Perspect Nurs Sci.
2016 Apr;13(1):29-35. 10.16952/pns.2016.13.1.29.
The Effect of Problem Based Learning on Nursing Students' Interaction and Self-directed Learning: A Social Network Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Cheju Halla University, Jeju, Korea. kim0424@snu.ac.kr
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2315722
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16952/pns.2016.13.1.29
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to explore the underlying structures of students' interaction networks to monitor network changes during the year, to verify the relationship with self-directed learning, and to identify the effect of problem-based learning on interaction and self-directed learning.
METHODS
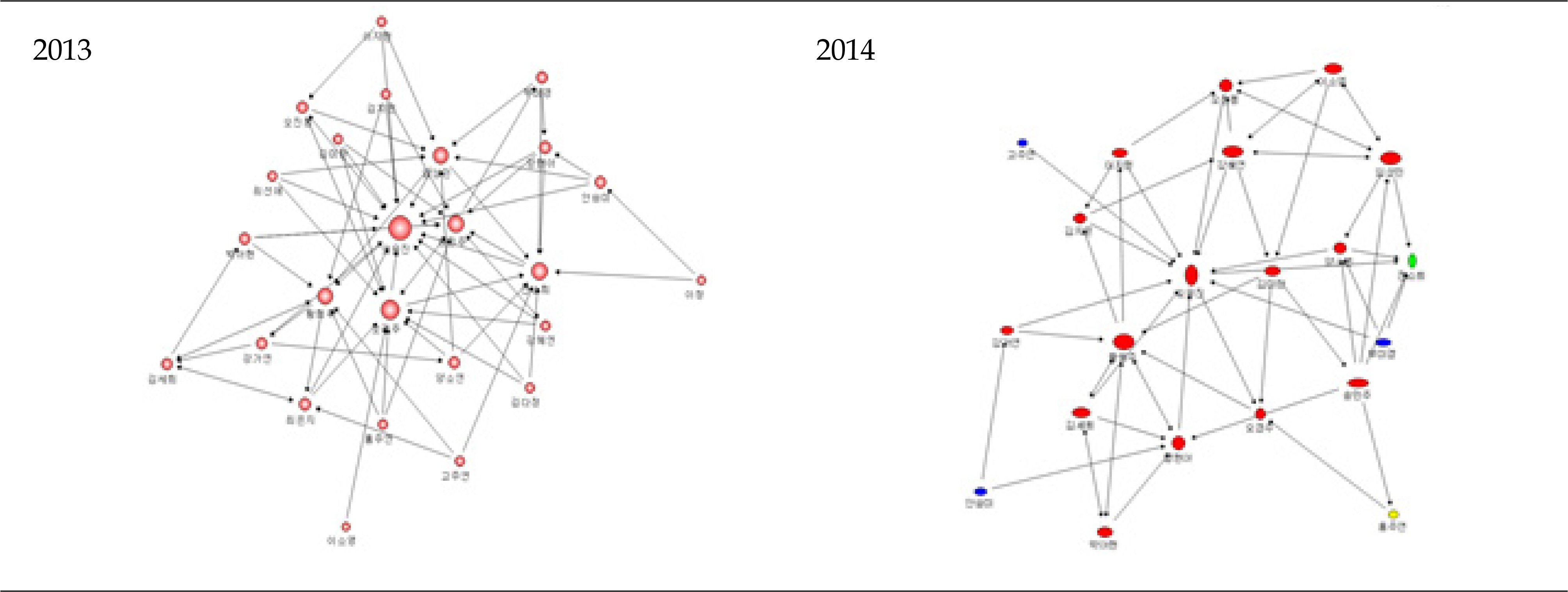
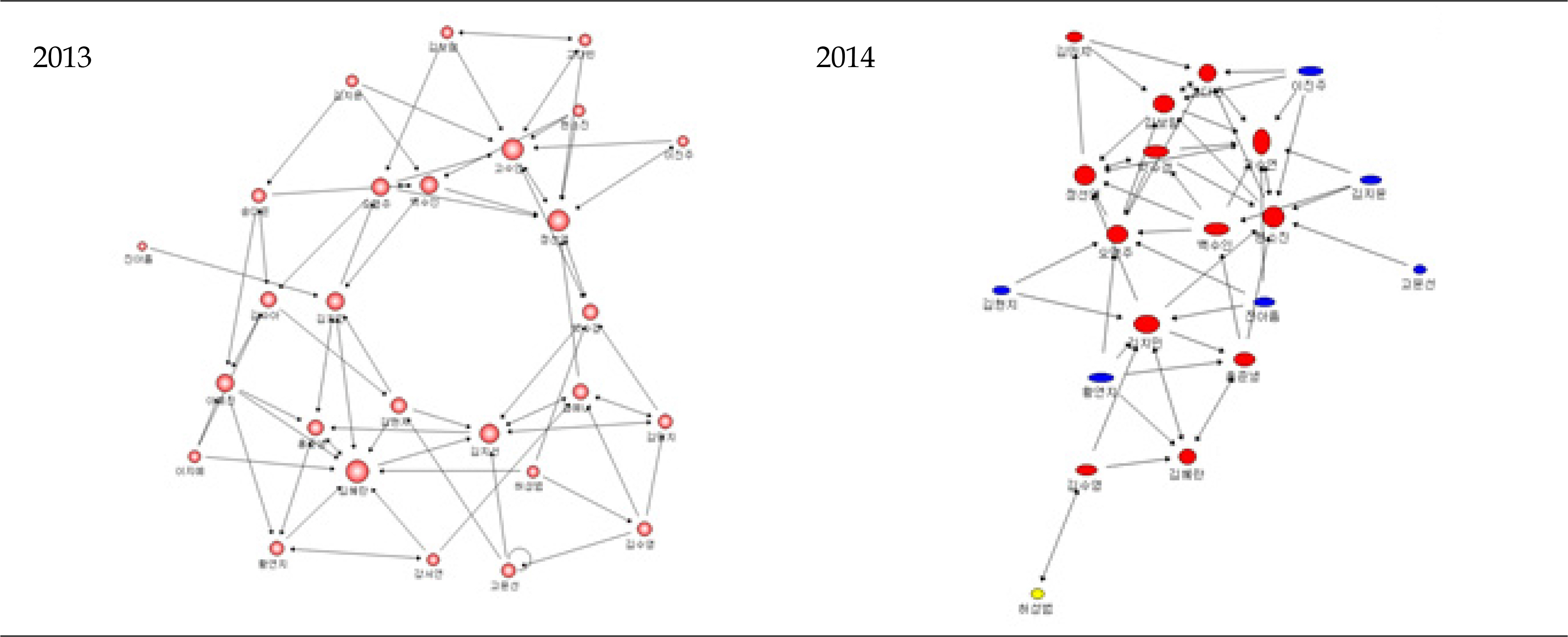
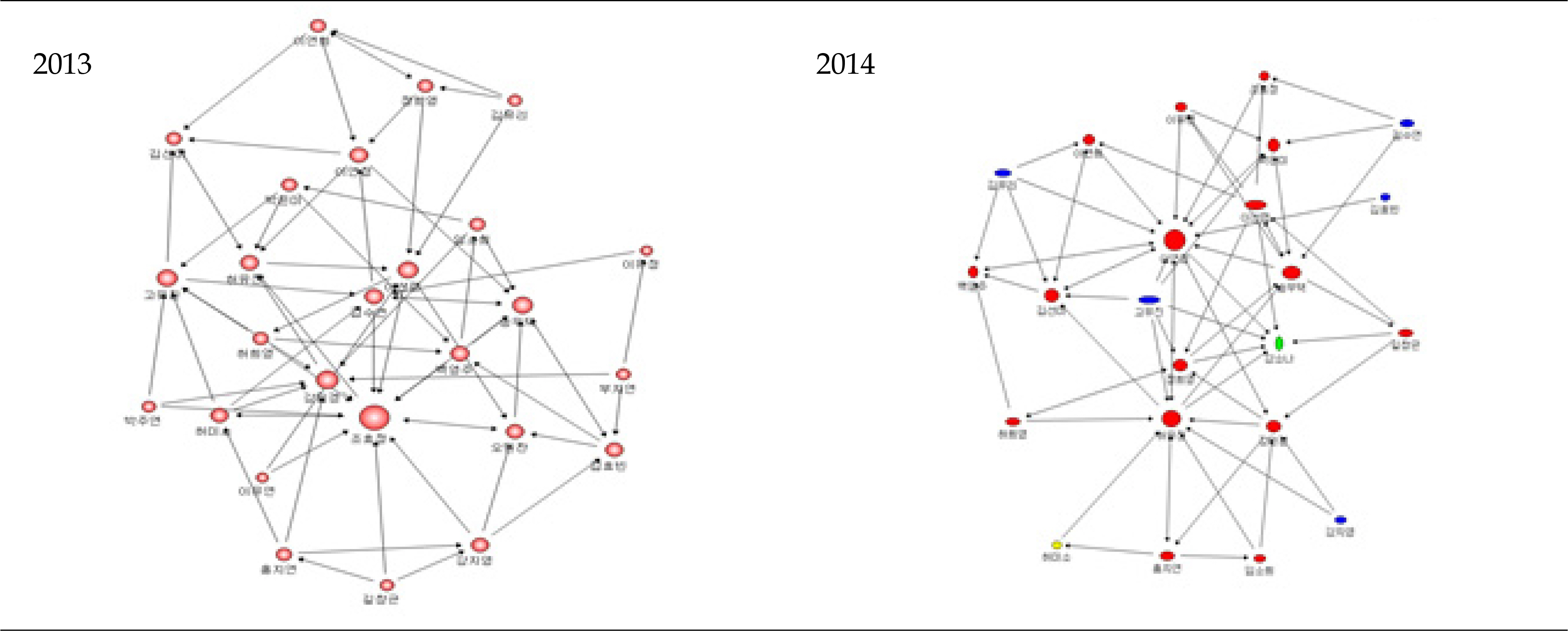
A longitudinal study was designed which included 3 parts (A=25, B=27, C=26) with a total of 78 second-year nursing students from 2013 to 2014. Interaction indicators used group network centralization and density, and individual in-degree centrality.
RESULTS
Group network centralization showed mean reversion patterns, however, centralization and density showed a slight increase from 2013 to 2014 (Centralization of A part from 52.78 to 36.96, B part from 20.56 to 32.20, C part from 34.40 to 37.24; Density of A part from 0.122 to 0.123, B part from 0.111 to 0.121, C part from 0.109 to 0.121). The individual in-degree centrality is significantly correlated with self-directed learning and the correlation coefficient increased during the year (r=.274 in 2013, r=.356 in 2014, p<.001).
CONCLUSION
Students share information more interactively during the year and the more they share the higher the scores of self-directed learning.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Barrows HS. A taxonomy of problem-based learning methods. J Med Educ. 1986. 20(6):481–6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.1986.tb01386.x.
Article2.Hong GC. A meta-analysis on the effects of problem-based learning. J Educ Stud. 2008. 39(3):79–110.3.Kang MH., Kang JH., Choi HS., Um SY. The effects of learners' perceived roles of a tutor on interactions and learning outcomes of problem-based learning in medical education. J Educ Stud. 2008. 39(3):1–25.4.Moore MG., Kearsley G. Distance education: a systems view. Belmont: Wads Worth;1996.5.Cho H., Stefanone M., Gay G. Social network analysis of information sharing networks in a CSCL community. Proceeding of the Conference on Computer Support for Collaborative Learning: Foundation for a CSCL Community. 2002 Jan 7-11; Boulder, USA. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;. 2002.6.Kim DS., Kang YG. The effects of the social network data presentation on interaction processes and products in computer supported collaborative learning environment. J Educ Technol. 2004. 20(1):89–115.
Article7.Chang DJ. Classroom networks and study performance. J Soc Stud Educ. 2000. 4:161–85.8.Kim YH. Social network theory. Seoul: Pakyoungsa;2007.9.Shin IS., Kim JH. The effect of problem-based learning in nursing education: a meta-analysis. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013. 18(5):1103–20.
Article10.Kim YH. Social network analysis. Seoul: Parkyoungsa;2011.11.Park JY. A study on the development and the effects of self-directed learning model by project method [dissertation]. Gang-neung: Catholic Kwandong University;2008.12.Kim DH., Park JY., Lee NY. Factors influencing problem solving ability among nursing students. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2012. 14(3):1551–63.13.Mehra A., Kilduff M., Brass D. The social network of high and low self-monitors: implications for workplace performance. Adm Sci Q. 2001. 46(1):121–46. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2667127.14.Lee SS. An analysis of interaction patterns in face-to-face and online synchronous/asynchronous learning environments. J Educ Technol. 2004. 20(1):63–88.
Article15.Cho H., Gay G., Davidson B., Ingraffea A. Social networks, communication styles and learning performance in a CSCL community. Comput Educ. 2007. 49(2):309–29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2005.07.003.
Article16.Aviv R., Erlich Z., Ravid G., Geva A. Network analysis of knowledge construction in asynchronous learning networks. J Asynchronous Learn Netw. 2003. 7(3):1–23.
Article17.Park ES., Choi MS. The effect of learners' social network centralities on knowledge construction in online debating learning. J Educ Inf Media. 2011. 17(3):353–77.18.Nam CW. The effects of students' centrality of social network on their academic achievement and attitude toward online cooperative learning. J Yeolin Educ. 2012. 20(2):51–73.19.De Laat M. Network and content analysis in an online community discourse. Proceeding of the Conference on Computer Support for Collaborative Learning: Foundations for a CSCL Community; 2002 Jan 7-11; Boulder, USA. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;. 2002.20.Shin HS. The case studies about communication education, applying problem-based learning. J Korean Educ Forum. 2011. 10(3):137–69.21.Jo YS. The Theory and practice of problem based learning. Seoul: Hakjisa;2006.22.Chae SJ., Lim GY. An analysis of the relationship between intragroup peer assessment results and self-directed learning readiness in a leadership curriculum. Korean J Med Educ. 2008. 20(4):363–6.
Article23.Lee HJ., Kim MJ., Chung SK. The relationship between critical thinking disposition and lifelong core competency of college students. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2012. 14(3B):1535–49.24.Kim CH. Study on the relationships between participation in sport activities, social network and school life adjustment among the adolescents [dissertation]. Incheon: Inha University;2010.25.Lim KY., Heo HO., Kim YS. Team leaders' interaction patterns in online team project. J Educ Inf Media. 2009. 15(4):295–317.26.Palonen T., Hakkarainen K. Patterns of interaction in computer-supported learning: a social network analysis. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference of the Learning Sciences. 2000. June 14-17; Ann Arbor, USA. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associate; 2000.27.Kang MJ., Piao MH., Park CS. The effects of students' interaction on self-directed learning and learner satisfaction in PBL class-a social network analysis. J Korean Data Anal Soc. 2014. 16(5):2807–18.28.Cho YS., Chae JS., Baek EJ., Lim HH. A theoretic study on the teaching-learning process for problem-based learning (PBL) in elementary school classrooms. Korean J Educ Methodol Stud. 2004. 16(2):1–28.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effect of case-based learning based on flipped learning for nursing students
- The Clinical Competence and Related Factors of the Nursing Students: Focused on the Subjects Who Studied Problem-Based Learning
- The Effects of PBL (Problem-Based Learning) on the Self-Directed Learning, Critical Thinking Disposition, and Problem Solving Process of Nursing Students
- The effect of communication competency on self-directed learning ability among nursing students
- Perspectives of Nurse Students on Problem-Based Learning: Learning Experience in Pediatric Nursing