Ann Lab Med.
2013 Jan;33(1):34-38. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.1.34.
Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department: A Bioequivalence Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Emergency Department, Westmead Hospital, Sydney, Australia. samit36@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1781295
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.1.34
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
D-dimer is used widely as a diagnostic aid in low- and moderate-risk patients with suspected venous thromboembolism (VTE). While our laboratory utilizes VIDAS D-dimer analyzer (bioMerieux SA, France), our emergency department (ED) recently procured a D-dimer analyzer AQT90 FLEX (Radiometer Medical ApS, Denmark) for point of care testing (POCT) to facilitate patient management. We aimed to determine whether the time taken to receive D-dimer results using the 2 different analyzers differed significantly and to quantify the limits of agreement between the results of the 2 methods measured on the same patient.
METHODS
Adult patients presenting to the ED and requiring diagnostic workup for suspected VTE were included in this prospective observational study. Patients underwent simultaneous D-dimer measurements using the 2 different analyzers.
RESULTS
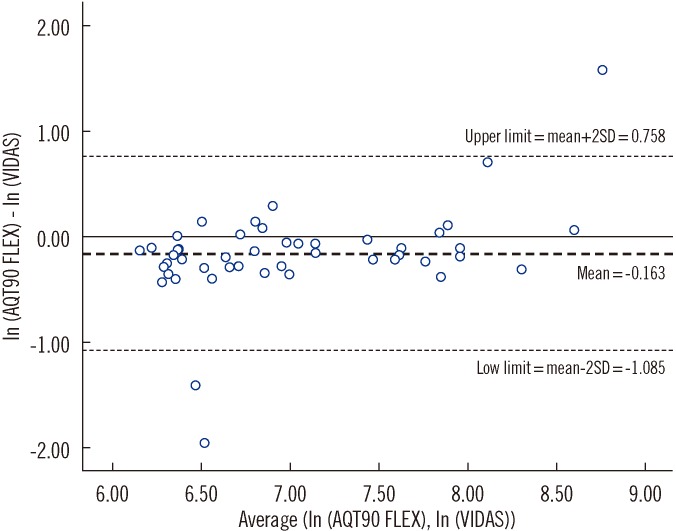
The paired results from 104 patients were analyzed. The median time for the D-dimer results from triage by VIDAS was 258 min (Inter-quartile range [IQR], 173-360) and by POCT was 146 min (IQR, 55-280.5); the median time difference was 101.5 min (IQR, 82-125.5). On an average, POCT D-dimer values were 15% lower on the same sample (limits of agreement, 34-213%). POCT predicted 83% of VIDAS positive results (sensitivity, 83.3% [95% confidence interval (CI), 70.4-91.3%]; specificity, 100% [95% CI, 93.6-100%]). All patients with positive imaging were identified correctly by both methods.
CONCLUSIONS
POCT delivers D-dimer results in significantly shorter turnaround times than pathology services; however, poor bioequivalence between VIDAS and POCT raises the issue of acceptability for use in the ED.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Emergency Service, Hospital
Female
Fibrin Fibrinogen Degradation Products/*analysis
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Point-of-Care Systems
Prospective Studies
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Sensitivity and Specificity
Time Factors
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Venous Thromboembolism/*diagnosis/radiography
Fibrin Fibrinogen Degradation Products
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comments on Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department: A Bioequivalence Study
Suzanne Ekelund, Eric Heilmann
Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(1):64-65. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.64.Response to the Comments on 'Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department-A Bioequivalence Study' and Erratum to the Results
Shuhana Perveen, Danielle Unwin, Amith L Shetty, Karen Byth
Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(1):66-67. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.1.66.
Reference
-
1. Lee-Lewandrowski E, Nichols J, Van Cott E, Grisson R, Louissaint A, Benzer T, et al. Implementation of a rapid whole blood D-dimer test in the emergency department of an urban academic medical center: impact on ED length of stay and ancillary test utilization. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009; 132:326–331. PMID: 19687307.2. Walker JB, Nesheim ME. The molecular weights, mass distribution, chain composition, and structure of soluble fibrin degradation products released from a fibrin clot perfused with plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:5201–5212. PMID: 9988770.
Article3. Greenberg CS, Devine DV, McCrae KM. Measurement of plasma fibrin D-dimer levels with the use of a monoclonal antibody coupled to latex beads. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987; 87:94–100. PMID: 3541576.
Article4. Dempfle CE. Validation, calibration, and specificity of quantitative D-dimer assays. Semin Vasc Med. 2005; 5:315–320. PMID: 16302152.
Article5. Pittet JL, de Moerloose P, Reber G, Durand C, Villard C, Piga N, et al. VIDAS D-dimer: fast quantitative ELISA for measuring D-dimer in plasma. Clin Chem. 1996; 42:410–415. PMID: 8598104.
Article6. Scarano L, Bernardi E, Prandoni P, Sardella C, Rossi L, Carraro P, et al. Accuracy of two newly described D-dimer tests in patients with suspected deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Res. 1997; 86:93–99. PMID: 9175231.
Article7. Di Nisio M, Squizzato A, Rutjes AW, Buller HR, Zwinderman AH, Bossuyt PM. Diagnostic accuracy of D-dimer test for exclusion of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. J Thromb Haemost. 2007; 5:296–304. PMID: 17155963.
Article8. Perrier A, Roy PM, Aujesky D, Chagnon I, Howarth N, Gourdier AL, et al. Diagnosing pulmonary embolism in outpatients with clinical assessment, D-dimer measurement, venous ultrasound, and helical computed tomography: a multicenter management study. Am J Med. 2004; 116:291–299. PMID: 14984813.
Article9. Sidelmann JJ, Gram J, Larsen A, Overgaard K, Jespersen J. Analytical and clinical validation of a new point-of-care testing system for determination of D-Dimer in human blood. Thromb Res. 2010; 126:524–530. PMID: 20846709.
Article10. Wells PS, Hirsh J, Anderson DR, Lensing AW, Foster G, Kearon C, et al. A simple clinical model for the diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis combined with impedance plethysmography: potential for an improvement in the diagnostic process. J Intern Med. 1998; 243:15–23. PMID: 9487327.
Article11. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986; 1:307–310. PMID: 2868172.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Response to the Comments on 'Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department-A Bioequivalence Study' and Erratum to the Results
- Comments on Point of Care D-Dimer Testing in the Emergency Department: A Bioequivalence Study
- Improving emergency department patient flow
- New cut-off point for D-dimer in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism during pregnancy
- Bioequivalence Test and Its Significance