Lab Med Online.
2012 Jul;2(3):119-125.
D-Dimer Testing in Laboratory Practice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center, Department of Internal Medicine, University of IRCCS and Mangiagalli, Milan, Italy.
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
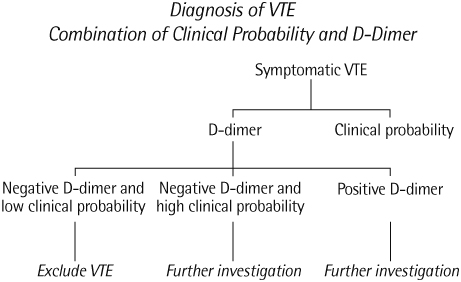
D-dimer is a reliable and sensitive index of fibrin deposition and stabilization. As such, its presence in plasma should be indicative of thrombus formation. There are many conditions unrelated to thrombosis in which D-dimer concentrations are high, however, making its positive predictive value rather poor. CONTENT: Notwithstanding these limitations, D-dimer can be regarded as a most valuable laboratory tool to diagnose and manage a vast array of thrombosis related clinical conditions, including (a) diagnosis of venous thromboembolism (VTE), (b) identification of individuals at increased risk of first thrombotic event (both arterial and venous), (c) identification of individuals at increased risk of recurrent VTE, (d) establishment of the optimal duration of secondary prophylaxis after a first episode of VTE, (e) pregnancy monitoring, and (f) diagnosis/monitoring of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). This article is aimed at reviewing the merits and pitfalls of these applications. SUMMARY: From my analysis of the literature, I draw the following conclusions. (a) D-dimer, as measured by a sensitive test, can be safely used to exclude VTE in symptomatic outpatients, provided that it is used in combination with the pretest clinical probability. (b) High concentrations of D-dimer are associated with an increased risk of recurrent VTE. (c) Patients who present with D-dimer above cutoff after stopping the regular course of oral anticoagulation benefit from extended prophylaxis. (d) Finally, D-dimer can be used as a fibrin-related degradation marker for the diagnosis/management of patients with DIC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Medved L, Nieuwenhuizen W. Molecular mechanisms of initiation of fibrinolysis by fibrin. Thromb Haemost. 2003. 89:409–419.
Article2. Gaffney PJ. Distinction between fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1975. 65:109–115.
Article3. Gaffney PJ. Fibrin degradation products: a review of structures found in vitro and in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. 936:594–610.4. Rylatt DB, Blake AS, Cottis LE, Massingham DA, Fletcher WA, Masci PP, et al. An immunoassay for human D dimer using monoclonal antibodies. Thromb Res. 1983. 31:767–778.
Article5. Greenberg CS, Devine DV, McCrae KM. Measurement of plasma fibrin D-dimer levels with the use of a monoclonal antibody coupled to latex beads. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987. 87:94.
Article6. Elms MJ, Bunce IH, Bundesen PG, Rylatt DB, Webber AJ, Masci PP, et al. Rapid detection of cross-linked fibrin degradation products in plasma using monoclonal antibody-coated latex particles. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986. 85:360–364.
Article7. Froehling DA, Daniels PR, Swensen SJ, Heit JA, Mandrekar JN, Ryu JH, et al. Evaluation of a quantitative D-dimer latex immunoassay for acute pulmonary embolism diagnosed by computed tomographic angiography. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007. 82:556–560.
Article8. Lensing AW, Prandoni P, Brandjes D, Huisman PM, Vigo M, Tomasella G, et al. Detection of deep-vein thrombosis by real-time B-mode ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320:342–345.
Article9. Cogo A, Lensing AW, Koopman MM, Piovella F, Siragusa S, Wells PS, et al. Compression ultrasonography for diagnostic management of patients with clinically suspected deep vein thrombosis: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 1998. 316:17–20.
Article10. Heijboer H, Büller HR, Lensing AW, Turpie AG, Colly LP, ten Cate JW. A comparison of real-time compression ultrasonography with impedance plethysmography for the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis in symptomatic outpatients. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:1365–1369.
Article11. Bounameaux H, Cirafici P, de Moerloose P, Schneider PA, Slosman D, Reber G, et al. Measurement of D-dimer in plasma as diagnostic aid in suspected pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 1991. 337:196–200.
Article12. Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, Forgie M, Kearon C, Dreyer J, et al. Evaluation of D-dimer in the diagnosis of suspected deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:1227–1235.
Article13. Wells PS. Integrated strategies for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. 5:Suppl 50.
Article14. van Belle A, Büller HR, Huisman MV, Huisman PM, Kaasjager K, Kamphuisen PW, et al. Effectiveness of managing suspected pulmonary embolism using an algorithm combining clinical probability, D-dimer testing, and computed tomography. JAMA. 2006. 295:172–179.
Article15. King V, Vaze AA, Moskowitz CS, Smith LJ, Ginsberg MS. D-dimer assay to exclude pulmonary embolism in high-risk oncologic population: correlation with CT pulmonary angiography in an urgent care setting. Radiology. 2008. 247:854–861.
Article16. de Maat MP, Meijer P, Nieuwenhuizen W, Haverkate F, Kluft C. Performance of semiquantitative and quantitative D-dimer assays in the ECAT external quality assessment program. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000. 26:625–630.
Article17. Meijer P, Kluft C. The harmonization of quantitative test results of different D-dimer methods. Semin Vasc Med. 2005. 5:321–327.
Article18. Tripodi A, Chantarangkul V. Performance of quantitative D-dimer methods: results of the Italian External Quality Assessment Scheme. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. 5:184–185.
Article19. Galle C, Papazyan JP, Miron MJ, Slosman D, Bounameaux H, Perrier A. Prediction of pulmonary embolism extent by clinical findings, D-dimer level and deep vein thrombosis shown by ultrasound. Thromb Haemost. 2001. 86:1156–1160.
Article20. Di Nisio M, Squizzato A, Rutjes AW, Büller HR, Zwinderman AH, Bossuyt PM. Diagnostic accuracy of D-dimer test for exclusion of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. 5:296–304.
Article21. Lowe GD. Can haematological tests predict cardiovascular risk? The 2005 Kettle Lecture. Br J Haematol. 2006. 133:232–250.
Article22. Cushman M, Folsom AR, Wang L, Aleksic N, Rosamond WD, Tracy RP, et al. Fibrin fragment D-dimer and the risk of future venous thrombosis. Blood. 2003. 101:1243–1248.
Article23. Palareti G, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Guazzaloca G, Pancani C, Coccheri S. Risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence: high negative predictive value of D-dimer performed after oral anticoagulation is stopped. Thromb Haemost. 2002. 87:7–12.
Article24. Verhovsek M, Douketis JD, Yi Q, Shrivastava S, Tait RC, Baglin T, et al. Systematic review: D-dimer to predict recurrent disease after stopping anticoagulant therapy for unprovoked venous thromboembolism. Ann Intern Med. 2008. 149:481–490.
Article25. Palareti G, Cosmi B, Legnani C, Tosetto A, Brusi C, Iorio A, et al. PROLONG Investigators. PROLONG Investigators. D-dimer testing to determine the duration of anticoagulation therapy. N Engl J Med. 2006. 355:1780–1789.
Article26. Kline JA, Williams GW, Hernandez-Nino J. D-dimer concentrations in normal pregnancy: new diagnostic thresholds are needed. Clin Chem. 2005. 51:825–829.
Article27. Epiney M, Boehlen F, Boulvain M, Reber G, Antonelli E, Morales M, et al. D-dimer levels during delivery and the postpartum. J Thromb Haemost. 2005. 3:268–271.
Article28. Chan WS, Chunilal S, Lee A, Crowther M, Rodger M, Ginsberg JS. A red blood cell agglutination D-dimer test to exclude deep venous thrombosis in pregnancy. Ann Intern Med. 2007. 147:165–170.
Article29. Levi M. Pathogenesis and treatment of DIC. Thromb Res. 2005. 115:Suppl 1. 54–55.30. Taylor FB Jr, Toh CH, Hoots WK, Wada H, Levi M. Scientific Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH). Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 2001. 86:1327–1330.
Article31. Wada H, Wakita Y, Nakase T, Shimura M, Hiyoyama K, Nagaya S, et al. Outcome of disseminated intravascular coagulation in relation to the score when treatment was begun. Mie DIC Study Group. Thromb Haemost. 1995. 74:848–852.
Article32. Wada H, Gabazza EC, Asakura H, Koike K, Okamoto K, Maruyama I, et al. Comparison of diagnostic criteria for disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): diagnostic criteria of the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis and of the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare for overt DIC. Am J Hematol. 2003. 74:17–22.
Article33. Takagi H, Manabe H, Kawai N, Goto S, Umemoto T. Plasma fibrinogen and D-dimer concentrations are associated with the presence of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009. 38:273–277.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New cut-off point for D-dimer in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism during pregnancy
- Diagnostic Efficacy of Rapid Whole-Blood Assay for D-dimer in Patients with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
- Correlation between plasma D-dimer levels and the severity of patients with chronic urticaria
- Deep Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Negative Age-Adjusted D-Dimer Level
- Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department: A Bioequivalence Study