Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Jun;15(2):117-121.
A Case of Idiopathic Congenital Neonatal Cholestasis in a Patient with Down Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. csassi@hanmail.net
Abstract
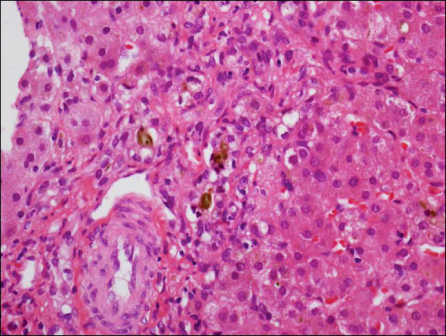
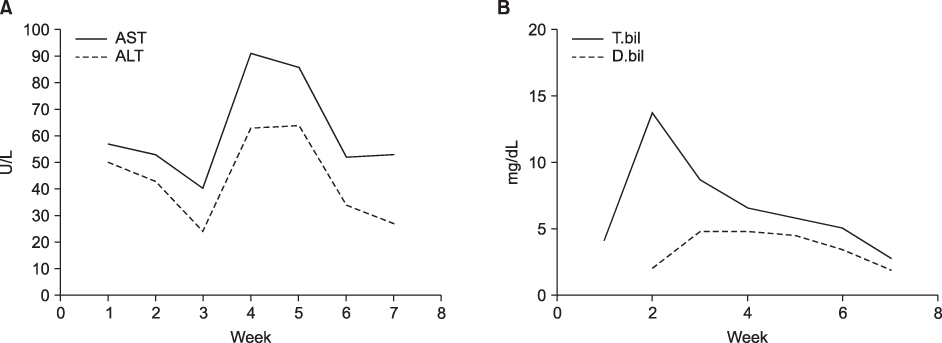
- Down syndrome is a rare cause of neonatal cholestasis. Neonatal cholestasis in a patient with Down syndrome is usually associated with severe liver diseases, such as neonatal hemochromatosis, myeloproliferative disorder and intrahepatic bile duct paucity. We experienced a case of idiopathic neonatal cholestasis in a patient with Down syndrome, which resolved spontaneously.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruchelli ED, Uri A, Dimmick JE, Bove KE, Huff DS, Duncan LM, et al. Severe perinatal liver disease and Down syndrome: an apparent relationship. Hum Pathol. 1991. 22:1274–1280.
Article2. Chang CH, Kim JH, Lee SJ, Lee DS, Kim DK, Choi SM, et al. A case of Nonsyndromic paucity of interlobular bile ducts in Down syndrome. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1999. 42:858–862.3. Crosti N, Bajer J, Gentile M, Resta G, Serra A. Catalase and glutathone peroxidase activity in cells with trisomy 21. Clin Genet. 1989. 36:107–116.4. Bacon BR, Tavill AS, Brittenham GM, Park CH, Recknagel RO. Hepatic lipid peroxidation in vivo in rats with chronic iron overload. J Clin Invest. 1983. 71:429–439.
Article5. Jacquemin E, Lykavieris P, Chaoui N, Hadchouel M, Bernard O. Transient neonatal cholestasis: Origin and outcome. J Pediatr. 1998. 133:563–567.
Article6. Suchy FJ, Bucuvalas JC, Novak DA. Determinants of bile formation during development: ontogeny of hepatic bile acid metabolism and transport. Semin Liver Dis. 1987. 7:77–84.
Article7. Lemasters JJ, Stemkowski CJ, Ji S, Thurman RG. Cell surface changes and enzyme release during hypoxia and reoxygenation in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1983. 97:778–786.
Article8. Choe BH. Early exclusive diagnosis of biliary atresia among infants with cholestasis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. 14:122–129.
Article9. Ko JS, JK Seo. The etiologies of neonatal cholestasis. Korean J Pediatr. 2007. 50:835–840.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
- A Case of Neonatal Cholestasis Associated with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Neonatal Cholestasis Associated with Congenital Hypopituitarism
- Clinical Evaluation of Syndromic and Nonsyndromic Intrahepatic Bile Duct Paucity
- Beta Thalassemia Presenting with Neonatal Cholestasis and Extensive Hemosiderosis: A Case Report