Pediatr Infect Vaccine.
2015 Dec;22(3):178-185. 10.14776/piv.2015.22.3.178.
The Impact of the Antibiotic Burden on the Selection of its Resistance among Gram Negative Bacteria Isolated from Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. entier@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2315683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2015.22.3.178
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We investigated trends in antibiotic pressure and the antibiotic susceptibility of gram negative bacteria isolated from Korean children over 10 consecutive years.
METHODS
From January 2004 to December 2013, the antibiotic susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii blood isolates obtained from children <18 years of age was determined according to the 2009 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines. Antibiotic consumption data were also analyzed.
RESULTS
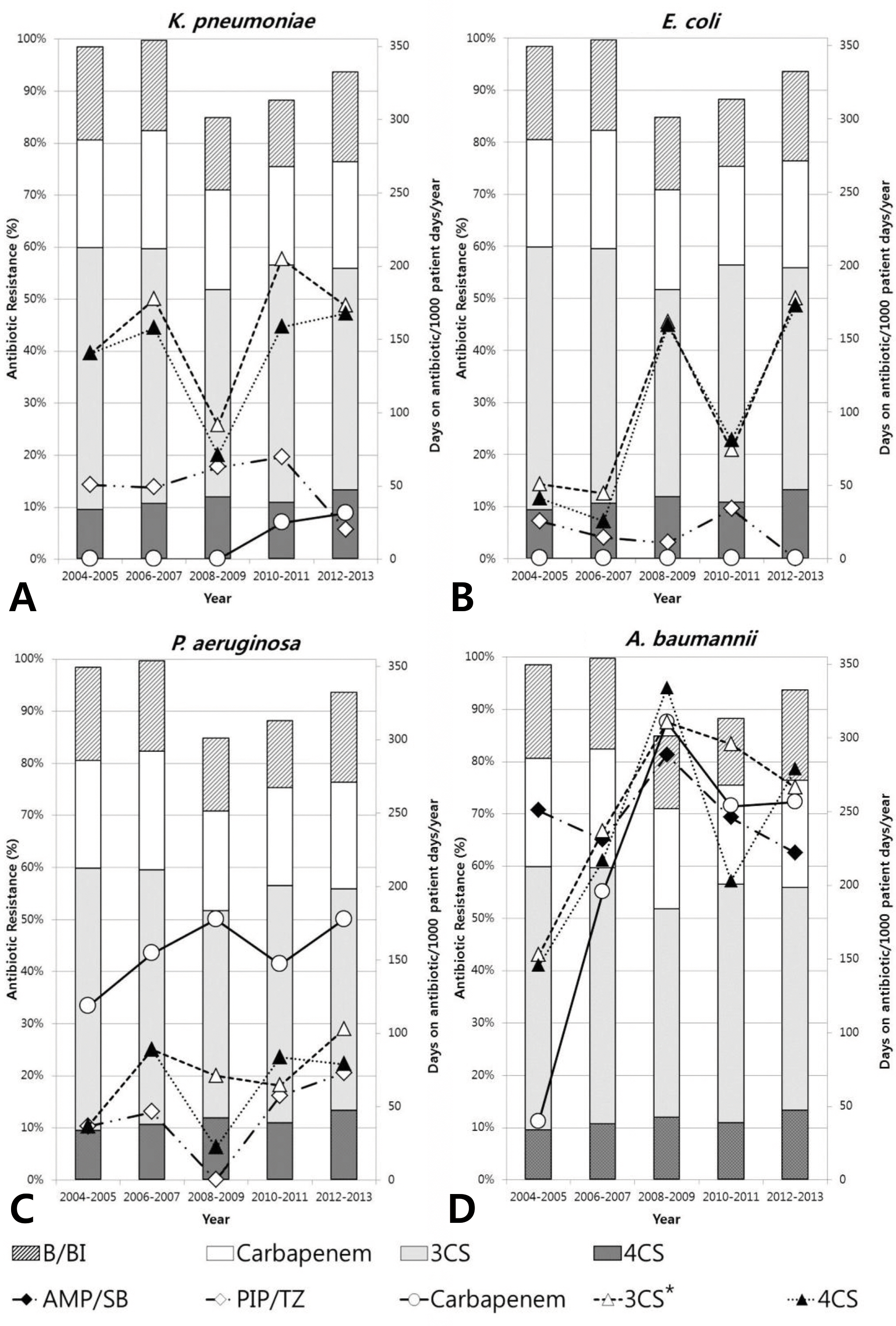
The prevalence of K. pneumoniae, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and A. baumannii bacteremia was 4.6, 3.5, 3.4, and 2.2 cases/1,000 blood cultures/year, respectively. In K. pneumoniae, resistance to the third and fourth cephalosporin did not increase significantly. However, carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae first appeared in 2010, and the resistance rate increased to 9% between 2012 and 2013. Resistance to 3rd and 4th cephalosporin increased from 10% to 50% in E. coli, and resistance to carbapenem rose abruptly from 11% to 71% in A. baumannii (P for trend <0.01). However, such an increase of resistance was not observed in P. aeruginosa. There is a positive correlation between the resistance rate of cefepime in E. coli and the consumption of cefepime (r=0.900, P=0.037).
CONCLUSION
The significant burden of antibiotic consumption and the high prevalence of antibiotic resistance to gram negative pathogen isolated from bacteremic children were observed. Empirical antibiotics should be wisely selected, and continued efforts to decrease the overall antibiotic pressure are mandatory, especially in highly resistant situations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo IE, Sharma S, et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34:1589–96.
Article2. Hartman ME, Linde—Zwirble WT, Angus DC, Watson RS. Trends in the epidemiology of pediatric severe sepsis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013; 14:686–93.
Article3. Kang CI, Kim SH, Park WB, Lee KD, Kim HB, Kim EC, et al. Bloodstream infections caused by antibiotic—resistant gram—negative bacilli: risk factors for mortality and impact of inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy on outcome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005; 49:760–6.
Article4. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit Care Med. 2013; 41:580–637.
Article5. Kim NH, Hwang JH, Song KH, Choe PG, Park WB, Kim ES, et al. Changes in antimicrobial susceptibility of blood isolates in a university hospital in South Korea, 1998-2010. Infect Chemother. 2012; 44:275–81.
Article6. Kang SH, Kim YR. Characteristics of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures at a university hospital located in an island region during 2003—2007. Korean I Clin Mi—crobiol. 2008; 11:11–7.
Article7. Kim SY, Lim G, Kim M], Suh IT, Lee H]. Trends in five—year blood cultures of patients at a university hospital (2003—2007). Korean I Clin Microbiol. 2009; 12:163–8.8. Ko EY, Kang H}, Kwon H], Choi UY, Lee ]W, Lee DG, et al. Clinical investigation of bacteremia in children with hemato-oncologic diseases. Infect Chemother. 2011; 43:191–7.
Article9. Kang IE, Seok IY, Yun KW, Kang H], Choi EH, Park KD, et al. Etiological agents in bacteremia of children With hemato—oncologic diseases (2006—2010): A single center study. Korean I Pediatr Infect Dis. 2012; 19:131–40.
Article10. Urbanek K, Kolar M, Loveckova Y, Strojil I, Santava L. Influ—ence of third—generation cephalosporin utilization on the occurrence of ESBL—positive Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. I Clin Pharm Ther. 2007; 32:403–8.11. Chaouch C, Hassairi A, Riba M, Boujaafar N. Association between bacterial resistance and antimicrobial consumption. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2014; 72:555–60.
Article12. Sedlakova MH, Urbanek K, Vojtova V, Suchankova H, Im—wensi P, Kolar M. Antibiotic consumption and its influence on the resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. BMC Res Notes. 2014; 7:454.
Article13. Asensio A, Alvarez—Espejo T, Fernandez—Crehuet I, Ramos A, Vaque—Rafart I, Bishopberger C, et al. Trends in yearly prevalence of third—generation cephalosporin and fluoro—quinolone resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections and anti—microbial use in Spanish hospitals, Spain, 1999 to 2010. Euro Surveill. 2011. 16.14. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Nineteenth Informational Supplement. M100—Sl9. 2009; 29(3):15. Kim YK, Pai H, Lee H], Park SE, Choi EH, Kim I, et al. Blood—stream infections by extended—spectrum beta—lactamase—producing Escherichia 6011' and Klebsiella pneumoniae in children: epidemiology and clinical outcome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002; 46:1481–91.16. Schwaber M]. Navon—Venezia S, Kaye KS, Ben—Ami R, Schwartz D, Carmeli Y. Clinical and economic impact of bacteremia with extended—spectrum beta—lactamase—pro-ducing Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:1257–62.17. Leibovici L, Shraga I, Drucker M, Konigsberger H, Samra Z, Pitlik SD. The benefit of appropriate empirical antibiotic treatment in patients with bloodstream infection. J Intern Med. 1998; 244:379–86.
Article18. Kim HT, Iang HO, Moon IS, Nam SY, ij DW, Lee CG, et al. Etiology of community-acquired bacteremia in healthy children. Korean I Pediatr. 2005; 48:716–22.19. Kim H]. Lee NY, Kim S, Shin IH, Kim MN, Kim EC, et al. Characteristics of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures at nine university hospitals in Korea during 2009. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 14:48–54.
Article20. Rhee IY, Park YK, Shin IY, Choi IY, Lee MY, Peck KR, et al. KPC—producing extreme drug—resistant Klebsiella pneumo— njae isolate from a patient with diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure on hemodialysis in South Korea. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010; 54:2278–9.21. Yoo IS, Kim HM, Yoo 11, Yang IW, Kim HS, Chung GT, et al. Detection of clonal KPC—Z-producing Hebsie/lapneumom'ae ST258 in Korea during nationwide surveillance in 2011. J Med Microbiol. 2013; 62:1338—42.22. Hong SK, Yong D, Kim K, Hong SS, Hong SG, Khosbayar T, et al. First outbreak of KPC—Z-producing Klebsiella pneu— moniae sequence type 258 in a hospital in South Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:3877–9.23. Decousser IW, Lamy B, Pina P, Allouch PY. Trends in anti—biotic susceptibility ofbloodstream pathogens in hospitalized patients in France, 1996 to 2007. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010; 66:292–300.24. Lee 1, Oh CE, Choi EH, Lee H]. The impact of the increased use of piperacillin/tazobactam 0n the selection of antibiotic resistance among invasive Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Int I Infect Dis. 2013. 172e638–43.25. Yong D, Shin HB, Kim YK, Cho J, Lee WG, Ha GY, et al. Increase in the prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Acine—tobacter isolates and ampicfllin—resistant non—typhoidal Sal—monella species in Korea: a KONSAR study conducted in 2011. Infect Chemother. 2014; 46:84–93.26. lung SI, Park KH, Kwon KT, K0 KS, Oh WS, Chung DR, et al. Relationship between beta—lactam antmicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates at 5 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2007; 39:189–95.27. Hsueh PR, Chen WH, Luh KT. Relationships between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in gram—negative bacteria causing nosocomial infections from 1991—2003 at a university hospital in Taiwan. Int I Antimicrob Agents. 2005; 26:463–72.
Article28. Kim BN. Overview of antibiotic use in Korea. Infect Che—mother. 2012; 44:250–62.
Article29. Park S, Chae SM. Quality assessment of outpatient antibiotic consumptions in Korea compared with other countries. Yakhak Hoeji. 2014; 58:200–7.30. Lee I, Pai H, Kim YK, Kim NH, Eun BW, Kang H], et al. Control of extended—spectrum beta—lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in a children's hospital by changing antimicrobial agent usage policy. JAnti—microb Chemother. 2007; 60:629–37.31. Du B, Chen D, Liu D, Long Y, Shi Y, Wang H, et al. Restriction of third—generation cephalosporin use decreases infection— related mortality. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:1088–93.32. Meyer E, Lapatschek M, Bechtold A, Schwarzkopf G, Gastmeier P, Schwab F. Impact of restriction of third genera—tion cephalosporins on the burden of third generation cephalosporin resistant K. pneumoniae and E. coli in an ICU. Intensive Care Med. 2009; 35:862–70.
Article33. Sistanizad M, Kouchek M, Miri M, Goharani R, Solouki M, Ayazkhoo L, et al. Carbapenem restriction and its effect on bacterial resistance in an intensive care unit of a teaching hospital. Iran I Pharm Res. 2013; 12:503–9.34. Ntagiopoulos PG, Paramythiotou E, Antoniadou A, Giama—rellou H, Karabinis A. Impact of an antibiotic restriction policy on the antibiotic resistance patterns of gram—negative microorganisms in an intensive care unit in Greece. Int I Antimicrob Agents. 2007; 30:360–5.
Article35. de Araujo OR, da Silva DC, Diegues AR, Arkader R, Cabral EA, Afonso MR, et al. Cefepime restriction improves gram—negative overall resistance patterns in neonatal intensive care unit. Braz J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:277–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Impact of Antibiotic Burden on the Selective Resistance of Gram Negative Bacteria in Children
- Increase in Antibiotic-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections in Febrile Neutropenic Children
- Bacteriologic Study on Normal Conjunctival Flora and Change of Antibiotic Susceptability
- Metallo-beta-lactamase Producing Gram-negative Bacilli
- Bacteriologic Study on Conjunctiva of Eyeball Donor and Antibiotic Sensitivity Test