454.19. Zorn KC, Orvieto MA, Mikhail AA, Gofrit ON, Lin S, Schaeffer AJ, et al. Effect of prostate weight on operative and postoperative outcomes of robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. Urology. 2007. 69:300–305.20. Link BA, Nelson R, Josephson DY, Yoshida JS, Crocitto LE, Kawachi MH, et al. The impact of prostate gland weight in robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2008. 180:928–932.21. Menon M, Tewari A, Baize B, Guillonneau B, Vallancien G. Prospective comparison of radical retropubic prostatectomy and robot-assisted anatomic prostatectomy: the Vattikuti Urology Institute experience. Urology. 2002. 60:864–868.22. Malcolm JB, Fabrizio MD, Barone BB, Given RW, Lance RS, Lynch DF, et al. Quality of life after open or robotic prostatectomy, cryoablation or brachytherapy for localized prostate cancer. J Urol. 2010. 183:1822–1828.23. Abbou CC, Salomon L, Hoznek A, Antiphon P, Cicco A, Saint F, et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: preliminary results. Urology. 2000. 55:630–634.24. Joseph JV, Vicente I, Madeb R, Erturk E, Patel HR. Robot-assisted vs pure laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: are there any differences? BJU Int. 2005. 96:39–42.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Radical Prostatectomy
- Advantages of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy in Obese Patients: Comparison with the Open Procedure
- Erratum: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- A Case of Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy in Primary Small Cell Prostate Cancer