Korean J Urol.
2012 Aug;53(8):573-576.
Category Migration of Renal Cystic Masses with Use of Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wonjya@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nephrology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
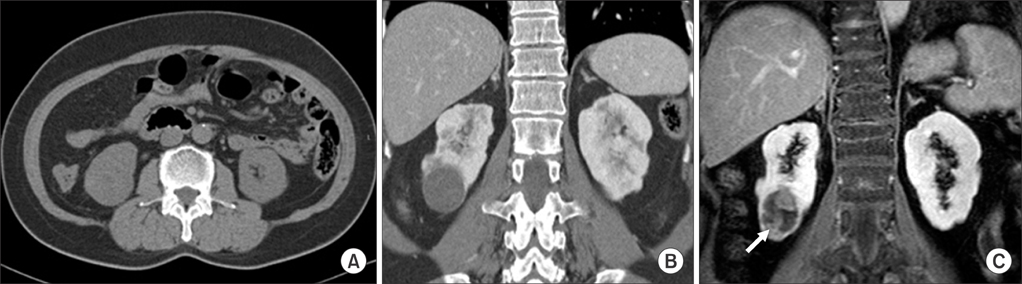
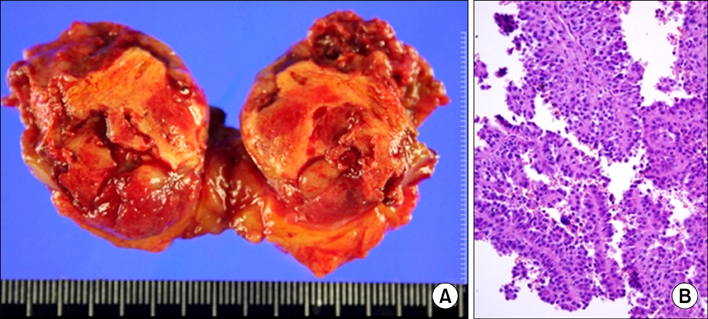
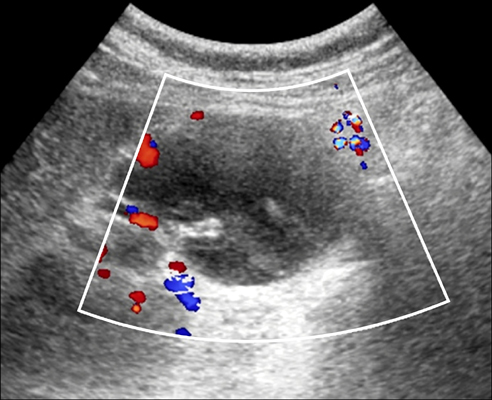
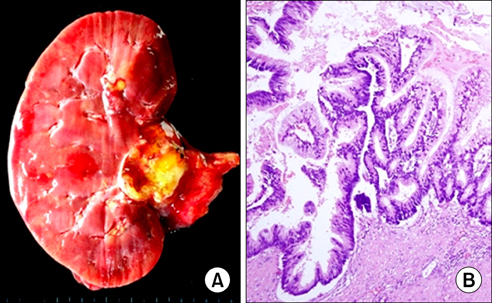
- The Bosniak renal cyst classification has been accepted by urologists and radiologists as a way of diagnosing cystic renal masses and determining the management approach. We report two cases of a renal cystic mass that showed a category change from category II on the basis of enhanced computed tomography to category IV after further gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. In both cases, the cysts were later confirmed as kidney cancer by pathology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bosniak MA. The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology. 1986. 158:1–10.2. Curry NS, Cochran ST, Bissada NK. Cystic renal masses: accurate Bosniak classification requires adequate renal CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:339–342.3. Koga S, Nishikido M, Inuzuka S, Sakamoto I, Hayashi T, Hayashi K, et al. An evaluation of Bosniak's radiological classification of cystic renal masses. BJU Int. 2000. 86:607–609.4. Balci NC, Semelka RC, Patt RH, Dubois D, Freeman JA, Gomez-Caminero A, et al. Complex renal cysts: findings on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:1495–1500.5. Israel GM, Hindman N, Bosniak MA. Evaluation of cystic renal masses: comparison of CT and MR imaging by using the Bosniak classification system. Radiology. 2004. 231:365–371.6. Israel GM, Bosniak MA. Calcification in cystic renal masses: is it important in diagnosis? Radiology. 2003. 226:47–52.7. Israel GM, Bosniak MA. Follow-up CT of moderately complex cystic lesions of the kidney (Bosniak category IIF). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:627–633.8. Israel GM, Bosniak MA. MR imaging of cystic renal masses. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2004. 12:403–412.9. Israel GM, Bosniak MA. An update of the Bosniak renal cyst classification system. Urology. 2005. 66:484–488.10. Inci E, Hocaoglu E, Aydin S, Cimilli T. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of primary solid and cystic renal masses using the Bosniak classification. Eur J Radiol. 2012. 81:815–820.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Significance of Bosniak Classification in Cystic Renal Masses : Usefulness of Preoperative Computerized Tomography in Cystic Renal Masses
- Assessment of Cystic Renal Masses Based on Bosniak Classification: Comparison of CT, Contrast-enhanced US, and MR Imaging
- Imaging Diagnosis and Management of Cystic Renal Masses: Introduction of an Update Proposal Bosniak Classification Version 2019
- Usefulness of the Bosniak Classification in Cystic Renal Mass on CT
- Novel Experience of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography to Differentiate Between Renal Cysts and Renal Cell Carcinoma