J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 Jul;59(4):392-399. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.4.392.
Clinical Outcomes of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors from Gynecologic Cancer : Prognostic Factors in Local Treatment Failure and Survival
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ykwon@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2315976
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.4.392
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Brain metastases in gynecologic cancer (ovarian, endometrial, and cervical cancer) patients are rare, and the efficacy of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS) to treat these had not been evaluated. We assessed the efficacy of GKRS and prognostic factors for tumor control and survival in brain metastasis from gynecologic cancers.
METHODS
This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board. From May 1995 to October 2012, 26 women (mean age 51.3 years, range 27-70 years) with metastatic brain tumors from gynecologic cancer were treated with GKRS. We reviewed their outcomes, radiological responses, and clinical status.
RESULTS
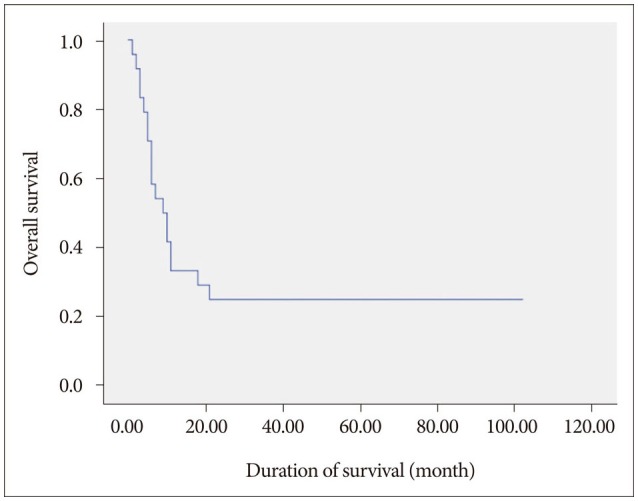
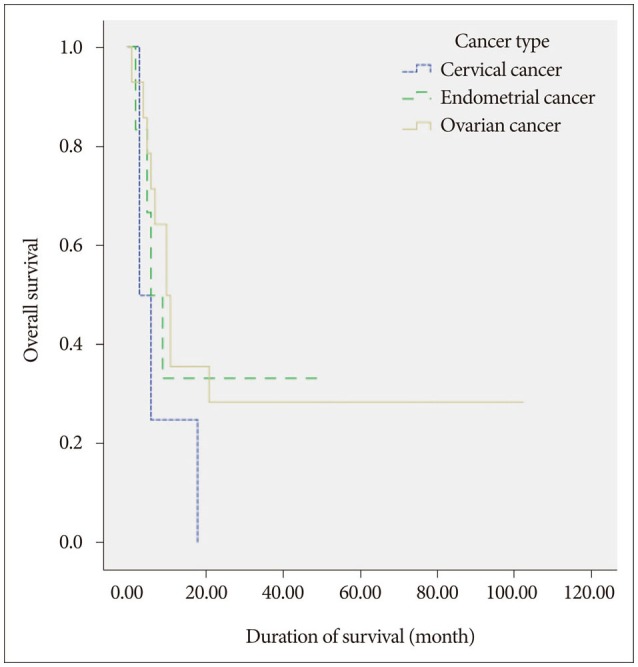
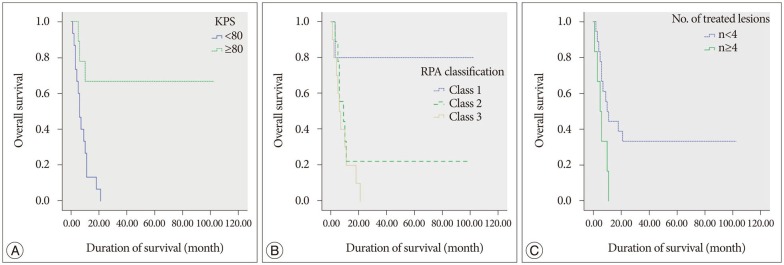
In total 24 patients (59 lesions) were available for follow-up imaging. The median follow-up time was 9 months. The mean treated tumor volume at the time of GKRS was 8185 mm³ (range 10-19500 mm³), and the median dose delivered to the tumor margin was 25 Gy (range, 10-30 Gy). A local tumor control rate was 89.8% (53 of 59 tumors). The median overall survival was 9.5 months after GKRS (range, 1-102 months). Age-associated multivariate analysis indicated that the Karnofsky performance status (KPS), the recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) classification, and the number of treated lesions were significant prognostic factors for overall survival (HR=0.162, p=0.008, HR=0.107, p=0.038, and HR=2.897, p=0.045, respectively).
CONCLUSION
GKRS is safe and effective for the management of brain metastasis from gynecologic cancers. The clinical status of the patient is important in determining the overall survival time.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bindal RK, Sawaya R, Leavens ME, Lee JJ. Surgical treatment of multiple brain metastases. J Neurosurg. 1993; 79:210–216. PMID: 8331402.
Article2. Bradley JD, Paulus R, Graham MV, Ettinger DS, Johnstone DW, Pilepich MV, et al. Phase II trial of postoperative adjuvant paclitaxel/carboplatin and thoracic radiotherapy in resected stage II and IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer : promising long-term results of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group--RTOG 9705. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:3480–3487. PMID: 15908657.
Article3. Brown JV 3rd, Goldstein BH, Duma CM, Rettenmaier MA, Micha JP. Gamma-knife radiosurgery for the treatment of ovarian cancer metastatic to the brain. Gynecol Oncol. 2005; 97:858–861. PMID: 15943990.
Article4. Chen PG, Lee SY, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Saxton JP, Fleming PA, et al. Use of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group recursive partitioning analysis classification system and predictors of survival in 19 women with brain metastases from ovarian carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 104:2174–2180. PMID: 16208705.
Article5. Chi A, Komaki R. Treatment of brain metastasis from lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2010; 2:2100–2137. PMID: 24281220.
Article6. Chura JC, Marushin R, Boyd A, Ghebre R, Geller MA, Argenta PA. Multimodal therapy improves survival in patients with CNS metastasis from uterine cancer : a retrospective analysis and literature review. Gynecol Oncol. 2007; 107:79–85. PMID: 17588647.
Article7. Cohen ZR, Suki D, Weinberg JS, Marmor E, Lang FF, Gershenson DM, et al. Brain metastases in patients with ovarian carcinoma : prognostic factors and outcome. J Neurooncol. 2004; 66:313–325. PMID: 15015663.
Article8. Cormio G, Lissoni A, Losa G, Zanetta G, Pellegrino A, Mangioni C. Brain metastases from endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1996; 61:40–43. PMID: 8626115.
Article9. Corn BW, Mehta MP, Buatti JM, Wolfson AH, Greven KM, Kim RY, et al. Stereotactic irradiation : potential new treatment method for brain metastases resulting from ovarian cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999; 22:143–146. PMID: 10199447.10. Eccles SA, Welch DR. Metastasis : recent discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet. 2007; 369:1742–1757. PMID: 17512859.11. Flickinger JC. Radiotherapy and radiosurgical management of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep. 2001; 3:484–489. PMID: 11595116.
Article12. Geisler JP, Geisler HE. Brain metastases in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1995; 57:246–249. PMID: 7729743.
Article13. Kim TJ, Song S, Kim CK, Kim WY, Choi CH, Lee JH, et al. Prognostic factors associated with brain metastases from epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2007; 17:1252–1257. PMID: 17442021.
Article14. Kim YZ, Kwon JH, Lim S. A clinical analysis of brain metastasis in gynecologic cancer : a retrospective multi-institute analysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:66–73. PMID: 25552885.
Article15. Kolomainen DF, Larkin JM, Badran M, A'Hern RP, King DM, Fisher C, et al. Epithelial ovarian cancer metastasizing to the brain : a late manifestation of the disease with an increasing incidence. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:982–986. PMID: 11844820.
Article16. Lee YK, Park NH, Kim JW, Song YS, Kang SB, Lee HP. Gamma-knife radiosurgery as an optimal treatment modality for brain metastases from epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008; 108:505–509. PMID: 18191184.
Article17. Mayer RJ, Berkowitz RS, Griffiths CT. Central nervous system involvement by ovarian carcinoma : a complication of prolonged survivial with metastatic disease. Cancer. 1978; 41:776–783. PMID: 630551.
Article18. McMeekin DS, Kamelle SA, Vasilev SA, Tillmanns TD, Gould NS, Scribner DR, et al. Ovarian cancer metastatic to the brain : what is the optimal management? J Surg Oncol. 2001; 78:194–200. discussion 200-201. PMID: 11745806.19. Menendez JY, Bauer DF, Shannon CN, Fiveash J, Markert JM. Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of brain metastasis of primary tumors that rarely metastasize to the central nervous system. J Neurooncol. 2012; 109:513–519. PMID: 22870850.
Article20. Momose T, Nariai T, Kawabe T, Inaji M, Tanaka Y, Watanabe S, et al. Clinical benefit of 11C methionine PET imaging as a planning modality for radiosurgery of previously irradiated recurrent brain metastases. Clin Nucl Med. 2014; 39:939–943. PMID: 25140562.
Article21. Monaco E 3rd, Kondziolka D, Mongia S, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Management of brain metastases from ovarian and endometrial carcinoma with stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer. 2008; 113:2610–2614. PMID: 18780313.
Article22. Muacevic A, Kreth FW, Horstmann GA, Schmid-Elsaesser R, Wowra B, Steiger HJ, et al. Surgery and radiotherapy compared with gamma knife radiosurgery in the treatment of solitary cerebral metastases of small diameter. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91:35–43. PMID: 10389878.
Article23. Nasu K, Satoh T, Nishio S, Nagai Y, Ito K, Otsuki T, et al. Clinicopathologic features of brain metastases from gynecologic malignancies : a retrospective study of 139 cases (KCOG-G1001s trial). Gynecol Oncol. 2013; 128:198–203. PMID: 23142074.
Article24. Navarro-Martín A, Maitz A, Manders M, Ducharme E, Chen P, Grills I. Gamma Knife radiosurgery as a primary treatment option for solitary brain metastases from ovarian carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009; 11:326–328. PMID: 19451067.
Article25. Ogawa K, Yoshii Y, Aoki Y, Nagai Y, Tsuchida Y, Toita T, et al. Treatment and prognosis of brain metastases from gynecological cancers. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2008; 48:57–62. discussion 62-63. PMID: 18296873.
Article26. Ogino A, Hirai T, Fukushima T, Serizawa T, Watanabe T, Yoshino A, et al. Gamma knife surgery for brain metastases from ovarian cancer. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:1669–1677. PMID: 22588338.
Article28. Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:494–500. PMID: 2405271.
Article29. Piura E, Piura B. Brain metastases from cervical carcinoma : overview of pertinent literature. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2012; 33:567–573. PMID: 23327047.30. Piura E, Piura B. Brain metastases from endometrial carcinoma. ISRN Oncol. 2012; 2012:581749. PMID: 22523707.
Article31. Piura E, Piura B. Brain metastases from ovarian carcinoma. ISRN Oncol. 2011; 2011:527453. PMID: 22191058.
Article32. Ratner ES, Toy E, O'Malley DM, McAlpine J, Rutherford TJ, Azodi M, et al. Brain metastases in epithelial ovarian and primary peritoneal carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009; 19:856–859. PMID: 19574773.
Article33. Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA, Twijnstra A. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer. 2002; 94:2698–2705. PMID: 12173339.
Article34. Shepard MJ, Fezeu F, Lee CC, Sheehan JP. Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of gynecologic malignancies metastasizing to the brain : clinical article. J Neurooncol. 2014; 120:515–522. PMID: 25129546.
Article35. Simonová G, Liscák R, Novotný J Jr, Novotný J. Solitary brain metastases treated with the Leksell gamma knife : prognostic factors for patients. Radiother Oncol. 2000; 57:207–213. PMID: 11054525.36. Sohn MJ, Kwon Y, Kim JH, Jeon SR, Lee DJ, Kim CJ, et al. Clinical analysis of gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 1999; 28:649–657.37. Tendulkar RD, Liu SW, Barnett GH, Vogelbaum MA, Toms SA, Jin T, et al. RPA classification has prognostic significance for surgically resected single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006; 66:810–817. PMID: 17011454.
Article38. Terakawa Y, Tsuyuguchi N, Iwai Y, Yamanaka K, Higashiyama S, Takami T, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 11C-methionine PET for differentiation of recurrent brain tumors from radiation necrosis after radiotherapy. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:694–699. PMID: 18413375.
Article39. Tsuyuguchi N, Sunada I, Iwai Y, Yamanaka K, Tanaka K, Takami T, et al. Methionine positron emission tomography of recurrent metastatic brain tumor and radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery : is a differential diagnosis possible? J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:1056–1064. PMID: 12744366.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
- How to use Leksell GammaPlan
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Single & Multiple brain Metastasis
- Clinical Outcome in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors from the Primary Breast Cancer : Prognostic Factors in Local Treatment Failure and Survival