Korean J Urol.
2013 Dec;54(12):858-864.
Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels and Response to 5 mg Tadalafil Once Daily in Patients With Erectile Dysfunction and Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Pusan National University Hospital, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. joon501@naver.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We studied the relative importance of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) concentrations in patients with erectile dysfunction (ED) and diabetes and determined whether the hs-CRP level predicts the response to treatment with 5 mg tadalafil once daily.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We enrolled 102 men (aged 40-60 years) with diabetes and ED. All patients completed the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) questionnaire and were given 5 mg tadalafil daily. The IIEF and serum hs-CRP levels in patients and healthy controls and in patient responders and nonresponders to 5 mg tadalafil once daily were compared.
RESULTS
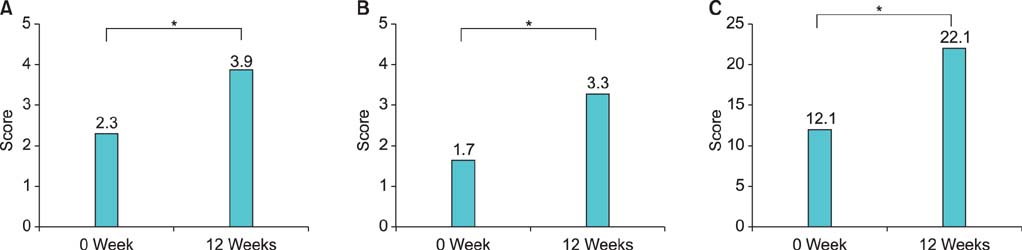
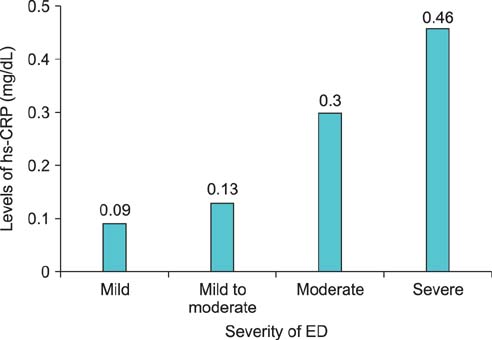
Median age was 53.2 years (range, 45 to 62 years) in patients and 55.6 years (range, 47 to 64 years) in healthy controls (p=0.158). The median duration of diabetes was 54.3 months (range, 34 to 70 months). The median IIEF and hs-CRP level were 12.1 (range, 5 to 20) and 0.21 mg/dL (range, 0.05 to 0.6 mg/dL) in patients and 28.2 (range, 13 to 31) and 0.09 mg/dL (range, 0.04 to 0.2 mg/dL) in the controls, respectively (pIIEF=0.000, pCRP=0.031). After tadalafil treatment, 71 patients (69.6%) achieved an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse, whereas 31 (30.4%) did not. The median age of the tadalafil nonresponders was 56.2 years (range, 45 to 64 years) and that of the responders was 51.3 years (range, 42 to 62 years; p=0.065). Median hs-CRP levels were 0.31 mg/dL (range, 0.18 to 0.62 mg/dL) in nonresponders and 0.14 mg/dL (range, 0.09 to 0.4 mg/dL) in responders, respectively (p=0.028).
CONCLUSIONS
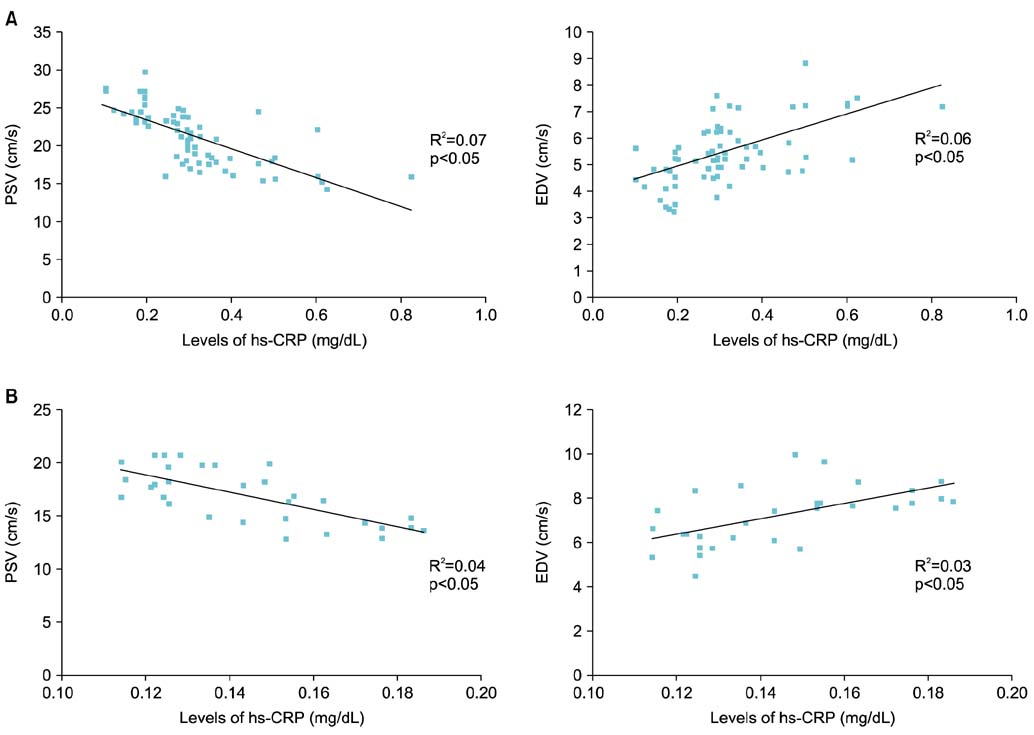
Serum hs-CRP was significantly higher in patients with ED and diabetes mellitus than in patients without ED. A significant correlation was observed between serum hs-CRP levels, the degree of ED, and responsiveness to tadalafil.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldstein I, Jones LA, Belkoff LH, Karlin GS, Bowden CH, Peterson CA, et al. Avanafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind study in men with diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012; 87:843–852.2. Schwartz BG, Jackson G, Stecher VJ, Campoli-Richards DM, Kloner RA. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors improve endothelial function and may benefit cardiovascular conditions. Am J Med. 2013; 126:192–199.3. Guo YL, Viswanathan VP, Chiang HS, Choi HK, Yip AW, Shen W, et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil taken as needed for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in Asian men: results of an integrated analysis. Asian J Androl. 2009; 11:423–433.4. Safarinejad MR. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men: a randomized double-blind and placebo-controlled study. J Diabetes Complications. 2004; 18:205–210.5. Pegge NC, Twomey AM, Vaughton K, Gravenor MB, Ramsey MW, Price DE. The role of endothelial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction in diabetes and in determining response to treatment. Diabet Med. 2006; 23:873–878.6. Israilov S, Shmuely J, Niv E, Engelstein D, Livne P, Boniel J. Evaluation of a progressive treatment program for erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:431–436.7. Karavanaki K, Kakleas K, Georga S, Bartzeliotou A, Mavropoulos G, Tsouvalas M, et al. Plasma high sensitivity C-reactive protein and its relationship with cytokine levels in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes and ketoacidosis. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:1383–1388.8. Esposito K, Ciotola M, Giugliano F, De Sio M, Giugliano G, D'armiento M, et al. Mediterranean diet improves erectile function in subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Int J Impot Res. 2006; 18:405–410.9. Padma-Nathan H. Efficacy and tolerability of tadalafil, a novel phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, in treatment of erectile dysfunction. Am J Cardiol. 2003; 92(9A):19M–25M.10. Hatzichristou D, Gambla M, Rubio-Aurioles E, Buvat J, Brock GB, Spera G, et al. Efficacy of tadalafil once daily in men with diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction. Diabet Med. 2008; 25:138–146.11. Popovic S, Nale D, Dabetic M, Matanovic D, Dimitrijevic-Sreckovic V, Milic G, et al. Effect of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction in male patients with diabetes mellitus. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2007; 64:399–404.12. Buvat J, van Ahlen H, Schmitt H, Chan M, Kuepfer C, Varanese L. Efficacy and safety of two dosing regimens of tadalafil and patterns of sexual activity in men with diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction: Scheduled use vs. on-demand regimen evaluation (SURE) study in 14 European countries. J Sex Med. 2006; 3:512–520.13. Goldstein I, Young JM, Fischer J, Bangerter K, Segerson T, Taylor T, et al. Vardenafil, a new phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes: a multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled fixed-dose study. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:777–783.14. El-Sakka AI. Efficacy of sildenafil citrate in treatment of erectile dysfunction: effect of type 2 diabetes. Eur Urol. 2004; 46:503–509.15. Saenz de Tejada I, Anglin G, Knight JR, Emmick JT. Effects of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:2159–2164.16. Bank AJ, Kelly AS, Kaiser DR, Crawford WW, Waxman B, Schow DA, et al. The effects of quinapril and atorvastatin on the responsiveness to sildenafil in men with erectile dysfunction. Vasc Med. 2006; 11:251–257.17. Blans MC, Visseren FL, Banga JD, Hoekstra JB, van der Graaf Y, Diepersloot RJ, et al. Infection induced inflammation is associated with erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006; 36:497–502.18. Eaton CB, Liu YL, Mittleman MA, Miner M, Glasser DB, Rimm EB. A retrospective study of the relationship between biomarkers of atherosclerosis and erectile dysfunction in 988 men. Int J Impot Res. 2007; 19:218–225.19. Yao F, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Dong Y, Ma H, Deng C, et al. Subclinical endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation play roles in the development of erectile dysfunction in young men with low risk of coronary heart disease. Int J Androl. 2012; 35:653–659.20. Ockene IS, Matthews CE, Rifai N, Ridker PM, Reed G, Stanek E. Variability and classification accuracy of serial high-sensitivity C-reactive protein measurements in healthy adults. Clin Chem. 2001; 47:444–450.21. Macy EM, Hayes TE, Tracy RP. Variability in the measurement of C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: implications for reference intervals and epidemiological applications. Clin Chem. 1997; 43:52–58.22. Campbell B, Badrick T, Flatman R, Kanowski D. Limited clinical utility of high-sensitivity plasma C-reactive protein assays. Ann Clin Biochem. 2002; 39(Pt 2):85–88.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy and Safety of Tadalafil 5 mg Once Daily in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction After Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: 1-Year Follow-up
- Chronic Low Dosing of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor for Erectile Dysfunction
- Effects of Administration of Tadalafil for 24 Weeks on Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Erectile Dysfunction
- Adjuvant daily therapy with L-arginine 2,500 mg and tadalafil 5 mg increases efficacy and duration of benefits of low-intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy for erectile dysfunction: A prospective, randomized, single-blinded study with 1-year follow-up
- Recovery of the Spontaneous Erections after Radical Prostatectomy with Early Tadalafil Treatment