Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Apr;40(2):356-361. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.356.
Therapeutic Experience on Stance Control Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthosis With Electromagnetically Controlled Knee Joint System in Poliomyelitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Eulji University Hospital & Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. rehabkjh@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Physical Therapy, Eulji University Hospital & Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2309937
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.356
Abstract
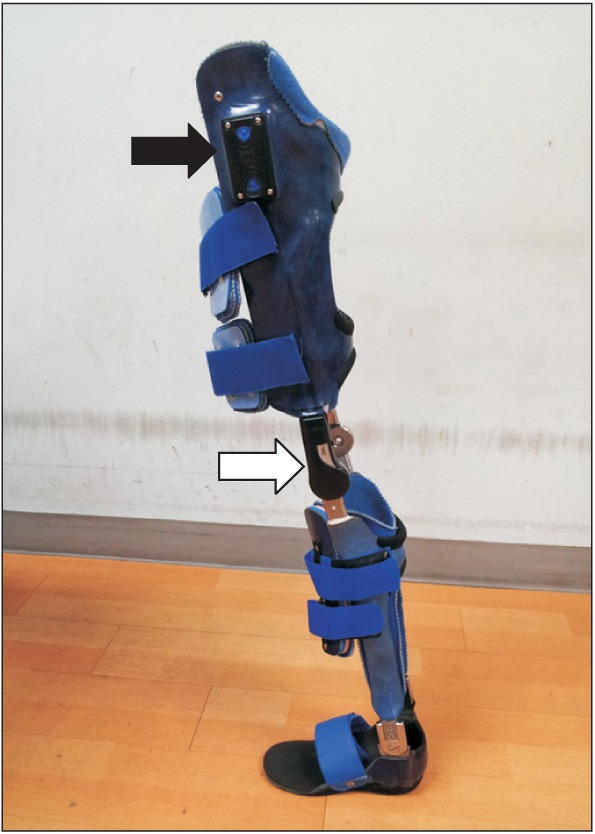
- A 54-year-old man with poliomyelitis had been using a conventional, passive knee-ankle-foot orthosis (KAFO) with a drop ring lock knee joint for about 40 years. A stance control KAFO (SCKAFO) with an electromagnetically controlled (E-MAG) knee joint system was prescribed. To correct his gait pattern, he also underwent rehabilitation therapy, which included muscle re-education, neuromuscular electrical stimulation, strengthening exercises for the lower extremities, and balance training twice a week for about 4 months. Both before and after rehabilitation, we conducted a gait analysis and assessed the physiological cost index in energy expended during walking in a locked-knee state and while he wore a SCKAFO with E-MAG. When compared with the pre-rehabilitation data, the velocity, step length, stride length, and knee kinematic data were improved after rehabilitation. Although the SCKAFO with E-MAG system facilitated the control of knee motion during ambulation, appropriate rehabilitative therapy was also needed to achieve a normal gait pattern.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cullell A, Moreno JC, Rocon E, Forner-Cordero A, Pons JL. Biologically based design of an actuator system for a knee–ankle–foot orthosis. Mech Mach Theory. 2009; 44:860–872.
Article2. Tian F, Hefzy MS, Elahinia M. State of the art review of knee-ankle-foot orthoses. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015; 43:427–441. PMID: 25631201.
Article3. Hislop H, Montgomery J. Daniels and Worthingham's muscle testing: techniques of manual examination. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2002.4. Jaiyesimi AO, Fashakin OG. Reliability of physiological cost index measurements. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2007; 36:229–234. PMID: 18390062.5. Arazpour M, Chitsazan A, Bani MA, Rouhi G, Ghomshe FT, Hutchins SW. The effect of a knee ankle foot orthosis incorporating an active knee mechanism on gait of a person with poliomyelitis. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2013; 37:411–414. PMID: 23327836.
Article6. McMillan AG, Kendrick K, Michael JW, Aronson J, Horton GW. Preliminary evidence for effectiveness of a stance control orthosis. J Prosthet Orthot. 2004; 16:6–13.
Article7. Yakimovich T, Lemaire ED, Kofman J. Engineering design review of stance-control knee-ankle-foot orthoses. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009; 46:257–267. PMID: 19533539.8. Shamaei K, Napolitano PC, Dollar AM. Design and functional evaluation of a quasi-passive compliant stance control knee-ankle-foot orthosis. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2014; 22:258–268. PMID: 24608684.
Article9. Irby SE, Bernhardt KA, Kaufman KR. Gait changes over time in stance control orthosis users. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2007; 31:353–361. PMID: 17852777.
Article10. Hachisuka K, Makino K, Wada F, Saeki S, Yoshimoto N. Oxygen consumption, oxygen cost and physiological cost index in polio survivors: a comparison of walking without orthosis, with an ordinary or a carbon-fibre reinforced plastic knee-ankle-foot orthosis. J Rehabil Med. 2007; 39:646–650. PMID: 17896057.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Conservative Treatment of Genu Recurvatum: A Case Report
- A Study on the Effect of Degree of Freedom of Ankle Motion on Gait of Transfemoral Amputees with SNS Control Prosthesis
- Comparison between the Barefeet Gait and the Shoe Gaitin the Transtibial Amputees
- Efficacy of a Knee Walker for Foot and Ankle Patients: Comparative Study with an Axillary Crutch
- Changes of Gait Patterns by the Ankle Foot Orthoses with a Variable Ankle Joint Stop