Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2013 Sep;56(5):349-351.
Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. garden.lee@samsung.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
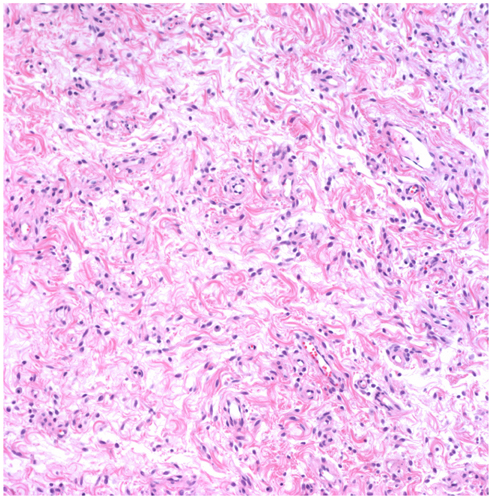
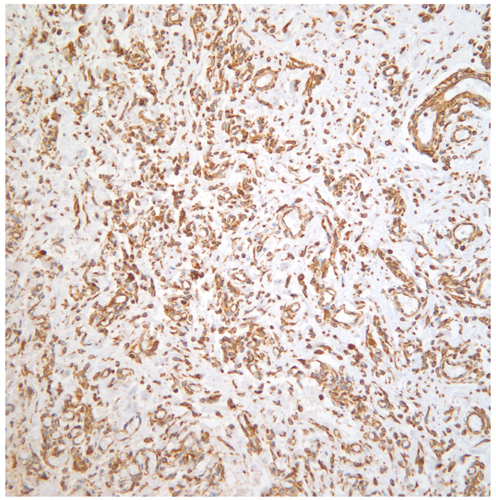
- Angiomyofibroblastoma (AMFB) is an uncommon benign mesenchymal tumor. AMFB occurs almost in the vulvo-vaginal area of women. The gross features of AMFB are well-circumscribed so it clinically is often thought as Bartholin gland cyst or aggressive angiomyxoma. Usually, most tumors grow slowly, and patients do not feel pain. It also has low tendency for local recurrence. The histologic findings of the tumors are abundant thin-walled blood vessels with hypocellular and hypercellular areas. Almost all tumor cells have immunoreactivity for both desmin and vimentin. It also has estrogen and/or progesterone receptors, but staining for cytokeratin is negative. Here is a case of AMFB of the vulva occurring in a 40-year-old woman, involving the right labia majora. The patient described that her vulva mass grew in about few months. The maximum dimension of the tumor was measured as 2 cm, and we resected the tumor one month after as her second visit.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hsu IH, Chang TC, Wu CT, Chen RJ, Chow SN. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva. J Formos Med Assoc. 2004; 103:467–471.2. Laiyemo R, Disu S, Vijaya G, Wise B. Post-menopausal vaginal angiomyofibroblastoma: a case report. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005; 273:129–130.3. Varras M, Akrivis C, Demou A, Kitsiou E, Antoniou N. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vagina in a postmenopausal breast cancer patient treated with tamoxifen: clinicopathologic analysis of a case and review of the literature. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006; 16:581–585.4. Nucci MR, Fletcher CD. Vulvovaginal soft tissue tumours: update and review. Histopathology. 2000; 36:97–108.5. Nielsen GP, Young RH. Mesenchymal tumors and tumor-like lesions of the female genital tract: a selective review with emphasis on recently described entities. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2001; 20:105–127.6. Horiguchi H, Matsui-Horiguchi M, Fujiwara M, Kaketa M, Kawano M, Ohtsubo-Shimoyamada R, et al. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: report of a case with immunohistochemical and molecular analysis. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2003; 22:277–284.7. Omori M, Toyoda H, Hirai T, Ogino T, Okada S. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: a large pedunculated mass formation. Acta Med Okayama. 2006; 60:237–242.8. Fletcher CD, Tsang WY, Fisher C, Lee KC, Chan JK. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: a benign neoplasm distinct from aggressive angiomyxoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992; 16:373–382.9. Ockner DM, Sayadi H, Swanson PE, Ritter JH, Wick MR. Genital angiomyofibroblastoma: comparison with aggressive angiomyxoma and other myxoid neoplasms of skin and soft tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1997; 107:36–44.10. Nielsen GP, Young RH, Dickersin GR, Rosenberg AE. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva with sarcomatous transformation ("angiomyofibrosarcoma"). Am J Surg Pathol. 1997; 21:1104–1108.11. Tochika N, Takeshita A, Sonobe H, Matsumoto M, Kobayashi M, Araki K. Angiomyofibroblastoma of the vulva: report of a case. Surg Today. 2001; 31:557–559.12. Granter SR, Nucci MR, Fletcher CD. Aggressive angiomyxoma: reappraisal of its relationship to angiomyofibroblastoma in a series of 16 cases. Histopathology. 1997; 30:3–10.