J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 Jul;59(4):420-424. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.4.420.
Novalis Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Brain Tumor Institute, Novalis Stereotactic Radiosurgery Center, Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. kukim@donga.ac.kr
- KMID: 2315983
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.4.420
Abstract
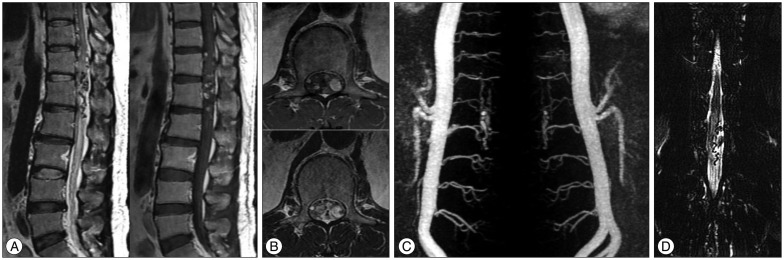
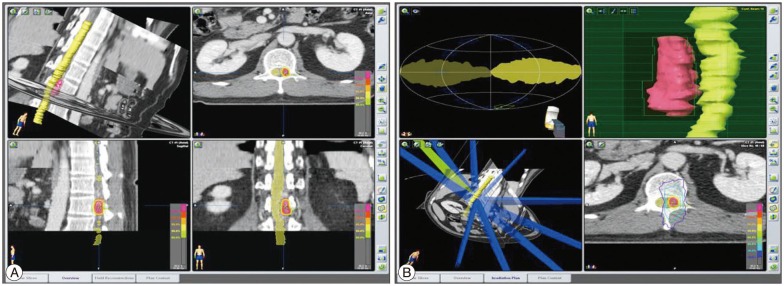
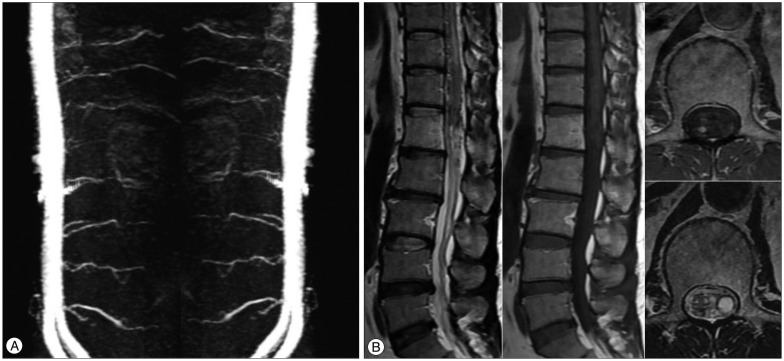
- The spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (SDAVF) is rare, presenting with progressive, insidious symptoms, and inducing spinal cord ischemia and myelopathy, resulting in severe neurological deficits. If physicians have accurate and enough information about vascular anatomy and hemodynamics, they achieve the good results though the surgery or endovascular embolization. However, when selective spinal angiography is unsuccessful due to neurological deficits, surgery and endovascular embolization might be failed because of inadequate information. We describe a patient with a history of vasospasm during spinal angiography, who was successfully treated by spinal stereotactic radiosurgery using Novalis system.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akakin A, Ozkan A, Akgun E, Koc DY, Konya D, Pamir MN, et al. Endovascular treatment increases but gamma knife radiosurgery decreases angiogenic activity of arteriovenous malformations : an in vivo experimental study using a rat cornea model. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66:121–129. discussion 129-130. PMID: 20023542.2. Boeckh-Behrens T, Bitterling H, Schichor C, Brückmann H, Seelos K. [Improved localization of spinal AV fistulas using contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3 T]. Rofo. 2010; 182:53–57. PMID: 19517337.3. Cao JB, Cui LL, Jiang XY, Gao SJ, Sun WG, Xu K. Clinical application and diagnostic value of noninvasive spinal angiography in spinal vascular malformations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014; 38:474–479. PMID: 24681867.
Article4. Dalyai RT, Ghobrial G, Chalouhi N, Dumont AS, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, et al. Radiosurgery for dural arterio-venous fistulas : a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:512–516. PMID: 23481896.5. Dehdashti AR, Da Costa LB, terBrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Tymianski M, Wallace MC. Overview of the current role of endovascular and surgical treatment in spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 26:E8. PMID: 19119894.
Article6. Donghai W, Ning Y, Peng Z, Shuo X, Xueen L, Peng Z, et al. The diagnosis of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E546–E553. PMID: 23380827.
Article7. Gao P, Chen Y, Lawton MT, Barbaro NM, Yang GY, Su H, et al. Evidence of endothelial progenitor cells in the human brain and spinal cord arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:1029–1035. PMID: 20881566.
Article8. Grunwald I, Thron A, Reith W. [Spinal angiography : vascular anatomy, technique and indications]. Radiologe. 2001; 41:961–967. PMID: 11765537.9. Jahan R, Solberg TD, Lee D, Medin P, Tateshima S, De Salles A, et al. An arteriovenous malformation model for stereotactic radiosurgery research. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:152–159. discussion 159. PMID: 17621031.
Article10. Kikuchi Y, Miyasaka K. Treatment strategy of spinal arteriovenous malformations based on a simple classification. J Clin Neurosci. 5(Suppl):1998; 16–19. PMID: 18639093.
Article11. Kirkpatrick JP, van der Kogel AJ, Schultheiss TE. Radiation dose-volume effects in the spinal cord. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76(3 Suppl):S42–S49. PMID: 20171517.
Article12. Luetmer PH, Lane JI, Gilbertson JR, Bernstein MA, Huston J 3rd, Atkinson JL. Preangiographic evaluation of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas with elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR angiography and effect on radiation dose and volume of iodinated contrast material. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:711–718. PMID: 15814910.13. Marcus J, Schwarz J, Singh IP, Sigounas D, Knopman J, Gobin YP, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas : a review. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013; 15:335. PMID: 23666862.14. Milano MT, Usuki KY, Walter KA, Clark D, Schell MC. Stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy : normal tissue dose constraints of the central nervous system. Cancer Treat Rev. 2011; 37:567–578. PMID: 21571440.
Article15. Mull M, Nijenhuis RJ, Backes WH, Krings T, Wilmink JT, Thron A. Value and limitations of contrast-enhanced MR angiography in spinal arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:1249–1258. PMID: 17698524.
Article16. Oumerzouk J, Jouehari A, Hssaini Y, Raggabi A, Bourazza A. Sudden worsening of paraparesis complicating dorsal dural arteriovenous fistula after spinal angiography : case report and review of literature. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2013; 169:356–358. PMID: 23465839.
Article17. Park KW, Park SI, Im SB, Kim BT. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula with supply from the lateral sacral artery-case report and review of literature-. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 45:115–117. PMID: 19274124.
Article18. Rashad S, Abdel-Bary M, Aziz W, Hassan T. Management of spinal dural arterio-venous fistulas. Report of 12 cases and review of literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2014; 125:81–86. PMID: 25108697.
Article19. Reith W, Kettner M, Simgen A, Yilmaz U. [Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas : diagnostics and therapy]. Radiologe. 2012; 52:437–441. PMID: 22584480.20. Saindane AM, Boddu SR, Tong FC, Dehkharghani S, Dion JE. Contrast-enhanced time-resolved MRA for pre-angiographic evaluation of suspected spinal dural arterial venous fistulas. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 7:135–140. PMID: 24463440.
Article21. Saraf-Lavi E, Bowen BC, Quencer RM, Sklar EM, Holz A, Falcone S, et al. Detection of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae with MR imaging and contrast-enhanced MR angiography : sensitivity, specificity, and prediction of vertebral level. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:858–867. PMID: 12006294.22. Steiger HJ, Hänggi D, Schmid-Elsaesser R. Cranial and spinal dural arteriovenous malformations and fistulas : an update. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005; 94:115–122. PMID: 16060250.23. Steinmetz MP, Chow MM, Krishnaney AA, Andrews-Hinders D, Benzel EC, Masaryk TJ, et al. Outcome after the treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae : a contemporary single-institution series and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2004; 55:77–87. discussion 87-88. PMID: 15214976.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistula
- Stereotactic radiosurgery as an alternative treatment for dural arteriovenous fistula
- Endovascular Treatment of Spinal Dural and Epidural Arteriovenous Fistula as Complication of Lumbar Surgery
- Radiosurgery for Spinal Lesions
- Syringomyelia Associated with Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Clinical and Radiological Improvement after Embolization