Korean J Urol.
2009 Apr;50(4):340-348.
Change in Patients' Perspectives after Education on the Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Dongkook University, Ilsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. s315@hallym.or.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
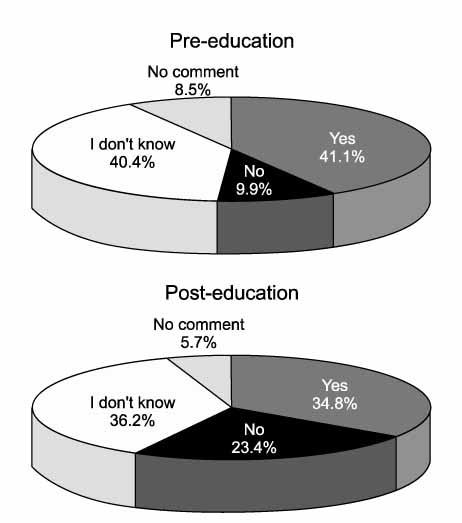
We assessed patients' understanding of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and their perspectives on the management of BPH through a questionnaire and evaluated changes in perspective after patient education. MATERIALS AND METHODS: From December 2007 to February 2008, 5 university hospitals participated in the study. A self-administered questionnaire was developed and was completed by patients before and after the patients read the patient's guide. The questionnaire was composed of 22 questions, which were grouped into 4 different categories. The patient's guide was written in everyday words and was based on the American Urological Association patient's guide. RESULTS: A total of 141 patients who visited the urology department for treatment of symptoms suggestive of BPH participated in the survey. Understanding about the statement, "BPH does not progress to become prostate cancer" was increased after reading the patient's guide (35.57%--> 73.87%, p<0.001). The most preferred treatment option was drug therapy (45.4%-->56.7%). Among the desirable effects of drug therapy, the patients' preferences were amelioration of symptoms within a few weeks (51.1%--> 48.9%), reduction in prostate size (18.4%-->24.1%), prevention of acute urinary retention (14.2%-->13.5%), and prevention of prostate surgery (7.8% -->8.5%). The potential side effect of drug therapy that patients were most concerned about was generalized weakness. Patients' reluctance to undergo surgery was increased after reading the patient guide (9.9%-->23.4%, p=0.002). CONCLUSIONS: Patients have considerable misunderstanding about BPH. More efforts should be exercised in patient education and in the development of public education programs. Because patients expect not only rapid symptom improvement but also a reduction in prostate size, physicians should consider these points when treating patients with BPH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HL, Seo JW, Kim WJ. The prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia: community-based study in Chungbuk province. Korean J Urol. 1999. 40:1500–1505.2. Bosch JL, Hop WC, Kirkels WJ, Schroder FH. Natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia: appropriate case definition and estimation of its prevalence in the community. Urology. 1995. 46(3 Suppl A):34–40.3. Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C, Keech M, Hobbs FD, Fourcade R, et al. The prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms in men and women in four centres. The UrEpik study. BJU Int. 2003. 92:409–414.4. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the international continence society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002. 21:167–178.5. AUA Practice Guidelines Committee. AUA guideline on management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (2003). Chapter 1: diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol. 2003. 170:530–547.6. Emberton M, Marberger M, de la Rosette J. Understanding patient and physician perceptions of benign prostatic hyperplasia in Europe: The Prostate Research on Behaviour and Education (probe) Survey. Int J Clin Pract. 2008. 62:18–26.7. Verhamme KM, Dieleman JP, Bleumink GS, van der Lei J, Sturkenboom MC, Artibani W, et al. Incidence and prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in primary care-the Triumph project. Eur Urol. 2002. 42:323–328.8. Chung BH. Medical management for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2007. 48:233–243.9. Oesterling JE. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Medical and minimally invasive treatment options. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:99–109.10. Marberger M, Harkaway R, de la Rosette J. Optimising the medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2004. 45:411–419.11. McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole GL Jr, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:2387–2398.12. Roehrborn CG, Marks LS, Fenter T, Freedman S, Tuttle J, Gittleman M, et al. Efficacy and safety of dutasteride in the four-year treatment of men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2004. 63:709–715.13. Harkaway RC. What are the views of patients and urologists on benign prostatic hyperplasia and its management? Eur Urol. 2007. 6(Suppl 6):454–459.14. Kawakami J, Nickel JC. Acute urinary retention and surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia: the patient's perspective. Can J Urol. 1999. 6:819–822.15. Teillac P. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: patients' perception of medical treatment and their expectations. Results of a french survey involving patients treated with finasteride. Therapie. 2002. 57:473–478.16. Watson V, Ryan M, Brown CT, Barnett G, Ellis BW, Emberton M. Eliciting preferences for drug treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2004. 172:2321–2325.17. Kaplan S, Naslund M. Public, patient, and professional attitudes towards the diagnosis and treatment of enlarged prostate: a landmark national US survey. Int J Clin Pract. 2006. 60:1157–1165.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Prominently Large Glans penis as a Possible sign of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Medical Management for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The Effects of Abdominal Obesity on the Increased Prevalence Rate of Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients
- The influence of age and endocrine factors on the volume of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Indwelling of an intraprostatic stent(prostakath/TM and nissenkorn catheter): possibilities as a definitive management for benign prostatic hyperplasia