Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Apr;40(2):263-270. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.263.
Correlation Between the Severity of Diabetic Peripheral Polyneuropathy and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels: A Quantitative Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. 2seok@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2309925
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.263
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate risk factors for diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy and their correlation with the quantified severity of nerve dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM).
METHODS
A total of 187 diabetic patients with clinically suspected polyneuropathy (PN) were subclassified into 2 groups according to electrodiagnostic testing: a DM-PN group of 153 diabetic patients without electrophysiological abnormality and a DM+PN group of 34 diabetic patients with polyneuropathy. For all patients, age, sex, height, weight, duration of DM, and plasma glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level were comparatively investigated. A composite score was introduced to quantitatively analyze the results of the nerve conduction studies. Logistic regression analysis and multiple regression analysis were used to evaluate correlations between significant risk factors and severity of diabetic polyneuropathy.
RESULTS
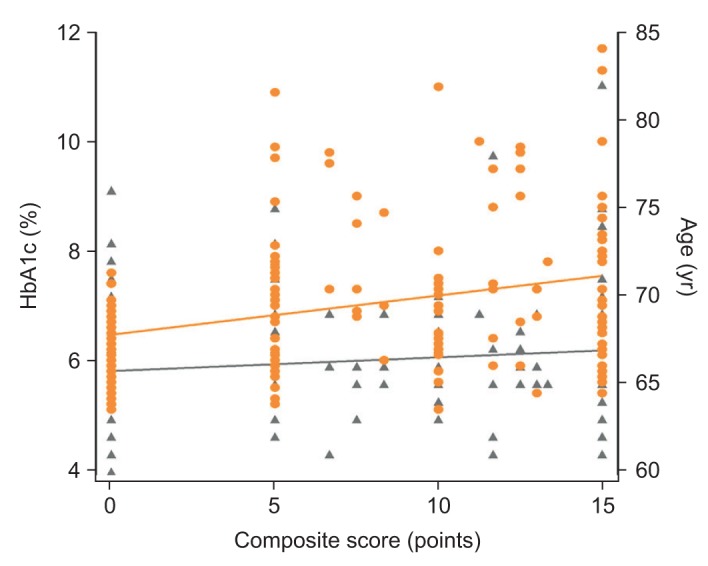
The DM+PN group showed a significantly higher HbA1c level and composite score, as compared with the DM-PN group. Increased HbA1c level and old age were significant predictive factors for polyneuropathy in diabetic patients (odds ratio=5.233 and 4.745, respectively). In the multiple linear regression model, HbA1c and age showed a significant positive association with composite score, in order (β=1.560 and 0.253, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Increased HbA1c level indicative of a state of chronic hyperglycemia was a risk factor for polyneuropathy in diabetic patients and a quantitative measure of its severity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Nerve Conduction Study, Sympathetic Skin Response Test, and Demographic Correlates in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Younggon Lee, So Hun Kim, Chang-Hwan Kim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2025;49(1):40-48. doi: 10.5535/arm.240042.
Reference
-
1. Gallagher EJ, Leroith D, Karnieli E. The metabolic syndrome: from insulin resistance to obesity and diabetes. Med Clin North Am. 2011; 95:855–873. PMID: 21855696.2. Gionfriddo MR, McCoy RG, Lipska KJ. The 2013 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists' diabetes mellitus management recommendations: improvements needed. JAMA Intern Med. 2014; 174:179–180. PMID: 24322834.3. International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1327–1334. PMID: 19502545.4. Deli G, Bosnyak E, Pusch G, Komoly S, Feher G. Diabetic neuropathies: diagnosis and management. Neuroendocrinology. 2013; 98:267–280. PMID: 24458095.
Article5. Feng Y, Schlosser FJ, Sumpio BE. The Semmes Weinstein monofilament examination is a significant predictor of the risk of foot ulceration and amputation in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Vasc Surg. 2011; 53:220–226.e5. PMID: 20692793.
Article6. Kwon BC, Jung KI, Baek GH. Comparison of sonography and electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 2008; 33:65–71. PMID: 18261667.
Article7. Mythili A, Kumar KD, Subrahmanyam KA, Venkateswarlu K, Butchi RG. A comparative study of examination scores and quantitative sensory testing in diagnosis of diabetic polyneuropathy. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2010; 30:43–48. PMID: 20431806.
Article8. Dyck PJ, Davies JL, Litchy WJ, O'Brien PC. Longitudinal assessment of diabetic polyneuropathy using a composite score in the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study cohort. Neurology. 1997; 49:229–239. PMID: 9222195.
Article9. Dyck PJ, Davies JL, Wilson DM, Service FJ, Melton LJ 3rd, O'Brien PC. Risk factors for severity of diabetic polyneuropathy: intensive longitudinal assessment of the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study cohort. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:1479–1486. PMID: 10480512.
Article10. Shin YS, Kim MO, Kim CH, Nam MS. Relation of nerve conduction study and physical parameters in diabetic polyneuropathy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:112–117.11. Dyck PJ, Litchy WJ, Daube JR, Harper CM, Dyck PJ, Davies J, et al. Individual attributes versus composite scores of nerve conduction abnormality: sensitivity, reproducibility, and concordance with impairment. Muscle Nerve. 2003; 27:202–210. PMID: 12548528.
Article12. Meijer JW, Smit AJ, Sonderen EV, Groothoff JW, Eisma WH, Links TP. Symptom scoring systems to diagnose distal polyneuropathy in diabetes: the Diabetic Neuropathy Symptom score. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:962–965. PMID: 12421436.
Article13. Farooqui AA, Farooqui T, Panza F, Frisardi V. Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012; 69:741–762. PMID: 21997383.
Article14. Vijan S. Type 2 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 2010; 152:ITC3–ITC1.
Article15. Harttgen K, Kowal P, Strulik H, Chatterji S, Vollmer S. Patterns of frailty in older adults: comparing results from higher and lower income countries using the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) and the Study on Global AGEing and Adult Health (SAGE). PLoS One. 2013; 8:e75847. PMID: 24204581.
Article16. England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, Miller RG, Asbury AK, Carter GT, et al. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a definition for clinical research: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2005; 64:199–207. PMID: 15668414.
Article17. Jeong TS, Choi KS, Kim HJ, Park YS. Relations of glycosylated hemoglobin and parameters of nerve conduction study in diabetic peripheral polyneuropathy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2003; 27:80–84.18. Morimoto J, Suzuki Y, Tada A, Akui M, Ozawa Y, Maruyama T. Time-course changes in nerve conduction velocity (NCV) in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat. 2012; 26:237–240. PMID: 22502938.
Article19. Lee JH, Kim CH, Kim SH, Jeong HJ, Kim MO. Relationship of diabetic polyneuropathy severity with various balance parameters. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2010; 34:550–553.20. Strotmeyer ES, de Rekeneire N, Schwartz AV, Faulkner KA, Resnick HE, Goodpaster BH, et al. The relationship of reduced peripheral nerve function and diabetes with physical performance in older white and black adults: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) study. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:1767–1772. PMID: 18535192.21. Gregg EW, Sorlie P, Paulose-Ram R, Gu Q, Eberhardt MS, Wolz M, et al. Prevalence of lower-extremity disease in the US adult population >=40 years of age with and without diabetes: 1999-2000 national health and nutrition examination survey. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1591–1597. PMID: 15220233.22. Papanas N, Ziegler D. New diagnostic tests for diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2011; 25:44–51. PMID: 19896871.
Article23. Gallagher EJ, Leroith D, Karnieli E. Insulin resistance in obesity as the underlying cause for the metabolic syndrome. Mt Sinai J Med. 2010; 77:511–523. PMID: 20960553.
Article24. Sattar N, McConnachie A, Shaper AG, Blauw GJ, Buckley BM, de Craen AJ, et al. Can metabolic syndrome usefully predict cardiovascular disease and diabetes? Outcome data from two prospective studies. Lancet. 2008; 371:1927–1935. PMID: 18501419.
Article25. The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2560–2572. PMID: 18539916.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Follow-up Study on Peripheral Neuropathy in Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus in Childhood
- Evaluation of Peripheral Polyneuropathy in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using Quantitative Sensory Test
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin as a Predictor for Effectiveness of Sildenafil Citrate for Diabetic Patients with Erectile Dysfunction
- Relations of Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Parameters of Nerve Conduction Study in Diabetic Peripheral Polyneuropathy
- Diabetic Patients of the Community