Anat Cell Biol.
2016 Mar;49(1):73-77. 10.5115/acb.2016.49.1.73.
Morphometric study on the infraorbital foramen in relation to sex and side of the cranium in northeastern Brazil
- Affiliations
-
- 1Federal University of Sergipe (UFS), Aracaju, Brazil. jaafelipe@infonet.com.br
- 2Medical School of Tiradentes University (UNIT), Aracaju, Brazil.
- 3Department of Morphology and the Postgraduate Physical Education and Applied Health Science Programs, Federal University of Sergipe (UFS), Aracaju, Brazil.
- KMID: 2308934
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2016.49.1.73
Abstract
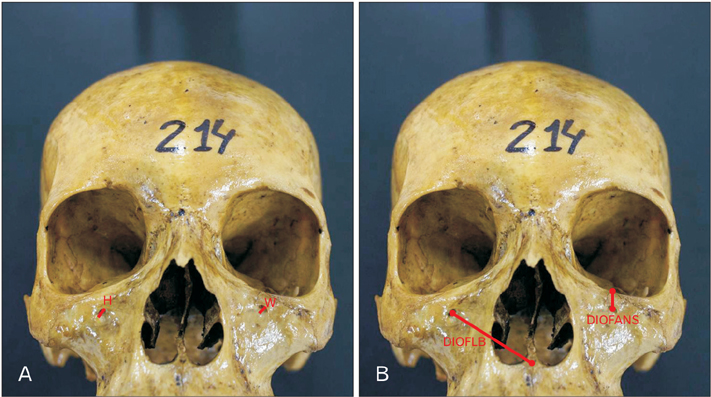
- Detailed knowledge of the possible anatomical and morphometric variations of the infraorbital foramen (IOF) is important for ensuring safe and successful regional anesthesia, and for avoiding iatrogenic nerve injuries during surgery on the middle third of the face. To conduct a morphometric study on the IOF, correlating this with sex and side of the cranium. Two hundred forty-two crania were used (148 male and 94 female). Measurements were made with the aid of digital calipers with precision to 0.01 mm. Presence of foramina and their multiplicity was also observed. The data were analyzed descriptively and analytically. Statistical significance was stipulated as 5% (P≤0.05). The IOF was found bilaterally in all the crania, and 26 of them presented multiplicity. The distance from the IOF to the anterior nasal spine was greater in males on both sides (P<0.001). Statistical differences between the sexes were also seen in relation to the following morphometric variables: height of the left IOF (P=0.007), width of the right IOF (P=0.004), and width of the left IOF (P=0.008), and the measurements were also larger among males. The IOF was present in all the crania and on both sides. It was morphometrically larger in males, on both sides.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee T, Lee H, Baek S. A three-dimensional computed tomographic measurement of the location of infraorbital foramen in East Asians. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1169–1173.2. Liu DN, Guo JL, Luo Q, Tian Y, Xia CL, Li YQ, Su L. Location of supraorbital foramen/notch and infraorbital foramen with reference to soft- and hard-tissue landmarks. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:293–296.3. Gour KK, Nair S, Trivedi GN, Gupta SD. Anthropometric measurements of infraorbital foramen in dried human skulls. Int J Biol Med Res. 2012; 3:2003–2006.4. Aziz SR, Marchena JM, Puran A. Anatomic characteristics of the infraorbital foramen: a cadaver study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 58:992–996.5. Kazkayasi M, Ergin A, Ersoy M, Tekdemir I, Elhan A. Microscopic anatomy of the infraorbital canal, nerve, and foramen. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 129:692–697.6. Singh R. Morphometric analysis of infraorbital foramen in Indian dry skulls. Anat Cell Biol. 2011; 44:79–83.7. Song WC, Kim JN, Yoo JY, Lee JY, Won SY, Hu KS, Kim HJ, Koh KS. Microanatomy of the infraorbital canal and its connecting canals in the maxilla using 3-D reconstruction of microcomputed tomographic images. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1184–1187.8. Cutright B, Quillopa N, Schubert W. An anthropometric analysis of the key foramina for maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:354–357.9. Joseph CC, Soman MA, Jacob M, Nallathamby R. Morphometric variations in infra orbital foramen of dry adult human south Indian skulls with its surgical and anaesthetic significance. Int J Health Sci Res. 2015; 5:130–134.10. Lopes PT, Pereira GA, Santos AM, Freitas CR, Abreu BR, Malafaia AC. Morphometric analysis of the infraorbital foramen related to gender and laterality in dry skulls of adult individuals in southern Brazil. Braz J Morphol Sci. 2009; 26:19–22.11. Macedo VC, Cabrini RR, Faig-Leite H. Infraorbital foramen location in dry human skulls. Braz J Morphol Sci. 2009; 26:35–38.12. Takahashi Y, Kakizaki H, Nakano T. Infraorbital foramen: horizontal location in relation to ala nasi. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 27:295–297.13. Zarringhalam P, Parbhoo A, Von Arx D. Accessory infra-orbital nerves: an important anatomical lesson. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 52:e118–e119.14. Ekambaram G, Shaik RA, Salmani D, Ekambaram G. A genderwise study on the morphometry of infraorbital foramen and its laterally in dry adult skulls oh south Indian population. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2014; 3:546–548.15. Lira Júnior R, Lima DM, Ferreira AC, de Sousa EM, de Lucena LB. Topographic evaluation of the infraorbital foramen in dry human skulls. Pesqui Bras Odontopediatria Clin Integr. 2011; 11:497–450.16. Saini K. Descriptive and topographic anatomy of infraorbital foramen and its clinical implication in nerve block. Int J Anat Res. 2014; 2:730–734.17. Ukoha UU, Umeasalugo KE, Udemezue OO, Nzeako HC, Ndukwe GU, Nwankwo PC. Anthropometric measurement of infraorbital foramen in south-east and south-south Nigeria. Natl J Med Res. 2014; 4:225–227.18. Apinhasmit W, Chompoopong S, Methathrathip D, Sansuk R, Phetphunphiphat W. Supraorbital notch/foramen, infraorbital foramen and mental foramen in Thais: anthropometric measurements and surgical relevance. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006; 89:675–682.19. Rossi M, Ribeiro E, Smith R. Craniofacial asymmetry in development: an anatomical study. Angle Orthod. 2003; 73:381–385.20. Russo PP, Smith RL. Asymmetry of human skull base during growth. Int J Morphol. 2011; 29:1028–1032.21. Przygocka A, Podgórski M, Jędrzejewski K, Topol M, Polguj M. The location of the infraorbital foramen in human skulls, to be used as new anthropometric landmarks as a useful method for maxillofacial surgery. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2012; 71:198–204.22. Boopathi S, Chakravarthy Marx S, Dhalapathy SL, Anupa S. Anthropometric analysis of the infraorbital foramen in a South Indian population. Singapore Med J. 2010; 51:730–735.23. Moss ML, Greenberg SN. Functional cranial analysis of the human maxillary bone: I, Basal bone. Angle Orthod. 1967; 37:151–164.24. Schwartz JH. Dentofacial growth and development in Homo sapiens: evidence from perinatal individuals from Punic Carthage. Anat Anz. 1982; 152:1–26.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphological analysis of the jugular foramen in dry human skulls in northeastern Brazil
- Morphometric analysis of infraorbital foramen in Indian dry skulls
- Accessory infraorbital foramen location using cone-beam computed tomography
- A clinical and anatomical study on the infraorbital foramen and infraorbital canal in Korean
- Non-Metrical Morphologic Variations of Korean Skull Foramina