Imaging Sci Dent.
2016 Jun;46(2):87-92. 10.5624/isd.2016.46.2.87.
Comparison of the diagnostic performance of panoramic and occlusal radiographs in detecting submandibular sialoliths
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Radiology, School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. drarthurcortes@gmail.com
- 2Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, USA.
- 3Department of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
- 4Department of Oral Radiology, School of Dentistry, University of Okayama, Okayama, Japan.
- KMID: 2308871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2016.46.2.87
Abstract
- PURPOSE
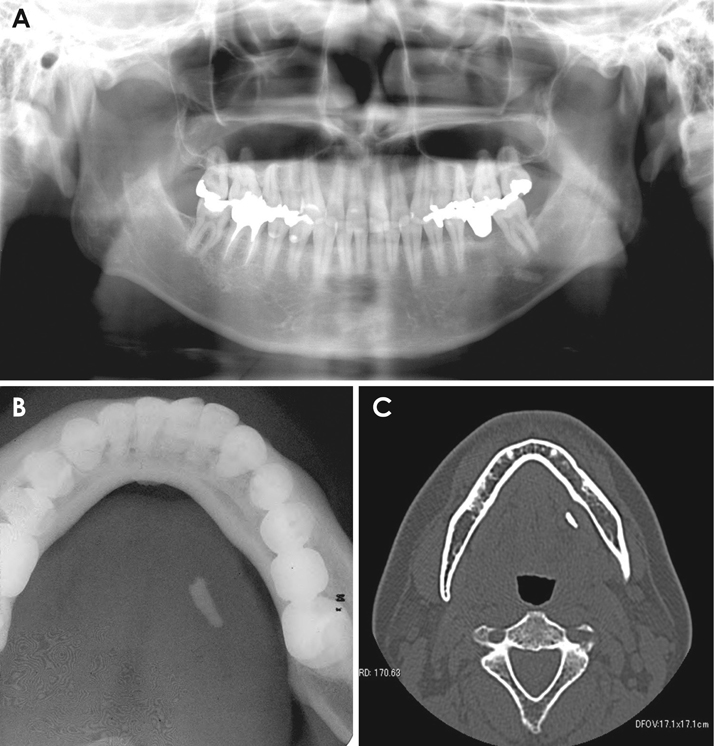
The aim of this study was to assess and compare the diagnostic performance of panoramic and occlusal radiographs in detecting submandibular sialoliths.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 40 patients (20 cases and 20 controls) were included in this retrospective study. Cases were defined as subjects with a submandibular sialolith confirmed by computed tomography (CT), whereas controls did not have any submandibular calcifications. Three observers with different expertise levels assessed panoramic and occlusal radiographs of all subjects for the presence of sialoliths. Intraobserver and interobserver agreement were assessed using the kappa test. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values, and the diagnostic odds ratio of panoramic and occlusal radiographs in screening for submandibular sialoliths were calculated for each observer.
RESULTS
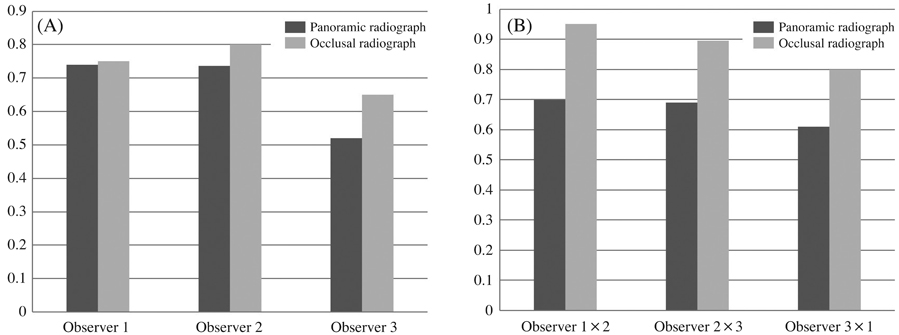
The sensitivity and specificity values for occlusal and panoramic radiographs all ranged from 80% to 100%. The lowest values of sensitivity and specificity observed among the observers were 82.6% and 80%, respectively (P=0.001). Intraobserver and interobserver agreement were higher for occlusal radiographs than for panoramic radiographs, although panoramic radiographs demonstrated a higher overall accuracy.
CONCLUSION
Both panoramic and occlusal radiographic techniques displayed satisfactory diagnostic performance and should be considered before using a CT scan to detect submandibular sialoliths.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Therapeutic effect of intraductal irrigation of the salivary gland: A technical report
Chena Lee, Jo-Eun Kim, Kyoung-Hoe Huh, Won-Jin Yi, Min-Suk Heo, Sam-Sun Lee, Soon-Chul Choi
Imaging Sci Dent. 2017;47(2):123-127. doi: 10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.123.Submandibular sialolithiasis with CT and scintigraphy: CT values and salivary gland excretion in the submandibular glands
Ichiro Ogura, Kazuhide Hayama, Mikiko Sue, Takaaki Oda, Yoshihiko Sasaki
Imaging Sci Dent. 2017;47(4):227-231. doi: 10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.227.A comprehensive review of the mental spine
Ross Champagne, Rithvik Vutukuri, Chung Yoh Kim, R. Shane Tubbs, Joe Iwanaga
Anat Cell Biol. 2024;57(1):1-6. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.220.
Reference
-
1. Williams MF. Sialolithiasis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1999; 32:819–834.
Article2. Marchal F, Kurt AM, Dulguerov P, Lehmann W. Retrograde theory in sialolithiasis formation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 127:66–68.
Article3. Lustmann J, Regev E, Melamed Y. Sialolithiasis. A survey on 245 patients and a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 19:135–138.4. Gritzmann N. Sonography of the salivary glands. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 153:161–166.
Article5. Schwarz D, Kabbasch C, Scheer M, Mikolajczak S, Beutner D, Luers JC. Comparative analysis of sialendoscopy, sonography, and CBCT in the detection of sialolithiasis. Laryngoscope. 2015; 125:1098–1101.
Article6. Markiewicz MR, Margarone JE 3rd, Tapia JL, Aguirre A. Sialolithiasis in a residual Wharton's duct after excision of a submandibular salivary gland. J Laryngol Otol. 2007; 121:182–185.
Article7. Sobrino-Guijarro B, Cascarini L, Lingam RK. Advances in imaging of obstructed salivary glands can improve diagnostic outcomes. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 17:11–19.
Article8. Becker M, Marchal F, Becker CD, Dulguerov P, Georgakopoulos G, Lehmann W, et al. Sialolithiasis and salivary ductal stenosis: diagnostic accuracy of MR sialography with a three-dimensional extended-phase conjugate-symmetry rapid spin-echo sequence. Radiology. 2000; 217:347–358.9. Jager L, Menauer F, Holzknecht N, Scholz V, Grevers G, Reiser M. Sialolithiasis: MR sialography of the submandibular duct - an alternative to conventional sialography and US? Radiology. 2000; 216:665–671.10. Madani G, Beale T. Inflammatory conditions of the salivary glands. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2006; 27:440–451.
Article11. Zenk J, Koch M, Klintworth N, König B, Konz K, Gillespie MB, et al. Sialendoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis: a study on more than 1000 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012; 147:858–863.12. Bialek EJ, Jakubowski W, Zajkowski P, Szopinski KT, Osmolski A. US of the major salivary glands: anatomy and spatial relationships, pathologic conditions, and pitfalls. Radiographics. 2006; 26:745–763.
Article13. Bodner L. Giant salivary gland calculi: diagnostic imaging and surgical management. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 94:320–323.
Article14. Vaiman M. Comparative analysis of methods of endoscopic surgery of the submandibular gland: 114 surgeries. Clin Otolaryngol. 2015; 40:162–166.
Article15. Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, et al. Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD initiative. Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:1–6.16. Ardekian L, Klein HH, Araydy S, Marchal F. The use of sialendoscopy for the treatment of multiple salivary gland stones. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:89–95.
Article17. Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology. 2000; 216:19–29.
Article18. Nahlieli O, Eliav E, Hasson O, Zagury A, Baruchin AM. Pediatric sialolithiasis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000; 90:709–712.
Article19. Zenk J, Iro H, Klintworth N, Lell M. Diagnostic imaging in sialadenitis. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2009; 21:275–292.
Article20. McGurk M, Makdissi J, Brown JE. Intra-oral removal of stones from the hilum of the submandibular gland: report of technique and morbidity. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 33:683–686.
Article21. Koch M, Zenk J, Iro H. Algorithms for treatment of salivary gland obstructions. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009; 42:1173–1192.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Multiple Sialoliths in Sublingual Gland Misdiagnosed as Sialoliths in Submandibular Gland
- Distortion of tooth axes on panoramic radiographs taken at various head positions
- A study of angle of mandibular canal and mental foramen on the panoramic radiograph
- Submandibular sialolithiasis with CT and scintigraphy: CT values and salivary gland excretion in the submandibular glands
- Comparison of the clinical examination with the panoramic radiography in the diagnosis of dental caries