Lab Med Online.
2012 Apr;2(2):74-79.
Evaluation of the AutoLab HbA1c Reagent by Using Hitachi Clinical Analyzer 7180
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea. pwpark@gilhospital.com
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a universally used parameter for monitoring glycemic control in diabetic patients. Various methods are used for the measurement of HbA1c levels. The AutoLab HbA1c reagent was recently developed for use in immunoturbidimetric assays for measurement of HbA1c levels. We evaluated the reliability of using the AutoLab HbA1c reagent with the Hitachi Clinical Analyzer 7180, an automated chemistry analyzer, for measuring HbA1c levels.
METHODS
We evaluated the precision, linearity, carryover rate, and stability of the samples analyzed using Hitachi clinical analyzer 7180 with the AutoLab HbA1c reagent and compared the results with those obtained with an HPLC method performed using the Variant II Turbo analyzer.
RESULTS
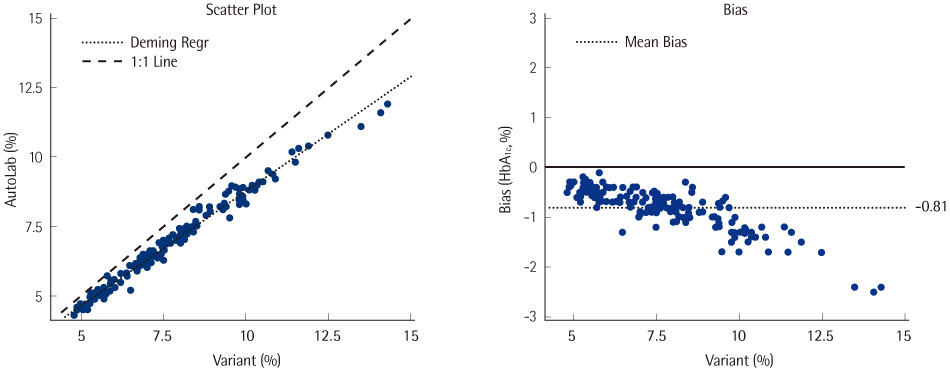
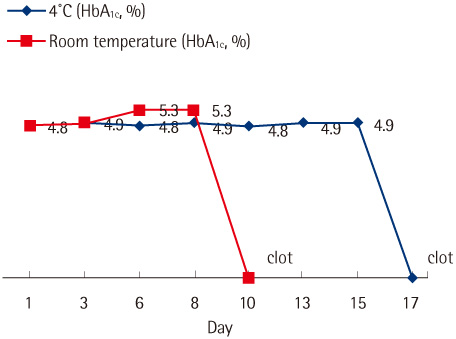
The CV values for within-run imprecision at low and high levels were 0.8% and 0.6%, respectively, and the CV values for between-run imprecision at low and high levels were 1.5% and 2.9%, respectively. The linearity of the results was good in the range of 4.3-12.3%, and comparison with the results obtained by Variant II Turbo showed an excellent correlation coefficient of 0.9914. The carryover rate was 0%, and the samples refrigerated at 4degrees C for 15 days were found to be stable.
CONCLUSIONS
In comparison with Variant II Turbo, Hitachi clinical analyzer 7180 with AutoLab HbA1c reagent showed good precision, linearity, and carryover rate. Hence, Hitachi clinical analyzer 7180 with AutoLab HbA1c reagent may be used for the diagnosis of diabetes and for monitoring blood glucose levels in diabetic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nathan DM, Kuenen J, Borg R, Zheng H, Schoenfeld D, Heine RJ. Translating the A1c assay into estimated average glucose values. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:1473–1478.
Article2. Steffes M, Cleary P, Goldstein D, Little R, Wiedmeyer HM, Rohlfing C, et al. Hemoglobin A1c measurements over nearly two decades: sustaining comparable values throughout the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study. Clin Chem. 2005. 51:753–758.
Article3. Saudek CD, Herman WH, Sacks DB, Bergenstal RM, Edelman D, Davidson MB. A new look at screening and diagnosing diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. 93:2447–2453.
Article4. Bry L, Chen PC, Sacks DB. Effects of hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 2001. 47:153–163.
Article5. Little RR. Recent progress in glycohemoglobin (HbA1c) testing. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:265–266.6. Lee SY, Kim JW. Evaluation of the tosoh HLC-723 G7 hemoglobin A1c analyzer. Korean J Lab Med. 2003. 23:180–185.7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP15-A2. User verification of performance for precision and trueness; approved guideline. 2005. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards.8. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP6-A. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach. Approved guideline. 2003. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards.9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI document EP9-A2. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline. 2002. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards.10. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:1047–1053.
Article11. Lee YS, Moon SS. The use of HbA1c for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in Korea. Korean J Med. 2011. 80:291–297.12. Perry RC, Shankar RR, Fineberg N, McGill J, Baron AD. HbA1c measurement improves the detection of type 2 diabetes in high-risk individuals with nondiagnostic levels of fasting plasma glucose: the Early Diabetes Intervention Program (EDIP). Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:465–471.
Article13. Nichols GA, Hillier TA, Brown JB. Normal fasting plasma glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes diagnosis. Am J Med. 2008. 121:519–524.
Article14. Tirosh A, Shai I, Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Pereg D, Shochat T, et al. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes in young men. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1454–1462.
Article15. International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1c assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:1327–1334.16. Lee H. The role of HbA1c testing in diagnosing diabetes. Korean J Med. 2010. 79:495–499.17. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2010. Diabetes Care. 2010. 33:Suppl 1. S11–S61.18. Little RR, Rohlfing CL, Wiedmeyer HM, Myers GL, Sacks DB, Goldstein DE. The national glycohemoglobin standardization program: a five-year progress report. Clin Chem. 2001. 47:1985–1992.19. Summary of NGSP criteria. National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program. Updated on Dec 2011. http://www.ngsp.org/critsumm.asp.20. Sacks DB. Hemoglobin variants and hemoglobin A1c analysis: problem solved? Clin Chem. 2003. 49:1245–1247.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance Evaluation of HbA1c Test on the Toshiba 200FR NEO Using AutoLab HbA1c Reagent
- Performance Evaluation of SENTiFIT 270 and FOB Gold Reagent for Detecting Fecal Occult Blood
- Evaluation of HbA1c Levels Via the Latex Immunoturbidimetric Method by Using Chemistry Autoanalyzer
- Performance Evaluation of Gentian Cystatin C on the Hitachi 7600 Automatic Analyzer
- Evaluation of Yeong Dong Reagent for the Automated Chemistry Test