Korean J Urol.
2010 Dec;51(12):824-830.
Association of Polymorphisms in the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Gene Promoter with Serum PSA Level and PSA Changes after Dutasteride Treatment in Korean Men with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Kwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. multiorigins@yahoo.com
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Studies of genetic variation in the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) gene have improved the diagnostic accuracy of PSA for diagnosing prostate diseases in Caucasians. However, the reference ranges and pharmacokinetics of PSA differ significantly according to race. Therefore, we evaluated the association between genetic variations in the PSA promoter area and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) phenotypes in Korean BPH patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
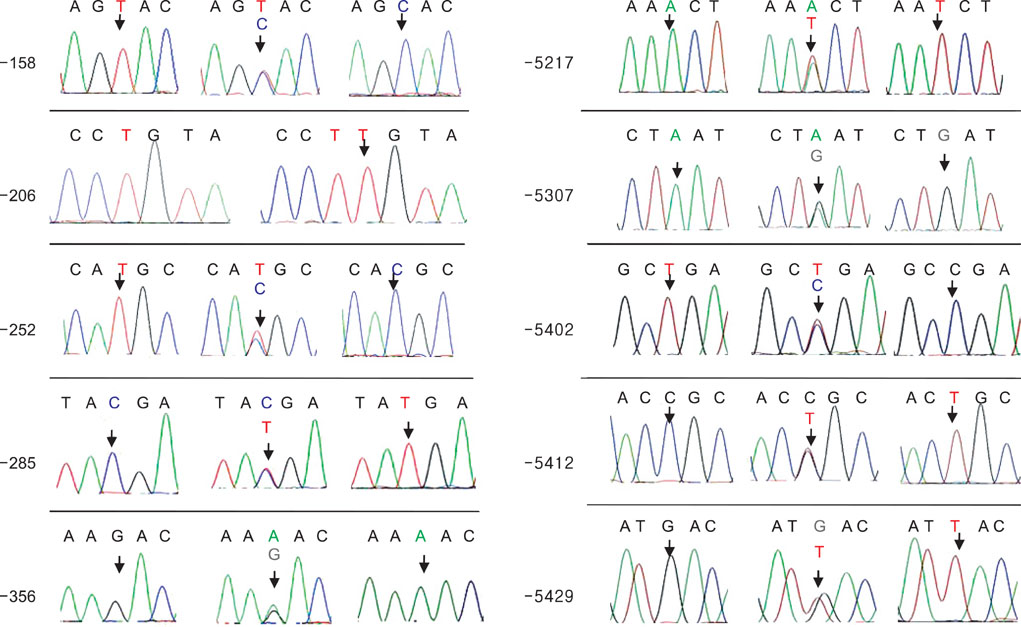
One hundred twenty-one men were enrolled. The initial serum PSA level, prostate size, and PSA changes at 3 months after treatment with dutasteride were determined. We amplified the promoter region of the PSA gene (nucleotide positions -158 to -356 and -5217 to -5429) and sequenced the products.
RESULTS
Three relatively well characterized single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs; rs3760722, rs266867, and rs266868), six uncharacterized SNPs (rs17554958, rs266882, rs4802754, rs2739448, rs2569733, and rs17526278), and one novel SNP (nucleotide position -5402) were found. There were no statistically significant correlations between any of the SNPs of the PSA promoter area and age-adjusted prostate sizes, initial PSA levels, or PSA variations after 3 months of dutasteride treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
SNPs in the PSA promoter area were not associated with BPH phenotypes. We could not predict serum PSA changes after dutasteride treatment on the basis of PSA promoter genotype in Korean patients with BPH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984. 132:474–479.2. Carson C 3rd, Rittmaster R. The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2003. 61:4 Suppl 1. 2–7.3. Marks LS, Andriole GL, Fitzpatrick JM, Schulman CC, Roehrborn CG. The interpretation of serum prostate specific antigen in men receiving 5alpha-reductase inhibitors: a review and clinical recommendations. J Urol. 2006. 176:868–874.4. Lilja H. A kallikrein-like serine protease in prostatic fluid cleaves the predominant seminal vesicle protein. J Clin Invest. 1985. 76:1899–1903.5. Ulmert D, O'Brien MF, Bjartell AS, Lilja H. Prostate kallikrein markers in diagnosis, risk stratification and prognosis. Nat Rev Urol. 2009. 6:384–391.6. Roehrborn CG. The utility of serum prostatic-specific antigen in the management of men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Impot Res. 2008. 20:Suppl 3. S19–S26.7. Pienta KJ. Critical appraisal of prostate-specific antigen in prostate cancer screening: 20 years later. Urology. 2009. 73:5 Suppl. S11–S20.8. Lee GH, Hong JH, Kim HJ. The effect of dutasteride on serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in patients with benign prostate hypertrophy. J Korean Continence Soc. 2008. 12:42–47.9. Fitzpatrick JM, Banu E, Oudard S. Prostate-specific antigen kinetics in localized and advanced prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2009. 103:578–587.10. Cramer SD, Chang BL, Rao A, Hawkins GA, Zheng SL, Wade WN, et al. Association between genetic polymorphisms in the prostate-specific antigen gene promoter and serum prostate-specific antigen levels. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003. 95:1044–1053.11. Ku JH, Ahn JO, Lee CH, Lee NK, Park YH, Byun SS, et al. Distribution of serum prostate-specific antigen in healthy Korean men: influence of ethnicity. Urology. 2002. 60:475–479.12. Oesterling JE, Kumamoto Y, Tsukamoto T, Girman CJ, Guess HA, Masumori N, et al. Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy Japanese men: lower values than for similarly aged white men. Br J Urol. 1995. 75:347–353.13. Song J, Kim DY, Kim CS, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Lee HM, et al. The association between Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) polymorphisms and the risk of prostate cancer in Korean men. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2009. 190:88–92.14. Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science. 2002. 296:2225–2229.15. Kim J, Coetzee GA. Prostate specific antigen gene regulation by androgen receptor. J Cell Biochem. 2004. 93:233–241.16. Andriole G, Bostwick D, Civantos F, Epstein J, Lucia MS, McConnell J, et al. The effects of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on the natural history, detection and grading of prostate cancer: current state of knowledge. J Urol. 2005. 174:2098–2104.17. Xue WM, Coetzee GA, Ross RK, Irvine R, Kolonel L, Henderson BE, et al. Genetic determinants of serum prostate-specific antigen levels in healthy men from a multiethnic cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001. 10:575–579.18. Xue W, Irvine RA, Yu MC, Ross RK, Coetzee GA, Ingles SA. Susceptibility to prostate cancer: interaction between genotypes at the androgen receptor and prostate-specific antigen loci. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:839–841.19. Medeiros R, Morais A, Vasconcelos A, Costa S, Pinto D, Oliveira J, et al. Linkage between polymorphisms in the prostate specific antigen ARE1 gene region, prostate cancer risk, and circulating tumor cells. Prostate. 2002. 53:88–94.20. Xu J, Meyers DA, Sterling DA, Zheng SL, Catalona WJ, Cramer SD, et al. Association studies of serum prostate-specific antigen levels and the genetic polymorphisms at the androgen receptor and prostate-specific antigen genes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2002. 11:664–669.21. Rao A, Chang BL, Hawkins G, Hu JJ, Rosser CJ, Hall MC, et al. Analysis of G/A polymorphism in the androgen response element I of the PSA gene and its interactions with the androgen receptor polymorphisms. Urology. 2003. 61:864–869.22. Tebbutt SJ, James A, Paré PD. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and lung disease: clinical implications. Chest. 2007. 131:1216–1223.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Dutasteride on Serum Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) in Patients with Benign Prostate Hypertrophy
- The Change of Prostate-specific Antigen and Prostate-specific Antigen Density in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia after Dutasteride Treatment
- Effects of Benign Prostatic Diseases on the Level of Serum Prostate Specific Antigen
- Effects of Medication with Dutasteride on Detection of Prostate Cancer in Patients with Serum Prostate-specific Antigen Level of 4~10 ng/ml
- Association of Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Velocity with Age and Initial PSA in Healthy Korean Men