J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2015 Mar;15(1):25-29.
Factor XI deficiency and orthognathic surgery: a case report on anesthesia management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Seoul, Korea. stone90@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
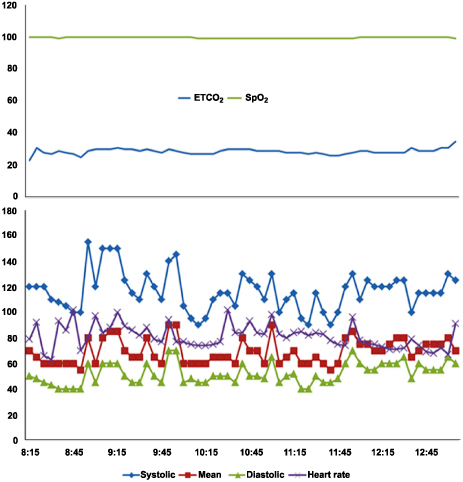
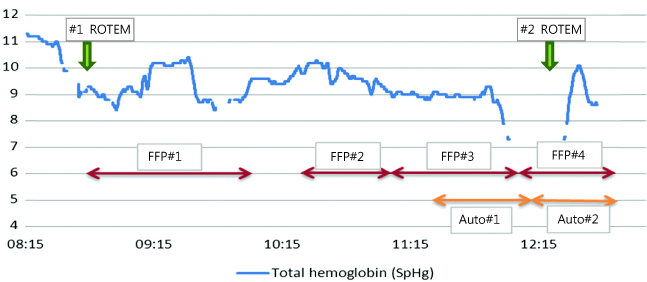
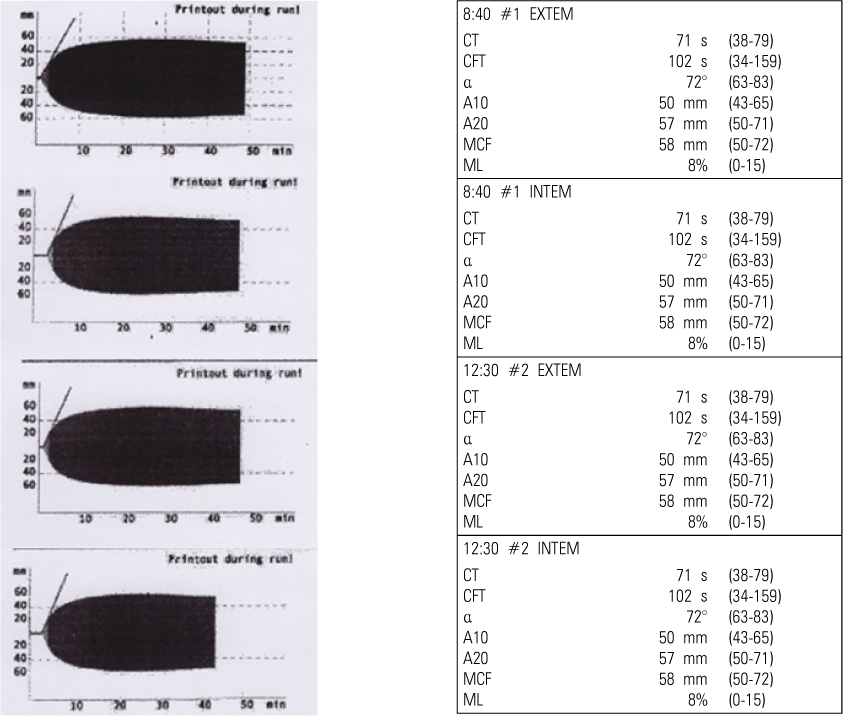
- Factor XI deficiency (Hemophilia C) is a very rare autosomal recessive bleeding disorder. Patients with factor XI deficiency do not typically show any spontaneous bleeding or specific symptoms. Sometimes those who have this disorder are identified during special situations such as trauma or surgery. Orthognathic surgery is particularly associated with a high bleeding risk. Therefore, great care must be taken when treating patients with bleeding disorders such as factor XI deficiency. There are a few reports that address the management of patients with bleeding disorders during orthognathic surgery. The current report describes a patient with factor XI deficiency who underwent Le Fort I osteotomy together with bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. The patient's condition was assessed using both rotation thromboelastometry (ROTEMâ„¢) and noninvasive measurements of total hemoglobin (SpHb) using Masimo Radical 7 (Masimo Co. CA, USA).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bolton-Maggs PH, Young Wan-Yin B, McCraw AH, Slack J, Kernoff PB. Inheritance and bleeding in factor xi deficiency. Br J Haematol. 1988; 69:521–528.
Article2. Salomon O, Steinberg DM, Seligshon U. Variable bleeding manifestations characterize different types of surgery in patients with severe factor xi deficiency enabling parsimonious use of replacement therapy. Haemophilia. 2006; 12:490–493.
Article3. Seligsohn U. Factor xi deficiency in humans. J Thromb Haemost. 2009. Suppl 1. p. 84–87.
Article4. Bouma BN, Mosnier LO. Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (tafi) at the interface between coagulation and fibrinolysis. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2003; 33:375–381.
Article5. Asakai R, Chung DW, Davie EW, Seligsohn U. Factor xi deficiency in ashkenazi jews in israel. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:153–158.
Article6. Dirkmann D, Hanke AA, Gorlinger K, Peters J. Perioperative use of modified thrombelastography in factor xi deficiency: A helpful method to assess drug effects. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007; 51:640–643.
Article7. Peyvandi F, Lak M, Mannucci PM. Factor xi deficiency in iranians: Its clinical manifestations in comparison with those of classic hemophilia. Haematologica. 2002; 87:512–514.8. Shpilberg O, Peretz H, Zivelin A, Yatuv R, Chetrit A, Kulka T, et al. One of the two common mutations causing factor xi deficiency in ashkenazi jews (type ii) is also prevalent in iraqi jews, who represent the ancient gene pool of jews. Blood. 1995; 85:429–432.
Article9. Kim SH, Choi JM, Kim HJ, Choi SS, Choi IC. Continuous noninvasive hemoglobin measurement is useful in patients undergoing double-jaw surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:1813–1819.
Article10. Ilankovan V, Blesing NE, Moos KF, Davidson JF. Correction of facial deformities in patients with mild bleeding disorders: A report of three cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 28:398–400.
Article11. Todd D, Galbraith D. Management of an orthognathic surgery patient with factor xi deficiency: Review and case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 51:417–420.
Article12. Abramowicz S, Staba SL, Dolwick MF, Chen DR. Orthognathic surgery in a patient with hemophilia a: Report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 105:437–439.
Article13. Redondo M, Solenthaler M, Zeerleder S, Wuillemin WA. Isolated increased aPTT with anamnestic hemorrhagic diathesis--severe fxi deficiency. Ther Umsch. 1999; 56:502–504.14. Singh A, Harnett MJ, Connors JM, Camann WR. Factor xi deficiency and obstetrical anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2009; 108:1882–1885.
Article15. Berliner S, Horowitz I, Martinowitz U, Brenner B, Seligsohn U. Dental surgery in patients with severe factor xi deficiency without plasma replacement. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1992; 3:465–468.
Article16. Lawler P, White B, Pye S, Hermans C, Riddell A, Costello C, et al. Successful use of recombinant factor viia in a patient with inhibitor secondary to severe factor xi deficiency. Haemophilia. 2002; 8:145–148.
Article17. Billon S, Le Niger C, Escoffre-Barbe M, Vicariot M, Abgrall JF. The use of recombinant factor viia (novoseven) in a patient with a factor xi deficiency and a circulating anticoagulant. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2001; 12:551–553.
Article18. Bern MM, Sahud M, Zhukov O, Qu K, Mitchell W Jr. Treatment of factor xi inhibitor using recombinant activated factor viia. Haemophilia. 2005; 11:20–25.
Article19. Faverani LP, Ramalho-Ferreira G, Fabris AL, Polo TO, Poli GH, Pastori CM, et al. Intraoperative blood loss and blood transfusion requirements in patients undergoing orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 18:305–310.
Article20. Pineiro-Aguilar A, Somoza-Martin M, Gandara-Rey JM, Garcia-Garcia A. Blood loss in orthognathic surgery: A systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:885–892.
Article21. Espahbod C, Veitz-Keenan A. Tranexamic acid reduces intraoperative blood loss in orthognathic surgery. Evid Based Dent. 2014; 15:63.
Article22. Whiting D, DiNardo JA. Teg and rotem: technology and clinical applications. Am J Hematol. 2014; 89:228–232.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Factor XI Deficiency in Sisters
- Anesthetic experience of a patient with hereditary factor XI deficiency (Hemophilia C) : A case report
- Three Cases of Factor XI Deficiency
- Successful Management of a Patient with Factor XI Deficiency and Unstable Angina by Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Orthognathic Surgery in a Patient with Factor VII Deficiency